
A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a hitch fastens a rope to another object; a bend fastens two ends of a rope to each another; a loop knot is any knot creating a loop; and splice denotes any multi-strand knot, including bends and loops. A knot may also refer, in the strictest sense, to a stopper or knob at the end of a rope to keep that end from slipping through a grommet or eye. Knots have excited interest since ancient times for their practical uses, as well as their topological intricacy, studied in the area of mathematics known as knot theory.

The bowline is an ancient and simple knot used to form a fixed loop at the end of a rope. It has the virtues of being both easy to tie and untie; most notably, it is easy to untie after being subjected to a load. The bowline is sometimes referred to as King of the knots because of its importance. Along with the sheet bend and the clove hitch, the bowline is often considered one of the most essential knots.

The butterfly loop, also known as lineman's loop, butterfly knot, alpine butterfly knot, Swiss loop and lineman's rider, is a knot used to form a fixed loop in the middle of a rope. Tied in the bight, it can be made in a rope without access to either of the ends; this is a distinct advantage when working with long climbing ropes. The butterfly loop is an excellent mid-line rigging knot; it handles multi-directional loading well and has a symmetrical shape that makes it easy to inspect. In a climbing context it is also useful for traverse lines, some anchors, shortening rope slings, and for isolating damaged sections of rope.

The constrictor knot is one of the most effective binding knots. Simple and secure, it is a harsh knot that can be difficult or impossible to untie once tightened. It is made similarly to a clove hitch but with one end passed under the other, forming an overhand knot under a riding turn. The double constrictor knot is an even more robust variation that features two riding turns.

A shank is a type of knot that is used to shorten a rope or take up slack, such as the sheepshank. The sheepshank knot is not stable. It will fall apart under too much load or too little load.

The trucker's hitch is a compound knot commonly used for securing loads on trucks or trailers. The general arrangement, using loops and turns in the rope itself to form a crude block and tackle, has long been used to tension lines and is known by multiple names. Knot author Geoffrey Budworth claims the knot can be traced back to the days when carters and hawkers used horse-drawn conveyances to move their wares from place to place.

The figure-eight knot or figure-of-eight knot is a type of stopper knot. It is very important in both sailing and rock climbing as a method of stopping ropes from running out of retaining devices. Like the overhand knot, which will jam under strain, often requiring the rope to be cut, the figure-eight will also jam, but is usually more easily undone than the overhand knot.
The figure-eight or figure-of-eight knot is also called the Flemish knot. The name figure-of-eight knot appears in Lever's Sheet Anchor; or, a Key to Rigging. The word "of" is nowadays usually omitted. The knot is the sailor's common single-strand stopper knot and is tied in the ends of tackle falls and running rigging, unless the latter is fitted with monkey's tails. It is used about ship wherever a temporary stopper knot is required. The figure-eight is much easier to untie than the overhand, it does not have the same tendency to jam and so injure the fiber, and is larger, stronger, and equally secure.

Figure-eight loop is a type of knot created by a loop on the bight. It is used in climbing and caving.
The Flemish loop or figure-eight loop is perhaps stronger than the loop knot. Neither of these knots is used at sea, as they are hard to untie. In hooking a tackle to any of the loops, if the loop is long enough it is better to arrange the rope as a cat's paw.

The taut-line hitch is an adjustable loop knot for use on lines under tension. It is useful when the length of a line will need to be periodically adjusted in order to maintain tension. It is made by tying a rolling hitch around the standing part after passing around an anchor object. Tension is maintained by sliding the hitch to adjust the size of the loop, thus changing the effective length of the standing part without retying the knot.
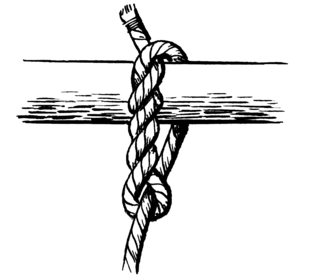
The timber hitch is a knot used to attach a single length of rope to a cylindrical object. Secure while tension is maintained, it is easily untied even after heavy loading.

A zeppelin bend is an end-to-end joining knot formed by two symmetrically interlinked overhand knots. It is stable, secure, and highly resistant to jamming. It is also resistant to the effects of slack shaking and cyclic loading.

A slipped half hitch is a knot in which the weight of the load the rope carries depresses the loop sufficiently to keep it in place until the load item is placed in its location. When no longer required the free end may be pulled and draw the loop through and so release the load.

A stopper knot is a knot that creates a fixed thicker point on an otherwise-uniform thickness rope for the purpose of preventing the rope, at that point, from slipping through a narrow passage, such as a hole in a block. To pass a rope through a block, or hole, is to reeve it. To pull it out is to unreeve it. Stopper knots prevent the rope from unreeving on its own.

The cow hitch, also called the lark's head, is a hitch knot used to attach a rope to an object. The cow hitch comprises a pair of single hitches tied in opposing directions, as compared to the clove hitch in which the single hitches are tied in the same direction. It has several variations and is known under a variety of names. It can be tied either with the end of the rope or with a bight.

Ashley's stopper knot, also known as the oysterman's stopper, is a knot developed by Clifford W. Ashley around 1910. It makes a well-balanced trefoil-faced stopper at the end of the rope, giving greater resistance to pulling through an opening than other common stoppers. Essentially, the knot is a common overhand noose, but with the end of the rope passing through the noose eye, which closes upon it. It may be multiplied to form a larger knot with more than three bights appearing around the knot. It is the result of implementing a double wall knot in one strand.

The rolling hitch is a knot used to attach a rope to a rod, pole, or another rope. A simple friction hitch, it is used for lengthwise pull along an object rather than at right angles. The rolling hitch is designed to resist lengthwise movement for only a single direction of pull.

The figure-of-nine loop is a type of knot to form a fixed loop in a rope. Tied in the bight, it is made similarly to a figure-of-eight loop but with an extra half-turn before finishing the knot.

A Yosemite bowline is a loop knot often perceived as having better security than a bowline. If the knot is not dressed correctly, it can potentially collapse into a noose, however testing reveals this alternative configuration to be strong and safe as a climbing tie-in.



















