The Cook River / Weheka is in the South Island of New Zealand. The headwaters are from the La Perouse Glacier on the western flanks of the Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana, and it flows west, then northeast, then northwest and into the Tasman Sea. Its tributaries include the Balfour River, fed by Balfour Glacier, and the Fox River, fed by Fox Glacier / Te Moeka o Tuawe. Much of the river lies within the Westland Tai Poutini National Park. The river was renamed from Cook River to Cook River / Weheka as a result of the Ngāi Tahu Claims Settlement Act 1998.

The Copland River is a river on the West Coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It flows for 20 kilometres (12 mi) from its headwaters in the Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana to its confluence with the Karangarua River.

Otehake River is located on the West Coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It flows northward through the Arthur's Pass National Park and into the Taramakau River.

Lake Hāwea is New Zealand's ninth largest lake.

The Manawatū River is a major river of the lower North Island of New Zealand. The river flows from the Ruahine Ranges, through both the Manawatū Gorge and the city of Palmerston North, and across the Manawatū Plains to the Tasman Sea at Foxton.

Brunner, originally called Brunnerton, is a town in the northwest of New Zealand's South Island. It is 12 kilometres (7 mi) east of Greymouth, on the south bank of the Grey River. It is on the Midland Line railway near its junction with the Stillwater–Westport Line (SWL) in neighbouring Stillwater. Passenger trains ceased running along the SWL to Reefton and Westport in 1967, but the TranzAlpine runs the length of the Midland Line from Christchurch to Greymouth and it continues to stop in Brunner.

Cronadun is a small village located in the West Coast region of New Zealand's South Island. It is situated on the east bank of the Inangahua River, near its junction with Boatmans Creek. SH 69 and the Stillwater–Westport Line railway pass through the village.

The Cust River is a river in the Canterbury region of New Zealand. It flows east across the upper Canterbury Plains from its source north of the town of Oxford, New Zealand, flowing into the Cam River / Ruataniwha close to the town of Rangiora. The small town of Cust lies on the banks of the river. The lower part of the river, to the south-west of Rangiora, is diverted into a channel and called the "Main Drain". The channel was built in 1862 to drain the swampy land between Rangiora and the Waimakariri River, and when it was enlarged in 1868 it accidentally captured the Cust.

The Doubtful River is a river in the Canterbury region of New Zealand. It rises near Mount Barron and flows south then south-east through Lake Sumner Forest Park, reaching the Boyle River 40 kilometres (25 mi) west of Hanmer Springs. The Doubtful Range lies to the south. The Doubtless River and Devilskin Stream are tributaries entering from the north.
The Douglas River, formerly known as the Twain, is a river of the West Coast of New Zealand's South Island. Its source is high in the Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana, five kilometres (3.1 mi) south of Mount Sefton, and its upper reaches are fed by water from the Douglas Glacier. It flows west for 18 kilometres (11 mi), joined by runoff from the Horace Walker Glacier, before joining the waters of the Karangarua River. The Douglas River's entire course is within Westland Tai Poutini National Park. The river and glacier are named after Charles Edward Douglas, a 19th-century explorer and mountaineer.

The Glentui River is a river in the Canterbury region of New Zealand. It arises on the slopes of Mount Richardson and flows south-east through the locality of Glentui and into Ashley River / Rakahuri, which exits in the Pacific Ocean. The river was earlier called Tui Creek, and the locality named from the station Glentui established by H.C.H. Knowles in 1854.
The Gorge River is a river on the West Coast of New Zealand. It arises in the Hope Blue River Range and flows south-west into the Tasman Sea. Its tributaries include the Duncan River and Jerry River. It passes through Cascade Forest. Its mouth is about 15 km north-east of Awarua Point. The Gorge Islands are very small islands near the mouth. At its mouth, it is a fast tidal river.
The Hacket River is a river on the West Coast of New Zealand. It starts in the Malcolm Range and flows south-west into the Tasman Sea.

Ikamatua is a small village on the West Coast of the South Island in New Zealand. Its name translates literally as ika (fish) and matua (mature/parent). It may be a contraction of Te Ika-a-matua, fish of my ancestor.
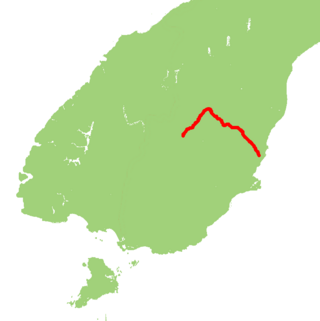
State Highway 85 (SH 85) is a South Island state highway in New Zealand, servicing the Maniototo Plains and the North and Central Otago regions of the South Island between the major settlements of Alexandra and Palmerston. It is wholly two lane and passes through some of the most extreme climatic regions in New Zealand. The highway is known colloquially as "The Pigroot". Though there is no definitive explanation for this name, A. W. Reed, in his book Place Names of New Zealand, mentions an incident during John Turnbull Thomson's survey of inland Otago in which local wild pigs were so unafraid of humans that a huge boar approached his party and rubbed its nose against that of Thomson's horse.
Woodstock is a small settlement in the Tasman District of the northern South Island of New Zealand. It is located on the Motueka Valley Highway, close to the eastern bank of the Motueka River, some 20 kilometres southwest of Motueka, at the junction of the Motueka River and its small tributary, the Dove River.

The Humboldt Mountains or Humboldt Range are one of the many ranges which make up the Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana in the South Island of New Zealand. They lie to the northwest of Lake Wakatipu in the Otago Region. Parts of the range lie within Fiordland National Park, and they form the southern extremity of Mount Aspiring National Park. The range was named by early explorer James McKerrow, and like many geographic features worldwide, it was named in honour of notable scientist Alexander von Humboldt.

The Bryant Range is a range of low mountains in the northern South Island of New Zealand. They form part of the boundary of the Nelson and Tasman Districts with Marlborough Region, as well as forming the western boundary of Mount Richmond Forest Park The range is traversed by State Highway 6 at the Rai Saddle close to its northern end.

The Olivine Ice Plateau is a glacier in the Olivine Wilderness Area and Aspiring National Park in New Zealand's South Island. The plateau is named after the mineral olivine, which is common within the Dun Mountain Ophiolite that underlies the area. The plateau extents to the west over the Forgotten River Col. into the Forgotten River and to the north it merges with the Andy Glacier, which feeds a tributary of the Arawhata River. The Olivine Ice Plateau is one of many glaciers in the region of the Arawhata, Dart / Te Awa Whakatipu, Hollyford / Whakatipu Kā Tuka and Matukituki rivers' headwaters.
The Darran Mountains are a prominent range within New Zealand's Fiordland National Park, the country's biggest national park. They contain the park's highest peak, Mount Tūtoko.