Milford Sound is a fiord in the south west of New Zealand's South Island within Fiordland National Park, Piopiotahi Marine Reserve, and the Te Wahipounamu World Heritage site. It has been judged the world's top travel destination in an international survey and is acclaimed as New Zealand's most famous tourist destination. Rudyard Kipling called it the eighth Wonder of the World. The fiord is most commonly accessed via road by tour coach, with the road terminating at a small village also called Milford Sound.

Fiordland, is a non-administrative geographical region of New Zealand in the south-western corner of the South Island, comprising the western third of Southland. Most of Fiordland is dominated by the steep sides of the snow-capped Southern Alps, deep lakes, and its steep, glacier-carved and now ocean-flooded western valleys. The name "Fiordland" derives from an alternate spelling of the Scandinavian word for steep glacial valleys, "fjord". The geographic area of Fiordland is dominated by, and roughly coterminous with, Fiordland National Park, New Zealand's largest national park.

Fiordland National Park is a national park in the south-west corner of South Island of New Zealand. It is the largest of the 13 national parks in New Zealand, with an area covering 12,607 km2 (4,868 sq mi), and a major part of the Te Wāhipounamu a UNESCO World Heritage Site established in 1990. The park is administered by the Department of Conservation. The southern ranges of the Southern Alps cover most of Fiordland National Park, combined with the deep glacier-carved valleys.

Jackson Bay / Okahu is a gently curving 24-kilometre (15 mi) bay on the southern West Coast of the South Island of New Zealand. It faces the Tasman Sea to the north, and is backed by the Southern Alps. It contains the settlements of Hannahs Clearing, Waiatoto, Neils Beach, and the fishing village of Jackson Bay at its western end. The bay is the southernmost terminus of the West Coast's roads.

The Routeburn Track is a 32 km tramping (hiking) track found in the South Island of New Zealand. The track can be done in either direction, starting on the Queenstown side of the Southern Alps, at the northern end of Lake Wakatipu or on the Te Anau side, at the Divide, several kilometres from the Homer Tunnel to Milford Sound.

The Hollyford River / Whakatipu Kā Tuka is in the southwest of the South Island of New Zealand. It runs for 72 kilometres (45 mi) through Fiordland, its sources being close to the Homer Tunnel and in Gertrude Valley in the southern Darran Mountains.

The Hollyford Track is a tramping track in New Zealand. Located at the northern edge of Fiordland, in the southwestern South Island, it is unusual among Fiordland's major tracks in that it is largely flat and accessible year-round. It follows the Hollyford River which in turn follows the course of the Hollyford Valley.
Awarua Point is located on the southwestern coast of New Zealand's South Island, at the northern end of Big Bay, 40 kilometres (25 mi) north of Milford Sound / Piopiotahi, and 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) north of the mouth of the Hollyford River / Whakatipu Kā Tuka.

Mitre Peak is a mountain in the South Island of New Zealand; it is located on the shore of Milford Sound.

Transport in Milford Sound in New Zealand is characterised by the remoteness of the area in which it is located. As a popular tourism destination in the South Island, Milford Sound and the village of the same name receive very large numbers of visitors. These tend to arrive and depart within just a few hours each day, as there is little accommodation at the village, leading to strong demand peaks for tourism services during the noon and early afternoon period. The journey from Te Anau is rated as one of the most photographic drives of the world.

Hollyford Valley is a valley in Fiordland, New Zealand, in the southwest of the South Island. It is named for the Hollyford River, which runs north-north-west along its length from the Southern Alps to the Tasman Sea. Beech forest dominates both the slopes and the bottom of the valley.

Lake Marian is an alpine lake at the southern end of the Darran Mountains in the Fiordland National Park in the South Island of New Zealand. The lake is located just above the treeline in a hanging valley leading northwest from the Hollyford Valley near The Divide pass. The valley is sheltered by steep snow-covered peaks of over 2,000 metres (6,600 ft) on all sides apart from the entrance.
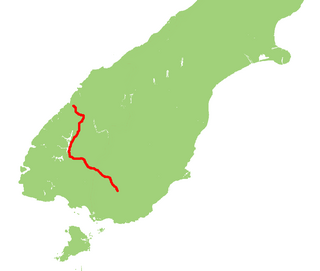
State Highway 94 is a New Zealand state highway connecting the large Southland town of Gore with one of New Zealand's most popular destinations, Milford Sound. It also passes the significant townships of Lumsden and Te Anau as well going through the Homer Tunnel. The road also goes through Fiordland and crosses the Main Divide of the Southern Alps.
David John Gunn was a New Zealander and promoter of the Hollyford Track. A farmer and bushman, he ran his almost wild cattle in the glacier-cut Hollyford Valley in Fiordland, South Westland, New Zealand.

The Haast-Hollyford road or Haast-Hollyford Highway is a long-standing proposal to link Haast via the Hollyford Valley to Milford Sound and Te Anau in the South Island of New Zealand. Proposals for this road have been mooted since the 1880s.

The Humboldt Mountains or Humboldt Range are one of the many ranges which make up the Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana in the South Island of New Zealand. They lie to the northwest of Lake Wakatipu in the Otago Region. Parts of the range lie within Fiordland National Park, and they form the southern extremity of Mount Aspiring National Park. The range was named by early explorer James McKerrow, and like many geographic features worldwide, it was named in honour of notable scientist Alexander von Humboldt.
Taitetimu / Caswell Sound is a fiord of the South Island of New Zealand. It is one of the fiords that form the coast of Fiordland.
Te Houhou / George Sound is a fiord of the South Island of New Zealand. It is one of the fiords that form the coast of Fiordland.
The Darran Mountains are a prominent range within New Zealand's Fiordland National Park, the country's biggest national park. They contain the park's highest peak, Mount Tūtoko.

Donald Sutherland was a Scottish-born New Zealand explorer, active in the late 19th century. Born in Wick, he served as a soldier in the Expedition of the Thousand, led by Giuseppe Garibaldi, in the Italian unification wars. Soon afterwards he travelled to New Zealand where he prospected for gold in Otago. He later joined the New Zealand military and fought in a number of engagements of the New Zealand Wars. In 1877, he settled in Milford Sound and lived as a hermit for a number of years, exploring the region. He later married and, with his wife, ran an accommodation facility for the increasing number of tourists visiting Milford Sound until his death in October 1919. The Sutherland Falls, located near Milford Sound and the highest waterfall in New Zealand, is named for him.