This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(February 2015) |

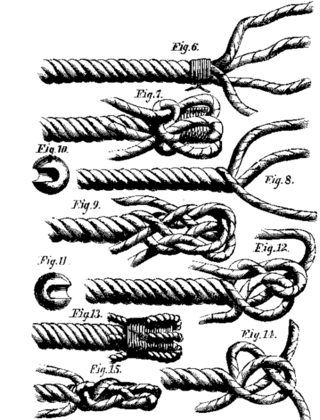
A fid is a conical tool traditionally made of wood or bone. It is used to work with rope and canvas in marlinespike seamanship. A fid differs from a marlinspike in material and purposes. A marlinspike is used in working with wire rope, natural and synthetic lines, may be used to open shackles, and is made of metal. A fid is used to hold open knots and holes in canvas, and to separate the "lays" (or strands) of synthetic or natural rope for splicing. A variation of the fid, the gripfid, is used for ply-split braiding. The gripfid has a jamming cleat to pull a cord back through the cord split by the fid's point.
Contents
Modern fids are typically made of aluminum, steel, or plastic. In addition to holding rope open to assist the creation of a rope splice, modern push fids have markings for precise measurements in a variety of sizes of rope. The length of these fids is typically 21 or 22 times the diameter of rope to be spliced. A one-half-inch (12.7 mm) diameter rope would have any accompanying fid 10.5–11 in (266.7–279.4 mm) in length with hash-marks denoting the long and short fid measurements. A short fid is 1⁄3 a fid length and a long fid is 2⁄3 the overall fid length.
Modern major rope manufacturers such as Yale Cordage, [1] New England Ropes, [2] and Samson Rope Technologies [3] each have full sets of published splicing directions available on their websites. Typically, all splice directions measurements use fid-length as the unit of measurement.
Below is a chart that shows exact measurements of full fid lengths, short fid lengths, and long fid lengths, using 21 times the diameter of the rope.
| Rope Diameter (in or mm) | Rope Circ. (in or mm) | Short Fid (in or mm) | Long Fid (in or mm) | Full Fid (in or mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3⁄32 in or 2.3813 mm | 9⁄32 in or 7.1438 mm | 2⁄3 in or 16.933 mm | 1+1⁄3 in or 33.867 mm | 2 in or 50.8 mm |
| 1⁄8 in or 3.175 mm | 3⁄8 in or 9.525 mm | 7⁄8 in or 22.225 mm | 2+3⁄8 in or 60.325 mm | 1+3⁄4 in or 44.45 mm |
| 5⁄32 in or 3.9688 mm | 1+15⁄32 in or 37.3063 mm | 1 in or 25.4 mm | 2+1⁄5 in or 55.88 mm | 3+2⁄7 in or 83.4571 mm |
| 3⁄16 in or 4.7625 mm | 9⁄16 in or 14.2875 mm | 1+1⁄3 in or 33.867 mm | 2+5⁄8 in or 66.675 mm | 4 in or 101.6 mm |
| 7⁄32 in or 5.5563 mm | 21⁄32 in or 16.6688 mm | 1+1⁄8 in or 28.575 mm | 3 in or 76.2 mm | 4+3⁄5 in or 116.84 mm |
| 1⁄4 in or 6.35 mm | 3⁄4 in or 19.05 mm | 1+1⁄4 in or 31.75 mm | 3+1⁄2 in or 88.9 mm | 5+1⁄5 in or 132.08 mm |
| 9⁄32 in or 7.1438 mm | 27⁄32 in or 21.4313 mm | 2 in or 50.8 mm | 4 in or 101.6 mm | 6 in or 152.4 mm |
| 5⁄16 in or 7.9375 mm | 1 in or 25.4 mm | 2+1⁄5 in or 55.88 mm | 4+3⁄8 in or 111.125 mm | 6+4⁄7 in or 166.9143 mm |
