
The Cherokee National Forest is a large National Forest created on June 14, 1920 and managed by the U.S. Forest Service and encompassing some 655,598 acres (2,653.11 km2).

The Chattooga River is the main tributary of the Tugaloo River. Its headwaters are located southwest of Cashiers, North Carolina, and it stretches 57 miles (92 km) to where it has its confluence with the Tallulah River within Lake Tugalo, held back by the Tugalo Dam. The Chattooga and the Tallulah combine to make the Tugaloo River starting at the outlet of Lake Tugalo. The Chattooga begins in southern Jackson County, North Carolina, then flows southwestward between northwestern Oconee County, South Carolina, and eastern Rabun County, Georgia. The "Chattooga" spelling was approved by the US Board on Geographic Names in 1897.

White River National Forest is a National Forest in northwest Colorado. It is named after the White River that passes through its northern section. It is the most visited National Forest in the United States, primarily from users of the twelve ski areas within its boundaries.

The Shasta–Trinity National Forest is a federally designated forest in northern California, USA. It is the largest National Forest in California and is managed by the U.S. Forest Service. The 2,210,485 acre forest encompasses five wilderness areas, hundreds of mountain lakes and 6,278 miles (10,103 km) of streams and rivers. Major features include Shasta Lake, the largest man-made lake in California and Mount Shasta, elevation 14,179 feet (4,322 m).

Pisgah National Forest is a National Forest in the Appalachian Mountains of western North Carolina. It is administered by the United States Forest Service, part of the United States Department of Agriculture. The Pisgah National Forest is completely contained within the state of North Carolina. The forest is managed together with the other three North Carolina National Forests from common headquarters in Asheville, North Carolina. There are local ranger district offices located in Pisgah Forest, Mars Hill, and Nebo.

The Conasauga River is a river that runs through southeast Tennessee and northwest Georgia. The Conasauga River is 93 miles (150 km) long and is home to 90 species of fish and 25 species of freshwater mussels. The Conasauga River watershed encompasses over 500,000 acres (2,000 km2) in two states, multiple counties, and two ecologically different regions.
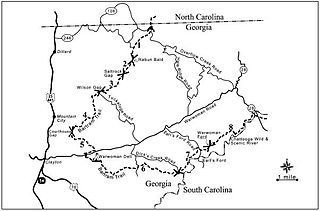
The Bartram Trail follows the approximate route of 18th-century naturalist William Bartram’s southern journey from March 1773 to January 1777. Bartram explored much of the territory which is now the states of North and South Carolina, Georgia, Florida, Alabama, Mississippi, Louisiana and Tennessee.

The Nantahala National Forest, established in 1920, is a national forest located in the American state of North Carolina. The word "Nantahala" is a Cherokee word meaning "Land of the Noonday Sun." The name is appropriate as, in some spots, the sun only reaches the floors of the deep gorges of the forest when high overhead at midday. The Spanish Conquistador Hernando de Soto explored the area in 1540, as did William Bartram in the 18th century. The Nantahala River flows through the Nantahala National Forest.
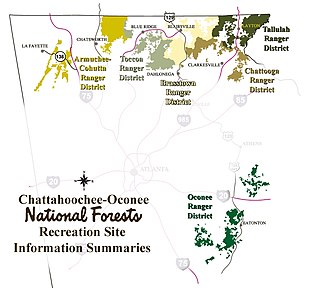
The Tallulah Ranger District is one of the five ranger districts of the Chattahoochee National Forest. The largest portion of the district is located in Rabun County, Georgia, which contains nearly 149,000 acres (600 km2). A portion of the Tallulah Ranger District is also found in Towns County. Both the Appalachian Trail and the Bartram Trail are located in the district.

The Southern Nantahala Wilderness was designated in 1984 and currently consists of 23,473 acres (94.99 km2). Approximately 11,770 acres (47.6 km2) are located in Georgia in the Chattahoochee National Forest and approximately 11,703 acres (47.36 km2) are located in North Carolina in the Nantahala National Forest. The Wilderness is managed by the United States Forest Service and is part of the National Wilderness Preservation System. The highest elevation in the Southern Nantahala Wilderness is the 5,499-foot peak of Standing Indian Mountain in North Carolina and the lowest elevation is approximately 2,400 feet (730 m). The Appalachian Trail passes through the Wilderness in both states.

The Tray Mountain Wilderness was designated in 1986 and currently consists of 9,702 acres (39.26 km2). The Wilderness is located within the borders of the Chattahoochee National Forest in Habersham, Rabun, Towns and White counties, Georgia and is managed in the Chattooga Ranger District. The Wilderness is managed by the United States Forest Service and is part of the National Wilderness Preservation System.

