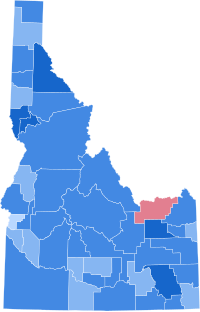
The 1936 United States presidential election was the 38th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 1936. In the midst of the Great Depression, incumbent Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt defeated Republican governor Alf Landon of Kansas in a landslide. Roosevelt won the highest share of the popular vote (60.8%) and the electoral vote since the largely uncontested 1820 election. The sweeping victory consolidated the New Deal Coalition in control of the Fifth Party System.

Alfred Mossman Landon was an American oilman and politician who served as the 26th governor of Kansas from 1933 to 1937. A member of the Republican Party, he was the party's nominee in the 1936 presidential election, and was defeated in a landslide by incumbent president Franklin D. Roosevelt. The margin of victory in the electoral college was the largest of Roosevelt's 4 elections to the office of president, as Landon won just 8 electoral votes to Roosevelt's 523. Landon lived to the age of 100 and died in October 1987. Landon would be the only presidential candidate from either party to live to 100 until Jimmy Carter in 2024 and Landon is the only Republican to do so.
The Union Party was a short-lived political party in the United States, formed in 1935 by a coalition of radio priest Father Charles Coughlin, old-age pension advocate Francis Townsend, and Gerald L. K. Smith, who had taken control of Huey Long's Share Our Wealth (SOW) movement after Long's assassination in 1935. Each of those people hoped to channel their wide followings into support for the Union Party, which proposed a populist alternative to the New Deal reforms of Franklin D. Roosevelt during the Great Depression.

William Edgar Borah was an outspoken Republican United States Senator, one of the best-known figures in Idaho's history. A progressive who served from 1907 until his death in 1940, Borah is often considered an isolationist, because he led the Irreconcilables, senators who would not accept the Treaty of Versailles, Senate ratification of which would have made the U.S. part of the League of Nations.

The 1936 Republican National Convention was held June 9–12 at the Public Auditorium in Cleveland, Ohio. It nominated Governor Alfred Landon of Kansas for president and Frank Knox of Illinois for vice president.

From March 12 to May 17, 1940, voters of the Republican Party chose delegates to nominate a candidate for president at the 1940 Republican National Convention. The nominee was selected at the convention in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania from June 24–28, 1940.

The 1936 United States elections were held on November 3, 1936, during the Great Depression. Democratic President Franklin D. Roosevelt trounced Governor Alf Landon of Kansas in a landslide and the Democrats built on their majorities in both chambers of Congress.

The 1936 United States presidential election in Vermont took place on November 3, 1936, as part of the 1936 United States presidential election which was held throughout all contemporary 48 states. Voters chose three representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
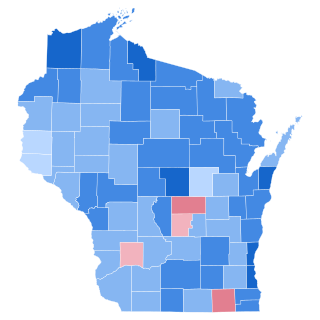
The 1936 United States presidential election in Wisconsin was held on November 3, 1936 as part of the 1936 United States presidential election. State voters chose 12 electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1936 United States presidential election in Maine was held on November 3, 1936 as part of the 1936 United States presidential election. The state voters chose five electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.
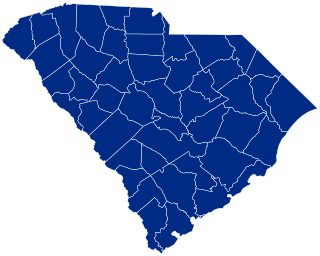
The 1936 United States presidential election in South Carolina was held on November 3, 1936. The state voters chose 8 electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president. With Roosevelt winning 98.57% of the vote, this was the most emphatic win for any presidential candidate against another in any state in American history.

The 1936 United States presidential election in Wyoming took place on November 3, 1936, as part of the 1936 United States presidential election. State voters chose three representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1936 United States presidential election in Delaware was held on November 3, 1936. The state voters chose three electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1936 United States presidential election in North Dakota took place on November 3, 1936, as part of the 1936 United States presidential election. Voters chose four representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1936 United States presidential election in South Dakota took place on November 3, 1936, as part of the 1936 United States presidential election. Voters chose four representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1936 United States presidential election in Alabama took place on November 3, 1936, as part of the nationwide presidential election. Voters chose eleven representatives, or electors to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president. In Alabama, voters voted for electors individually instead of as a slate, as in the other states.

The 1936 United States presidential election in Tennessee took place on November 3, 1936, as part of the 1936 United States presidential election. Tennessee voters chose 11 representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1936 United States presidential election in Oregon took place on November 3, 1936, as part of the 1936 United States presidential election. Voters chose five representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 1936 United States presidential election in North Carolina took place on November 3, 1936, as part of the 1936 United States presidential election. North Carolina voters chose 13 representatives, or electors, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.