
The human leg, in the general word sense, is the entire lower limb of the human body, including the foot, thigh and even the hip or gluteal region. However, the definition in human anatomy refers only to the section of the lower limb extending from the knee to the ankle, also known as the crus or, especially in non-technical use, the shank. Legs are used for standing, and all forms of locomotion including recreational such as dancing, and constitute a significant portion of a person's mass. Female legs generally have greater hip anteversion and tibiofemoral angles, but shorter femur and tibial lengths than those in males.
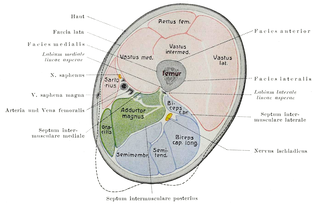
In human anatomy, the thigh is the area between the hip (pelvis) and the knee. Anatomically, it is part of the lower limb.

The patella, also known as the kneecap, is a flat, rounded triangular bone which articulates with the femur and covers and protects the anterior articular surface of the knee joint. The patella is found in many tetrapods, such as mice, cats, birds and dogs, but not in whales, or most reptiles.

The gluteus maximus is the main extensor muscle of the hip. It is the largest and outermost of the three gluteal muscles and makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of each side of the hips. It is the single largest muscle in the human body. Its thick fleshy mass, in a quadrilateral shape, forms the prominence of the buttocks. The other gluteal muscles are the medius and minimus, and sometimes informally these are collectively referred to as the glutes.

The gluteus minimus, or glutæus minimus, the smallest of the three gluteal muscles, is situated immediately beneath the gluteus medius.

The quadriceps femoris muscle is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large fleshy mass which covers the front and sides of the femur. The name derives from Latin four-headed muscle of the femur.
The biceps femoris is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it has two parts, one of which forms part of the hamstrings muscle group.

The vastus medialis is an extensor muscle located medially in the thigh that extends the knee. The vastus medialis is part of the quadriceps muscle group.

The adductor magnus is a large triangular muscle, situated on the medial side of the thigh.

The vastus intermedius (Cruraeus) arises from the front and lateral surfaces of the body of the femur in its upper two-thirds, sitting under the rectus femoris muscle and from the lower part of the lateral intermuscular septum. Its fibers end in a superficial aponeurosis, which forms the deep part of the quadriceps femoris tendon.

The vastus lateralis, also called the vastus externus, is the largest and most powerful part of the quadriceps femoris, a muscle in the thigh. Together with other muscles of the quadriceps group, it serves to extend the knee joint, moving the lower leg forward. It arises from a series of flat, broad tendons attached to the femur, and attaches to the outer border of the patella. It ultimately joins with the other muscles that make up the quadriceps in the quadriceps tendon, which travels over the knee to connect to the tibia. The vastus lateralis is the recommended site for intramuscular injection in infants less than 7 months old and those unable to walk, with loss of muscular tone.
The rectus femoris muscle is one of the four quadriceps muscles of the human body. The others are the vastus medialis, the vastus intermedius, and the vastus lateralis. All four parts of the quadriceps muscle attach to the patella by the quadriceps tendon.
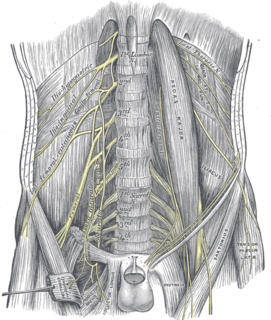
The femoral nerve is a nerve in the thigh that supplies skin on the upper thigh and inner leg, and the muscles that extend the knee.

The lateral circumflex femoral artery, also known as the lateral femoral circumflex artery, or the external circumflex artery, is an artery in the upper thigh.
The body of femur is the almost cylindrical, long part of the femur. It is a little broader above than in the center, broadest and somewhat flattened from before backward below. It is slightly arched, so as to be convex in front, and concave behind, where it is strengthened by a prominent longitudinal ridge, the linea aspera.

The tuberosity of the tibia or tibial tuberosity or tibial tubercle is an elevation on the proximal, anterior aspect of the tibia, just below where the anterior surfaces of the lateral and medial tibial condyles end.

The anterior compartment of thigh contains muscles which extend the knee and flex the hip.

A patellar dislocation is a knee injury in which the patella (kneecap) slips out of its normal position. Often the knee is partly bent, painful and swollen. The patella is also often felt and seen out of place. Complications may include a patella fracture or arthritis.

The vastus muscles are three of the four muscles that make up the quadriceps femoris muscle of the thigh. The three muscles are the vastus intermedius, the vastus lateralis, and the vastus medialis located in the middle, on the outside, and inside of the thigh, respectively. The fourth muscle is the rectus femoris muscle a large fleshy muscle which covers the front and sides of the femur.