Rich Mountain, elevation 4,040 feet (1,230 m), is the highest point in the Rich Mountain Wilderness of the Chattahoochee National Forest in Gilmer County, Georgia. It is the second-highest peak in Gilmer County; only Big Bald Mountain is taller, with its summit at 4,081 feet (1,244 m).

Ellicott Rock Wilderness is managed by the United States Forest Service and is part of the National Wilderness Preservation System. It was first designated by Congress in 1975 with the Eastern Wilderness Act. The majority of this land lays in South Carolina. Additional lands were added to Ellicott Rock Wilderness in 1984 with the passing of the North Carolina Wilderness Act and the Georgia Wilderness Act, today designated wilderness totals 8,274 acres (33.48 km2). Ellicott Rock Wilderness is the only wilderness that straddles three states, with boundaries located around the point at which Georgia, North Carolina, and South Carolina come together. Ellicott Rock Wilderness also spans three National Forests. Sumter National Forest in South Carolina is responsible for 2,859 acres (11.57 km2), receives the majority of recreation in the wilderness, and also acts as the lead manager of Ellicott Rock Wilderness. Nantahala National Forest in North Carolina is responsible for the majority of the wilderness at 3,394 acres (13.74 km2) and the Chattahoochee National Forest in Georgia manages 2,021 acres (8.18 km2) of wilderness. In 1979, Forest Service land was surveyed under the Roadless Area Review and Evaluation and 1,982 acres (8.02 km2) adjacent to the existing wilderness were classified as Roadless National Forest System land, named Ellicott Rock Extension. The Andrew Pickens Ranger district on the Sumter National Forest recommended the Ellicott Rock Extension as wilderness in 1995 in their Resource Management Plan. In June of 2017 during a land management plan revision, the Nantahala Ranger District on the Nantahala National Forest added 824 acres (3.33 km2) of proposed wilderness, currently called Ellicott Rock West Extension.

The Sumter National Forest is one of two forests in South Carolina that are managed together by the United States Forest Service, the other being the Francis Marion National Forest. The Sumter National Forest consists of 370,442 acres (1,499.13 km2) which are divided into several non-contiguous sections in western South Carolina. Overall, in descending order of land area the forest is located in parts of Oconee, Union, Newberry, McCormick, Edgefield, Abbeville, Laurens, Chester, Fairfield, Greenwood, and Saluda counties. Forest headquarters of both South Carolina forests are located together in the state's capital city of Columbia.

Horsetrough Falls are located on one of the flanks of Horsetrough Mountain in Union County, Georgia. This 70-foot (21 m) waterfall is located on a creek that is part of the headwaters of the Chattahoochee River and is in the Mark Trail Wilderness. There is an observation platform at the falls which can be reached by the 0.4-mile (0.64 km) Horsetrough Falls Trail. The trail begins at the nearby Upper Chattahoochee Campground camping area, which is maintained and operated by the Chattooga Ranger District of the Chattahoochee National Forest. The Eastern Continental Divide follows the main ridge line of Horsetrough Mountain and the water passes over Horsetrough Falls to begin a 500-mile (800 km) journey to the Gulf of Mexico via the Chattahoochee River.

The Armuchee-Cohutta Ranger District is one of the five ranger districts of the Chattahoochee National Forest. Armuchee is thought to be derived from the Cherokee word for "hominy," to be derived from the Choctaw word alurnushi, meaning "hiding place" or mean the "land of the flowers." Cohutta is derived from the Cherokee word cohutta, which means "frog" or could mean "a shed roof supported on poles." The district is spread through portions of Catoosa, Chattooga, Fannin, Floyd, Gilmer, Gordon, Murray, Walker and Whitfield Counties in Georgia. Some of the features within the borders of the district are the Big Frog Wilderness, the Cohutta Wilderness and the Rich Mountain Wilderness.

The protected areas of Georgia cover almost one million acres (4,000 km²) of the state. These areas are managed by different federal and state level authorities and receive varying levels of protection. Some areas are managed as wilderness while others are operated with acceptable commercial exploitation. On the Federal level, Georgia contains 1 Biosphere Reserve, 15 National Park Service Managed Sites, 1 National Forest and 8 Wildlife Refuges. Georgia is home to 63 state parks, 48 of which are state parks and 15 that are National Historic Sites, and many state wildlife preserves, under the supervision of the Georgia Department of Parks and Recreation, a division of the Georgia Department of Natural Resources.


