| 3⁄8 in or 9.525 mm | 1+1⁄8 in or 28.575 mm | 2+5⁄8 in or 66.675 mm | 5+1⁄8 in or 130.175 mm | 7+7⁄8 in or 200.025 mm |
| 7⁄16 in or 11.1125 mm | 1+1⁄4 in or 31.75 mm | 3 in or 76.2 mm | 6+1⁄8 in or 155.575 mm | 9+1⁄5 in or 233.68 mm |
| 1⁄2 in or 12.7 mm | 1+1⁄2 in or 38.1 mm | 3+1⁄2 in or 88.9 mm | 7 in or 177.8 mm | 10+1⁄2 in or 266.7 mm |
| 9⁄16 in or 14.2875 mm | 1+1⁄4 in or 31.75 mm | 4 in or 101.6 mm | 7+7⁄8 in or 200.025 mm | 11+4⁄5 in or 299.72 mm |
| 5⁄8 in or 15.875 mm | 2 in or 50.8 mm | 4+3⁄8 in or 111.125 mm | 8+3⁄4 in or 222.25 mm | 13+1⁄8 in or 333.375 mm |
| 11⁄16 in or 17.4625 mm | 2+1⁄4 in or 57.15 mm | 4+4⁄5 in or 121.92 mm | 9+3⁄8 in or 238.125 mm | 14+4⁄9 in or 366.8889 mm |
| 3⁄4 in or 19.05 mm | 2+1⁄4 in or 57.15 mm | 5+1⁄4 in or 133.35 mm | 10+1⁄2 in or 266.7 mm | 15+3⁄4 in or 400.05 mm |
| 7⁄8 in or 22.225 mm | 2+3⁄4 in or 69.85 mm | 6+1⁄8 in or 155.575 mm | 12+1⁄4 in or 311.15 mm | 18+3⁄8 in or 466.725 mm |
| 1 in or 25.4 mm | 3 in or 76.2 mm | 7 in or 177.8 mm | 14 in or 355.6 mm | 21 in or 533.4 mm |
| 1+1⁄8 in or 28.575 mm | 3+1⁄2 in or 88.9 mm | 7+7⁄8 in or 200.025 mm | 15+3⁄4 in or 400.05 mm | 23+3⁄8 in or 593.725 mm |
| 1+1⁄4 in or 31.75 mm | 3+3⁄4 in or 95.25 mm | 8+3⁄4 in or 222.25 mm | 17+1⁄2 in or 444.5 mm | 23+1⁄4 in or 590.55 mm |
| 1+5⁄16 in or 33.3375 mm | 4 in or 101.6 mm | 9+1⁄5 in or 233.68 mm | 18+3⁄8 in or 466.725 mm | 27+4⁄7 in or 700.3143 mm |
| 1+1⁄2 in or 38.1 mm | 4+1⁄2 in or 114.3 mm | 10+1⁄2 in or 266.7 mm | 21 in or 533.4 mm | 31+1⁄2 in or 800.1 mm |
| 1+5⁄8 in or 41.275 mm | 5 in or 127 mm | 11+3⁄8 in or 288.925 mm | 22+3⁄4 in or 577.85 mm | 34+1⁄8 in or 866.775 mm |
| 1+3⁄4 in or 44.45 mm | 5+1⁄2 in or 139.7 mm | 12+1⁄4 in or 311.15 mm | 24+1⁄2 in or 622.3 mm | 36+3⁄4 in or 933.45 mm |
| 2 in or 50.8 mm | 6 in or 152.4 mm | 14 in or 355.6 mm | 28 in or 711.2 mm | 42 in or 1,066.8 mm |
| 2+1⁄8 in or 53.975 mm | 6+1⁄4 in or 158.75 mm | 14+7⁄8 in or 377.825 mm | 29+3⁄4 in or 755.65 mm | 44+5⁄8 in or 1,133.475 mm |
| 2+1⁄4 in or 57.15 mm | 7 in or 177.8 mm | 15+3⁄4 in or 400.05 mm | 31+1⁄2 in or 800.1 mm | 47+1⁄4 in or 1,200.15 mm |
| 2+1⁄2 in or 63.5 mm | 7+1⁄2 in or 190.5 mm | 17+1⁄2 in or 444.5 mm | 35 in or 889 mm | 52+1⁄2 in or 1,333.5 mm |
| 2+5⁄8 in or 66.675 mm | 8 in or 203.2 mm | 18+5⁄8 in or 473.075 mm | 36+3⁄4 in or 933.45 mm | 55+1⁄8 in or 1,400.175 mm |
| 2+3⁄4 in or 69.85 mm | 8+1⁄2 in or 215.9 mm | 19+1⁄4 in or 488.95 mm | 38+1⁄2 in or 977.9 mm | 57+3⁄4 in or 1,466.85 mm |
| 3 in or 76.2 mm | 9 in or 228.6 mm | 21 in or 533.4 mm | 42 in or 1,066.8 mm | 63 in or 1,600.2 mm |
| 3+1⁄4 in or 82.55 mm | 10 in or 254 mm | 22+1⁄4 in or 565.15 mm | 45+1⁄2 in or 1,155.7 mm | 68+1⁄8 in or 1,730.375 mm |