This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2014) |
Transport in Hungary relies on several main modes, including transport by road, rail, air and water.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(September 2014) |
Transport in Hungary relies on several main modes, including transport by road, rail, air and water.


Hungary has a total of 159,568 km (99,150 mi) of public roads, of which 70,050 km (43,530 mi) are paved (including 1481 km of motorways, as of 2016); and 89,518 km (55,620 mi) are unpaved (2005 etc.):
Hungarian road categories are as follows:
Hungarian motorways and expressways are part of the national road network. As of October 2016, there are 1,481 kilometres (920 mi) of controlled-access highways.
Motorways (autópályák, singular - autópálya) in Hungary:
M1 | M3 | M4 | M5 | M6 | M7 | M8 | M15 | M19 | M30 | M31 | M35 | M43 | M60

Expressways (autóutak, singular - autóút) in Hungary:
M0 | M2 | M9 | M51 | M70 | M85 | M86
New motorway sections are being added to the existing network, which already connects many major economically important cities to the capital.
Bus transport between municipalities was provided by Volán Companies, twenty-four bus companies founded in 1970 and named after the regions they served. They also provided local transport in cities and towns that did not have their own public transport company (all cities except for Budapest, Miskolc, Pécs, Kaposvár and also Debrecen after 2009), and operated bus lines in cities where the local company operated only tram and trolley bus lines (Szeged and Debrecen, the latter until 2009, when DKV took over the bus lines). In early 2015 the 24 companies were organized into seven regional companies.


Note: Hungary and Austria jointly manage the cross-border standard-gauge railway between Győr – Sopron – Ebenfurt (GySEV/ROeEE), a distance of about 101 km in Hungary and 65 km in Austria.
In Budapest, the three main railway stations are the Eastern (Keleti), Western (Nyugati) and Southern (Déli), with other outlying stations like Kelenföld. Of the three, the Southern is the most modern but the Eastern and the Western are more decorative and architecturally interesting.
Other important railway stations countrywide include Szolnok (the most important railway intersection outside Budapest), Tiszai Railway Station in Miskolc and the stations of Pécs, Győr, Debrecen, Szeged and Székesfehérvár.
The only city with an underground railway system is Budapest with its Metro.
In Budapest there is also a suburban rail service in and around the city, operated under the name HÉV.


There are 43-45 airports in Hungary, including smaller, unpaved airports, too. The five international airports are Budapest-Liszt Ferenc, Debrecen Airport, Hévíz–Balaton International Airport (previously Sármellék, also called FlyBalaton for its proximity to Lake Balaton, Hungary's number one tourist attraction), Győr-Pér and Pécs-Pogány (as of 2015. there are no regular passenger flights from Győr-Pér and Pécs-Pogány). Malév Hungarian Airlines ceased operations in 2012.
Total: 20 (1999 est.)
Total: 27 (1999 est.)
List of airports in Hungary; The following are the largest airports in Hungary (In descending order for 2015):
Hungary has five heliports. [1]
1,373 km permanently navigable (1997)
The most important port is Budapest, the capital. Other important ones include Dunaújváros and Baja.
Ports on the Danube:
Ports on the Tisza:
In the rest of the cities and towns local transport is provided by Volánbusz companies that also provide intercity bus lines.

The Budapest Metro (Hungarian : Budapesti metró) is the rapid transit system in the Hungarian capital Budapest. Its line 1 (opened in 1896) is the oldest electrified underground railway on the European continent. The second (red) line was opened in 1970, third (blue) line was opened in 1976, the newest line is the fourth (green), it was opened in 2014.
The busiest traditional city tram line in the world is still route 4/6 in Budapest, where 50-meter long trams run at 120 to 180 second intervals [2] at peak time and are usually packed with people. A part of this route is the same as where electric trams made their world first run in 1887. Since the 2000s, the Budapest tram network has been improved, by ordering new trams (Combino Supra and CAF Urbos 3) as well as extending some lines (such as line 1 to Kelenföld railway station).
Cities with tram lines
| Cities with former tram lines
|
There were some towns, where narrow gauge railways were used as tram lines or interurban lines (for example: Sárospatak, Sátoraljaújhely, Békéscsaba, Békés, Cegléd). These lines were closed in the 1970s.
 Trolleybuses can be found in three cities: Budapest, Debrecen and Szeged.
Trolleybuses can be found in three cities: Budapest, Debrecen and Szeged.

