
Ellesmere Island is Canada's northernmost and third largest island, and the tenth largest in the world. It comprises an area of 196,236 km2 (75,767 sq mi), slightly smaller than Great Britain, and the total length of the island is 830 km (520 mi).

The Arctic Archipelago, also known as the Canadian Arctic Archipelago, is an archipelago lying to the north of the Canadian continental mainland, excluding Greenland and Iceland.

Baffin Bay, located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a sea of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea. The narrower Nares Strait connects Baffin Bay with the Arctic Ocean. The bay is not navigable most of the year because of the ice cover and high density of floating ice and icebergs in the open areas. However, a polynya of about 80,000 km2 (31,000 sq mi), known as the North Water, opens in summer on the north near Smith Sound. Most of the aquatic life of the bay is concentrated near that region.

This is a list of the extreme points of North America: the points that are highest and lowest, and farther north, south, east or west than any other location on the continent. Some of these points are debatable, given the varying definitions of North America.

Kennedy Channel is an Arctic sea passage between Greenland and Canada's most northerly island, Ellesmere Island.

Lincoln Sea is a body of water in the Arctic Ocean, stretching from Cape Columbia, Canada, in the west to Cape Morris Jesup, Greenland, in the east. The northern limit is defined as the great circle line between those two headlands. It is covered with sea ice throughout the year, the thickest sea ice in the Arctic Ocean, which can be up to 15 m (49 ft) thick. Water depths range from 100 m (330 ft) to 300 m (980 ft). Water and ice from Lincoln Sea empty into Robeson Channel, the northernmost part of Nares Strait, most of the time.

Robeson Channel is a body of water lying between Greenland and Canada's northernmost island, Ellesmere Island. It is the most northerly part of Nares Strait, linking Hall Basin to the south with the Arctic Ocean to the north. The Newman Fjord in Greenland has its mouth in the Robeson Channel.

Kane Basin is an Arctic waterway lying between Greenland and Canada's northernmost island, Ellesmere Island. It links Smith Sound to Kennedy Channel and forms part of Nares Strait. It is approximately 180 kilometres in length and 130 km at its widest.
Lady Franklin Bay is an Arctic waterway in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. The bay is located in Nares Strait northwest of Judge Daly Promontory and is an inlet into the northeastern shore of Ellesmere Island.

Petermann Glacier is a large glacier located in North-West Greenland to the east of Nares Strait. It connects the Greenland ice sheet to the Arctic Ocean at 81°10' north latitude, near Hans Island.

Cape Morton is a headland in North Greenland in Avannaata municipality. The cape is named after Arctic explorer William Morton, who surveyed the Nares Strait area together with Hans Hendrik in June 1854 during the Second Grinnell Expedition.
Hall Land is a peninsula in far northwestern Greenland. It is a part of the Northeast Greenland National Park. Hall Land is one of the coldest places in Greenland.

King Frederick VI Coast is a major geographic division of Greenland. It comprises the coastal area of Southeastern Greenland in Sermersooq and Kujalleq municipalities fronting the Irminger Sea of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is bordered by King Christian IX Land on the north and the Greenland Ice Sheet to the west.
Thorland is a peninsula in the King Frederick VI Coast, southeastern Greenland. It is a part of the Sermersooq municipality.

Odinland, also Odinsland in the Defense Mapping Agency Greenland Navigation charts, is a peninsula in the King Frederick VI Coast, southeastern Greenland. It is a part of the Sermersooq municipality.
Bessel Fjord is a fjord in northwestern Greenland. Administratively it belongs to the Avannaata municipality.
Joe Island is an island of the Nares Strait, Greenland. Administratively it belongs to the Avannaata municipality.

Petermann Fjord is a fjord in northwestern Greenland. Administratively it marks the boundary between the Avannaata municipality and the Northeast Greenland National Park.
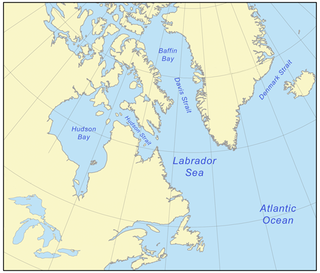
The Canadian Arctic Rift System is a major North American geological structure extending from the Labrador Sea in the southeast through Davis Strait, Baffin Bay and the Arctic Archipelago in the northwest. It consists of a series of interconnected rifts that formed during the Paleozoic, Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras. Extensional stresses along the entire length of the rift system have resulted in a variety of tectonic features, including grabens, half-grabens, basins and faults.
Repulse Harbour is a bay in northern Greenland. To the northwest it opens into the Lincoln Sea. Administratively it is a part of the Northeast Greenland National Park.














