
Lutetium is a chemical element; it has symbol Lu and atomic number 71. It is a silvery white metal, which resists corrosion in dry air, but not in moist air. Lutetium is the last element in the lanthanide series, and it is traditionally counted among the rare earth elements; it can also be classified as the first element of the 6th-period transition metals.

Ytterbium is a chemical element; it has symbol Yb and atomic number 70. It is a metal, the fourteenth and penultimate element in the lanthanide series, which is the basis of the relative stability of its +2 oxidation state. Like the other lanthanides, its most common oxidation state is +3, as in its oxide, halides, and other compounds. In aqueous solution, like compounds of other late lanthanides, soluble ytterbium compounds form complexes with nine water molecules. Because of its closed-shell electron configuration, its density, melting point and boiling point are much lower than those of most other lanthanides.

β-Carbon nitride (beta-carbon nitride), β-C3N4, is a superhard material predicted to be harder than diamond.

Control rods are used in nuclear reactors to control the rate of fission of the nuclear fuel – uranium or plutonium. Their compositions include chemical elements such as boron, cadmium, silver, hafnium, or indium, that are capable of absorbing many neutrons without themselves decaying. These elements have different neutron capture cross sections for neutrons of various energies. Boiling water reactors (BWR), pressurized water reactors (PWR), and heavy-water reactors (HWR) operate with thermal neutrons, while breeder reactors operate with fast neutrons. Each reactor design can use different control rod materials based on the energy spectrum of its neutrons. Control rods have been used in nuclear aircraft engines like Project Pluto as a method of control.

Titanium nitride is an extremely hard ceramic material, often used as a physical vapor deposition (PVD) coating on titanium alloys, steel, carbide, and aluminium components to improve the substrate's surface properties.

Ytterbium(III) oxide is the chemical compound with the formula Yb2O3. It is one of the more commonly encountered compounds of ytterbium. It occurs naturally in trace amounts in the mineral gadolinite. It was first isolated from this in 1878 by Jean Charles Galissard de Marignac.

Silicon nitride is a chemical compound of the elements silicon and nitrogen. Si
3N
4 is the most thermodynamically stable and commercially important of the silicon nitrides, and the term ″Silicon nitride″ commonly refers to this specific composition. It is a white, high-melting-point solid that is relatively chemically inert, being attacked by dilute HF and hot H
3PO
4. It is very hard. It has a high thermal stability with strong optical nonlinearities for all-optical applications.

Magnesium nitride, which possesses the chemical formula Mg3N2, is an inorganic compound of magnesium and nitrogen. At room temperature and pressure it is a greenish yellow powder.
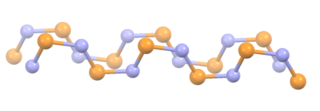
Polythiazyl, (SN)x, is an electrically conductive, gold- or bronze-colored polymer with metallic luster. It was the first conductive inorganic polymer discovered and was also found to be a superconductor at very low temperatures. It is a fibrous solid, described as "lustrous golden on the faces and dark blue-black", depending on the orientation of the sample. It is air stable and insoluble in all solvents.

Zinc nitride (Zn3N2) is an inorganic compound of zinc and nitrogen, usually obtained as (blue)grey crystals. It is a semiconductor. In pure form, it has the anti-bixbyite structure.

Tantalum nitride (TaN) is a chemical compound, a nitride of tantalum. There are multiple phases of compounds, stoichimetrically from Ta2N to Ta3N5, including TaN.

Uranium nitrides is any of a family of several ceramic materials: uranium mononitride (UN), uranium sesquinitride (U2N3) and uranium dinitride (UN2). The word nitride refers to the −3 oxidation state of the nitrogen bound to the uranium.
Praseodymium(III) nitride is a binary inorganic compound of praseodymium and nitrogen. Its chemical formula is PrN. The compound forms black crystals, and reacts with water.
Ytterbium(III) phosphide is an inorganic compound of ytterbium and phosphorus with the chemical formula YbP. This is one of the phosphides of ytterbium.
Ytterbium compounds are chemical compounds that contain the element ytterbium (Yb). The chemical behavior of ytterbium is similar to that of the rest of the lanthanides. Most ytterbium compounds are found in the +3 oxidation state, and its salts in this oxidation state are nearly colorless. Like europium, samarium, and thulium, the trihalides of ytterbium can be reduced to the dihalides by hydrogen, zinc dust, or by the addition of metallic ytterbium. The +2 oxidation state occurs only in solid compounds and reacts in some ways similarly to the alkaline earth metal compounds; for example, ytterbium(II) oxide (YbO) shows the same structure as calcium oxide (CaO).
Ytterbium(III) sulfide is a binary inorganic compound of ytterbium and sulfur with the chemical formula Yb2S3.

Ytterbium(II) fluoride is a binary inorganic compound of ytterbium and fluorine with the chemical formula YbF2.
Erbium nitride is a binary inorganic compound of erbium and nitrogen with the chemical formula ErN.
Europium(III) nitride is a binary inorganic compound of europium and nitrogen with the chemical formula EuN.
Ytterbium monotelluride is an inorganic compound, one of the tellurides of ytterbium, with the chemical formula YbTe.