Transport in Greece has undergone significant changes in the past two decades, vastly modernizing the country's infrastructure and transportation. Although ferry transport between islands remains the prominent method of transport between the nation's islands, improvements to the road infrastructure, rail, urban transport, and airports have all led to a vast improvement in transportation. These upgrades have played a key role in supporting Greece's economy, which in the past decade has come to rely heavily on the construction industry.
Transport in Poland involves air, water, road and rail transportation. The country has a large network of municipal public transport, such as buses, trams and the metro. As a country located at the 'cross-roads' of Europe, Poland is a nation with a large and increasingly modern network of transport infrastructure.
A number of public holidays and special events take place each year in Hungary.

MVK Zrt. is the name of the transport company of the city of Miskolc, Hungary. Unlike the transport companies of many other cities, MVK Zrt. is independent from the company responsible for municipal transport in the county (Volánbusz) and is responsible only for the mass transportation in Miskolc and the nearby town Felsőzsolca. The buses are usually dark blue; the trams on Line 1 are yellow or red, on Line 2 are dark red. Miskolc has recently invested much in its public transportation. By the year 2016 90% of the company's vehicles will be low-floor.

Hungarian State Railways is the Hungarian national railway company and the MÁV Zrt. is the railway infrastructure manager, with subsidiaries "MÁV-START Zrt.", and "Utasellátó".

Public transport in Debrecen, Hungary, is provided by DKV

Controlled-access highways in Hungary are dual carriageways, grade separated with controlled-access, designed for high speeds. The legislation amendments define two types of highways: motorways and expressways.
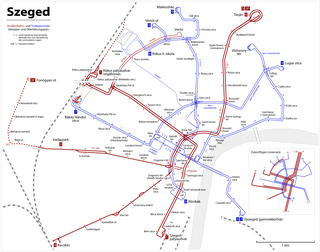
Public transport in Szeged, Hungary is provided by two companies, SzKT and Volánbusz. The former company operates trams and trolley buses, while the latter operates buses. SzKT is owned by the city.
Ferenc Pfaff was a Hungarian architect and academic.
There are currently several types of administrative divisions of Hungary; these include:

Maszovlet was a Hungarian airline founded on March 29, 1946. It was a predecessor of Malév.

Public roads in Hungary are ranked according to importance and traffic as follows:

The tram network of Budapest is part of the mass transit system of Budapest, the capital city of Hungary. Tram lines serve as the second-most important backbone of the transit system after the bus network, carrying almost 100 million more passengers annually than the Budapest Metro. In operation since 1866, the Budapest tram network is among the world's largest tram networks by route length—operating on 174 kilometres (108 mi) of total route—and is the busiest in the world.
The 2013–14 Magyar Kupa was the 74th season of Hungary's annual knock-out cup football competition. It started with the first match of Round 1 on 7 August 2013 and ended with the final held in May 2014 at Stadium Puskás Ferenc, Budapest. Debrecen were the defending champions, having won their sixth cup competition last season. The winner of the competition will qualify for the second qualifying round of the 2014–15 UEFA Europa League.
The Hungarian Fencing Federation is the national organization for fencing in Hungary. It was founded in 1914 and has been affiliated to the International Fencing Federation since 1917. Its headquarters is in Budapest.
The 2019–20 Magyar Kupa was the 80th season of Hungary's annual knock-out cup football competition. The title holders were MOL Vidi FC by winning the 2019 Magyar Kupa final. The competition was postponed on 16 March 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic and resumed on 23 May. Honvéd won the final by beating Mezőkövesdi SE at the Puskás Aréna.

The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints in Hungary refers to the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints and its members in Hungary. There were 75 members in Hungary in 1990. There were 5,259 members in 21 congregations as of December 2022.