
A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a hitch fastens a rope to another object; a bend fastens two ends of a rope to each another; a loop knot is any knot creating a loop; and splice denotes any multi-strand knot, including bends and loops. A knot may also refer, in the strictest sense, to a stopper or knob at the end of a rope to keep that end from slipping through a grommet or eye. Knots have excited interest since ancient times for their practical uses, as well as their topological intricacy, studied in the area of mathematics known as knot theory.

A miller's knot is a binding knot used to secure the opening of a sack or bag. Historically, large sacks often contained grains; thus the association of these knots with the miller's trade. Several knots are known interchangeably by these three names.

A shank is a type of knot that is used to shorten a rope or take up slack, such as the sheepshank. The sheepshank knot is not stable. It will fall apart under too much load or too little load.

The clove hitch is a type of knot. Along with the bowline and the sheet bend, it is often considered one of the most important knots. A clove hitch is two successive half-hitches around an object. It is most effectively used as a crossing knot. It can be used as a binding knot, but is not particularly secure in that role. A clove hitch made around the rope's own standing part is known as either two half-hitches or buntline hitch, depending on whether the turns of the clove hitch progress away from or towards the hitched object.
Although the name clove hitch is given by Falconer in his Dictionary of 1769, the knot is much older, having been tied in ratlines at least as early as the first quarter of the sixteenth century. This is shown in early sculpture and paintings. A round turn is taken with the ratline and then a hitch is added below. The forward end is always the first to be made fast.
The difference between two half hitches and the clove hitch is that the former, after a single turn around a spar, is made fast around its own standing part, while the latter is tied directly around the spar.

The marlinespike hitch is a temporary knot used to attach a rod to a rope in order to form a handle. This allows more tension than could be produced comfortably by gripping the rope with the hands alone. It is useful when tightening knots and for other purposes in ropework.

The taut-line hitch is an adjustable loop knot for use on lines under tension. It is useful when the length of a line will need to be periodically adjusted in order to maintain tension. It is made by tying a rolling hitch around the standing part after passing around an anchor object. Tension is maintained by sliding the hitch to adjust the size of the loop, thus changing the effective length of the standing part without retying the knot.
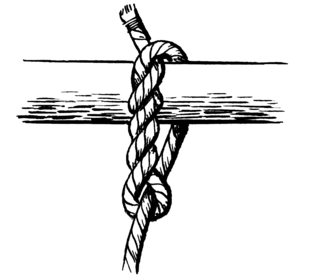
The timber hitch is a knot used to attach a single length of rope to a cylindrical object. Secure while tension is maintained, it is easily untied even after heavy loading.

The anchor bend is a knot used for attaching a rope to a ring or similar termination. The name is a misnomer, as it is technically not a bend, but a hitch.
The Cat's paw is a knot used for connecting a rope to an object. It is very similar to the cow hitch except there is an additional twist on each side of the bight, making it less prone to slipping.
The cat's-paw is the common hook hitch for slings. It is the same basic form as the bale sling hitch but has additional twists. Brady says "two or three altogether," and Steel, who mentioned the name in 1794, says "three twists." It is the best of all sling hitches and is often recommended for a slippery rope. But no hitch can slip when tied in a slings since it has no ends. All that is needed is a hitch that cannot jam, and this requirement the cat's-paw fills admirably. The knot spills instantly when removed from the hook. It is the hitch always used for heavy lifts.

A stopper knot is a knot that creates a fixed thicker point on an otherwise-uniform thickness rope for the purpose of preventing the rope, at that point, from slipping through a narrow passage, such as a hole in a block. To pass a rope through a block, or hole, is to reeve it. To pull it out is to unreeve it. Stopper knots prevent the rope from unreeving on its own.

The buntline hitch is a knot used for attaching a rope to an object. It is formed by passing the working end around an object, then making a clove hitch around the rope's standing part and taking care that the turns of the clove hitch progress towards the object rather than away from it. Secure and easily tied, the buntline hitch will jam when subjected to extreme loads. Given the knot's propensity to jam, it is often made in slipped form.
The buntline hitch, when bent to a yard, makes a more secure knot than two half hitches, but is more liable to jam. It differs from two half hitches in that the second half hitch is inside instead of outside the first one.

The Blake's hitch is a friction hitch commonly used by arborists and tree climbers as an ascending knot. Unlike other common climbing hitches, which often use a loop of cord, the Blake's hitch is formed using the end of a rope. Although it is a stable knot, it is often backed up with a stopper knot, such as a figure-of-eight knot, for safety. It is used for both ascending and descending, and is preferred by many arborists over other hitches, such as the taut-line hitch, as it is less prone to binding.

The rolling hitch is a knot used to attach a rope to a rod, pole, or another rope. A simple friction hitch, it is used for lengthwise pull along an object rather than at right angles. The rolling hitch is designed to resist lengthwise movement for only a single direction of pull.

A Prusik is a friction hitch or knot used to attach a loop of cord around a rope, applied in climbing, canyoneering, mountaineering, caving, rope rescue, ziplining, and by arborists. The term Prusik is a name for both the loops of cord used to tie the hitch and the hitch itself, and the verb is "to prusik". More casually, the term is used for any friction hitch or device that can grab a rope. Due to the pronunciation, the word is often misspelled Prussik, Prussick, or Prussic.
The magnus hitch is a knot similar to a rolling hitch or clove hitch, used to tie a rope or line to a pole, spar, or another line. It is tied similarly to a rolling hitch but with the final hitch in the opposite direction. It can be more tricky to snug up, since both lines emerge from the same side of the hitch, but it has less tendency to twist under load.

The gripping sailor's hitch is a secure, jam-proof friction hitch used to tie one rope to another, or a rope to a pole, boom, spar, etc., when the pull is lengthwise along the object. It will even grip a tapered object, such as a marlin spike, in the direction of taper, similar to the Icicle hitch, and it is much superior to the rolling hitch for that purpose.

The snuggle hitch is a modification of the clove hitch, and is stronger and more secure. Owen K. Nuttall of the International Guild of Knot Tyers came up with this unique hitch, and it was first documented in the Guild's Knotting Matters magazine issue of January, 1987. Generally, hitches are used to attach a line to another rope or spar, pole, etc., and are usually temporary. Thus, they should be relatively easy to untie.

A pipe hitch is a hitch-type knot used to secure smooth cylindrical objects, such as pipes, poles, beams, or spars. According to The Ashley Book of Knots, a pipe hitch is "used to lower a pipe or hoist one" and as "another method of tying to a rectangular timber."





















