Vancouver is a major city in western Canada, located in the Lower Mainland region of British Columbia. As the most populous city in the province, the 2021 Canadian census recorded 662,248 people in the city, up from 631,486 in 2016. The Metro Vancouver area had a population of 2.6 million in 2021, making it the third-largest metropolitan area in Canada. Greater Vancouver, along with the Fraser Valley, comprises the Lower Mainland with a regional population of over 3 million. Vancouver has the highest population density in Canada, with over 5,700 people per square kilometre, and fourth highest in North America.

Larry W. Campbell is a Canadian politician who was the 37th mayor of Vancouver, Canada, from 2002 until 2005, and a member of the Senate of Canada from 2005 until his retirement in 2023.

Thunder Bay is a city in and the seat of Thunder Bay District, Ontario, Canada. It is the most populous municipality in Northwestern Ontario and the second most populous municipality in Northern Ontario; its population is 108,843 according to the 2021 Canadian Census. Located on Lake Superior, the census metropolitan area of Thunder Bay has a population of 123,258 and consists of the city of Thunder Bay, the municipalities of Oliver Paipoonge and Neebing, the townships of Shuniah, Conmee, O'Connor, and Gillies, and the Fort William First Nation.

Frederick Cope was the third Mayor of Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, serving from 1892 to 1893.

BCE Inc., an abbreviation of its former name Bell Canada Enterprises Inc., is a publicly traded Canadian holding company for Bell Canada, which includes telecommunications providers and various mass media assets under its subsidiary Bell Media Inc. Founded through a corporate reorganization in 1983, when Bell Canada, Northern Telecom, and other related companies all became subsidiaries of Bell Canada Enterprises Inc., it is one of Canada's largest corporations. The company is headquartered at 1 Carrefour Alexander-Graham-Bell in the Verdun borough of Montreal, Quebec, Canada.

Julian David Cope is an English musician and author. He was the singer and songwriter in Liverpool post-punk band the Teardrop Explodes and has followed a solo career since 1983 in addition to working on musical side projects such as Queen Elizabeth, Brain Donor and Black Sheep.

Canadian Forces Base Goose Bay, commonly referred to as CFB Goose Bay, is a Canadian Forces Base located in the municipality of Happy Valley-Goose Bay in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is operated as an air force base by the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF). Its primary RCAF lodger unit is 5 Wing, commonly referred to as 5 Wing Goose Bay.

Frank Walter Yallop is a British-Canadian professional soccer coach. Yallop is currently the head coach and sporting director of USL Championship side Monterey Bay FC.

Jason Raymond Bay is a Canadian-American former professional baseball left fielder who played 11 seasons in Major League Baseball (MLB). Initially drafted by the Montreal Expos, he played for the San Diego Padres, Pittsburgh Pirates, Boston Red Sox, New York Mets and Seattle Mariners.

Derrike Wayne Cope is an American professional stock car racing driver and team owner. He is best known for his surprise win in the 1990 Daytona 500. He last competed in the NASCAR Cup Series, driving the No. 15 Chevrolet Camaro ZL1 for Rick Ware Racing in an alliance with his own StarCom Racing. Cope also served as team manager of StarCom. As of 2022, he is the last driver to compete in at least one NASCAR Cup Series race in five consecutive decades.

Tsawwassen is a ferry terminal and a major transportation facility in Delta, British Columbia, part of the BC Ferries system and Highway 17. Positioned less than 500 metres (1,600 ft) from the 49th parallel along the Canada–United States border, it is located at the southwestern end of a 2-kilometre (1.2 mi) causeway that juts out into the Strait of Georgia off the mainland at the community of Tsawwassen. With an approximate size of 23 hectares, it is the largest ferry terminal in North America.

Transit Cape Breton is a public transport agency operating buses in the Cape Breton Regional Municipality (CBRM), in Nova Scotia, Canada.

Katherine Leigh Copely, M.D. is a former American-born Ice Dancer who competed internationally for Lithuania. With partner Deividas Stagniūnas, she is the 4 time Lithuanian National Champion with Bronze Medals at both Golden Spin of Zagreb and Nebelhorn Trophy. Together they qualified for the 2010 Winter Olympics in Vancouver, Canada after placing in the top 20 at the 2009 World Figure Skating Championships in Los Angeles, California. She received her medical degree in 2018 from Central Michigan University College of Medicine.

The Congress of the People (COPE) is a South African political party formed in 2008 by former members of the African National Congress (ANC). The party was founded by former ANC members Mosiuoa Lekota, Mbhazima Shilowa and Mluleki George to contest the 2009 general election. The party was announced following a national convention held in Sandton on 1 November 2008, and was founded at a congress held in Bloemfontein on 16 December 2008. The name echoes the 1955 Congress of the People at which the Freedom Charter was adopted by the ANC and other parties, a name strongly contested by the ANC in a legal move dismissed by the Pretoria High Court.
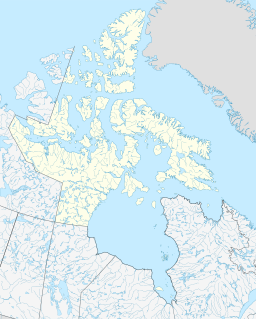
Woodward Bay is an Arctic waterway in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in Nares Strait, off eastern Ellesmere Island. Copes Bay is 12.2 km (7.6 mi) to the north, and Sawyer Bay is 13.4 km (8.3 mi) to the southwest.

Pauline Cope, whose married name is Pauline Cope-Boanas, is an English former football goalkeeper. She won 60 caps for the England women's national football team between her debut in 1995 and retirement from international football in 2004. Cope was England's first choice goalkeeper at the 1995 FIFA Women's World Cup and UEFA Women's Euro 2001. Ted Copeland, England's coach at the former competition, described Cope as the best female goalkeeper in the world.

Newfoundland is a large island within the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. It is situated off the eastern coast of the North American mainland and the geographical region of Labrador.
"Don't Cry Out Loud" is a song written in 1976 by Peter Allen with lyricist Carole Bayer Sager that is best known as a hit single for Melissa Manchester in the US and for Elkie Brooks in the UK.
Northern Rescue is a Canadian drama television series produced by Don Carmody Television (DCTV), distributed by CBC Television in Canada and internationally on Netflix. The first season of 10 episodes debuted on March 1, 2019. It stars William Baldwin as a search and rescue commander who, after the death of his wife, relocates from Boston with his three children to live with his sister-in-law in the fictional small town of Turtle Island Bay, Ontario, where he grew up.
Mirko Bibic is a Canadian businessman who is President and CEO of BCE Inc. and its wholly-owned subsidiary Bell Canada.