
A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a hitch fastens a rope to another object; a bend fastens two ends of a rope to each another; a loop knot is any knot creating a loop; and splice denotes any multi-strand knot, including bends and loops. A knot may also refer, in the strictest sense, to a stopper or knob at the end of a rope to keep that end from slipping through a grommet or eye. Knots have excited interest since ancient times for their practical uses, as well as their topological intricacy, studied in the area of mathematics known as knot theory.

The overhand knot, also known as a knot and half knot, is one of the most fundamental knots, and it forms the basis of many others, including the simple noose, overhand loop, angler's loop, reef knot, fisherman's knot, Half hitch, and water knot. The overhand knot is a stopper, especially when used alone, and hence it is very secure, to the point of jamming badly. It should be used if the knot is intended to be permanent. It is often used to prevent the end of a rope from unraveling. An overhand knot becomes a trefoil knot, a true knot in the mathematical sense, by joining the ends. It can also be adjusted, faired, or mis-tied as a half hitch

The figure-eight knot or figure-of-eight knot is a type of stopper knot. It is very important in both sailing and rock climbing as a method of stopping ropes from running out of retaining devices. Like the overhand knot, which will jam under strain, often requiring the rope to be cut, the figure-eight will also jam, but is usually more easily undone than the overhand knot.
The figure-eight or figure-of-eight knot is also called the Flemish knot. The name figure-of-eight knot appears in Lever's Sheet Anchor; or, a Key to Rigging. The word "of" is nowadays usually omitted. The knot is the sailor's common single-strand stopper knot and is tied in the ends of tackle falls and running rigging, unless the latter is fitted with monkey's tails. It is used about ship wherever a temporary stopper knot is required. The figure-eight is much easier to untie than the overhand, it does not have the same tendency to jam and so injure the fiber, and is larger, stronger, and equally secure.

Figure-eight loop is a type of knot created by a loop on the bight. It is used in climbing and caving
The Flemish loop or figure-eight loop is perhaps stronger than the loop knot. Neither of these knots is used at sea, as they are hard to untie. In hooking a tackle to any of the loops, if the loop is long enough it is better to arrange the rope as a cat's paw.

A grief knot is a knot which combines the features of a granny knot and a thief knot, producing a result which is not generally useful for working purposes. The word grief does not carry its usual meaning but is a portmanteau of granny and thief.

A blood knot is a bend knot most usefully employed for joining sections of monofilament nylon line while maintaining a high portion of the line's inherent strength. Other knots used for this purpose can cause a substantial loss of strength. In fly fishing, this serves to build a leader of gradually decreasing diameter with the castable fly line attached at the large diameter end and the fly or hook at the small diameter end. The principal drawback to the blood knot is the dexterity required to tie it. It is also likely to jam, which is not a concern in fishing line, which is no great loss to cut, but may be a concern in normal rope. "Blood knot" may refer to "a double overhand knot tied in a cat-o'-nine-tails."
The barrel knot, called blood knot by Keith Rollo, is the best bend there is for small, stiff or slippery line. The ends may be trimmed short and the knot offers the least resistance possible when drawn through water.

The diamond knot is a knot for forming a decorative loop on the end of a cord such as on a lanyard. A similar knot, also called the diamond knot, is a multistrand stopper knot, that is similar in appearance. To avoid confusion, it is advisable to call this knot the knife lanyard knot. This knot is a four strand diamond knot implemented in two strands. The knife lanyard knot is "tied alike" the Chinese button knot, "but they are worked differently."
The sailor's knife lanyard knot, also called marling-spike lanyard knot, single-strand diamond knot, two-strand diamond knot, and Bosun's whistle knot.

The slip knot is a stopper knot which is easily undone by pulling the tail. The slip knot is related to the running knot, which will release when the standing end is pulled. Both knots are identical and are composed of a slipped overhand knot, where a bight allows the knot to be released by pulling on an end; the working end for a slip knot, and the standing end for a running knot. The slip knot is used as a starting point for crochet and knitting.
The slip knot is a stopper knot that may be spilled or slipped instantly by pulling on the end to withdraw a loop. There is but one knot entitled to the name; any others having a similar feature are merely " slipped" knots.

A stopper knot is a knot that creates a fixed thicker point on an otherwise-uniform thickness rope for the purpose of preventing the rope, at that point, from slipping through a narrow passage, such as a hole in a block. To pass a rope through a block, or hole, is to reeve it. To pull it out is to unreeve it. Stopper knots prevent the rope from unreeving on its own.

The half hitch is a simple overhand knot, where the working end of a line is brought over and under the standing part. Insecure on its own, it is a valuable component of a wide variety of useful and reliable hitches, bends, and knots.

The stevedore knot is a stopper knot, often tied near the end of a rope. It is more bulky and less prone to jamming than the closely related figure-eight knot.
The bight is given one more half turn than in the former knot [which itself is given, "one additional half twist," more than the figure-eight knot], before the end is finally stuck.

The figure-of-nine loop is a type of knot to form a fixed loop in a rope. Tied in the bight, it is made similarly to a figure-of-eight loop but with an extra half-turn before finishing the knot.

Two half-hitches is a type of knot, specifically a binding knot or hitch knot. One variety consists of an overhand knot tied around a post, followed by a half-hitch. This knot is less often referred to as a clove hitch over itself, double half-hitch, or full-hitch.
Two half hitches is the commonest of all hitches for mooring in particular and also for general utility. Steel gives the name in 1794. The difference between two half hitches and the clove hitch is that the former, after a single turn around a spar, is made fast around its own standing part, while the latter is tied directly around the spar.

The Flemish bend, also known as a figure eight bend, a rewoven figure eight is a knot for joining two ropes of roughly similar size.

The double overhand knot is simply an extension of the regular overhand knot, made with one additional pass. The result is slightly larger and more difficult to untie. It forms the first part of the surgeon's knot and both sides of a double fisherman's knot. The strangle knot is a rearranged double overhand knot made around an object. It is sometimes used to secure items to posts. According to The Ashley Book of Knots, "A double overhand knot tied in a cat-o'-nine-tails is termed a blood knot."
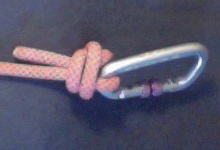
The double overhand noose is a very secure hitch knot. It might be used by cavers and canyoneers to bind a cow tail or a foot loop to a carabiner.

A button knot is a knot that forms a bulge of thread. Button knots are essentially stopper knots, but may be esthetically pleasing enough to be used as a button on clothes.
The single-strand button is a third type of knob knot, in which the working end leaves the knot at the neck, parallel with the standing part, so that the two parts, or ends, together form a stem. The lay of the two ends is the same, and the knot is symmetrical throughout.

A Tensionless hitch is an anchor knot used for rappelling or rope rescue. Unlike most knots, the tensionless hitch retains a 100% efficiency rating, meaning the strength of the knot is equal to the strength of the rope; it is not a significant stress riser.



















