In biochemistry, hydrolases constitute a class of enzymes that commonly function as biochemical catalysts that use water to break a chemical bond:
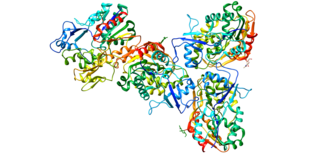
Lecithin–cholesterol acyltransferase is an enzyme, in many animals including humans, that converts free cholesterol into cholesteryl ester, which is then sequestered into the core of a lipoprotein particle, eventually making the newly synthesized HDL spherical and forcing the reaction to become unidirectional since the particles are removed from the surface. The enzyme is bound to high-density lipoproteins (HDLs) (alpha-LCAT) and LDLs (beta-LCAT) in the blood plasma. LCAT deficiency can cause impaired vision due to cholesterol corneal opacities, anemia, and kidney damage. It belongs to the family of phospholipid:diacylglycerol acyltransferases.

Monoacylglycerol lipase is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the MGLL gene. MAGL is a 33-kDa, membrane-associated member of the serine hydrolase superfamily and contains the classical GXSXG consensus sequence common to most serine hydrolases. The catalytic triad has been identified as Ser122, His269, and Asp239.

Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase also known as cholesterol 7-alpha-monooxygenase or cytochrome P450 7A1 (CYP7A1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP7A1 gene which has an important role in cholesterol metabolism. It is a cytochrome P450 enzyme, which belongs to the oxidoreductase class, and converts cholesterol to 7-alpha-hydroxycholesterol, the first and rate limiting step in bile acid synthesis.

Hormone-sensitive lipase (EC 3.1.1.79, HSL), also previously known as cholesteryl ester hydrolase (CEH), sometimes referred to as triacylglycerol lipase, is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the LIPE gene, and catalyzes the following reaction:

Cholesteryl esters are a type of dietary lipid and are ester derivatives of cholesterol. The ester bond is formed between the carboxylate group of a fatty acid and the hydroxyl group of cholesterol. Cholesteryl esters have a lower solubility in water due to their increased hydrophobicity. Esters are formed by replacing at least one –OH (hydroxyl) group with an –O–alkyl (alkoxy) group. They are hydrolyzed by pancreatic enzymes, such as cholesterol esterase, to produce cholesterol and free fatty acids. They are associated with atherosclerosis.

Bile salt-dependent lipase, also known as carboxyl ester lipase is an enzyme produced by the adult pancreas and aids in the digestion of fats. Bile salt-stimulated lipase is an equivalent enzyme found within breast milk. BSDL has been found in the pancreatic secretions of all species in which it has been looked for. BSSL, originally discovered in the milk of humans and various other primates, has since been found in the milk of many animals including dogs, cats, rats, and rabbits.
The enzyme acetylsalicylate deacetylase (EC 3.1.1.55) catalyzes the reaction

The enzyme acetylxylan esterase catalyzes the deacetylation of xylans and xylo-oligosaccharides.
The enzyme α-amino-acid esterase (EC 3.1.1.43) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme carboxylesterase (or carboxylic-ester hydrolase, EC 3.1.1.1; systematic name carboxylic-ester hydrolase) catalyzes reactions of the following form:
The enzyme feruloyl esterase (EC 3.1.1.73) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme lysophospholipase (EC 3.1.1.5) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a phosphatidylcholine---sterol O-acyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Sterol O-acyltransferase is an intracellular protein located in the endoplasmic reticulum that forms cholesteryl esters from cholesterol.
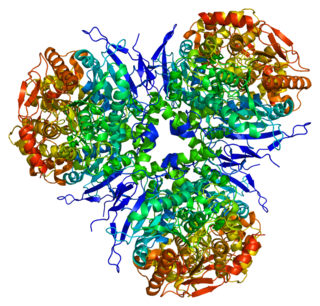
Liver carboxylesterase 1 also known as carboxylesterase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CES1 gene. The protein is also historically known as serine esterase 1 (SES1), monocyte esterase and cholesterol ester hydrolase (CEH). Three transcript variants encoding three different isoforms have been found for this gene. The various protein products from isoform a, b and c range in size from 568, 567 and 566 amino acids long, respectively.

Lathosterol oxidase is a Δ7-sterol 5(6)-desaturase enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SC5D gene.

In biochemistry, lipase refers to a class of enzymes that catalyzes the hydrolysis of fats. Some lipases display broad substrate scope including esters of cholesterol, phospholipids, and of lipid-soluble vitamins and sphingomyelinases; however, these are usually treated separately from "conventional" lipases. Unlike esterases, which function in water, lipases "are activated only when adsorbed to an oil–water interface". Lipases perform essential roles in digestion, transport and processing of dietary lipids in most, if not all, organisms.

The enzyme triacylglycerol lipase (also triglyceride lipase, EC 3.1.1.3;systematic name triacylglycerol acylhydrolase) catalyses the hydrolysis of ester linkages of triglycerides:

Lipase A, lysosomal acid type is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LIPA gene.












