Victoria Island is a large island in the Arctic Archipelago that straddles the boundary between Nunavut and the Northwest Territories of Canada. It is the eighth-largest island in the world, and at 217,291 km2 (83,897 sq mi)1 in area, it is Canada's second-largest island. It is nearly double the size of Newfoundland (111,390 km2 [43,010 sq mi]), and is slightly larger than the island of Great Britain (209,331 km2 [80,823 sq mi]) but smaller than Honshu (225,800 km2 [87,200 sq mi]). The western third of the island lies in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories; the remainder is part of Nunavut's Kitikmeot Region. The population of 2,168 is divided between two settlements, the larger of which is Cambridge Bay (Nunavut) and the other Ulukhaktok.

Melville Island is an uninhabited member of the Queen Elizabeth Islands of the Arctic Archipelago. With an area of 42,149 km2 (16,274 sq mi), it is the 33rd largest island in the world and Canada's eighth largest island.
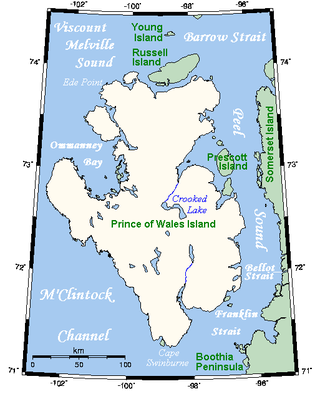
Prince of Wales Island is an Arctic island in Nunavut, Canada. One of the larger members of the Arctic Archipelago, it lies between Victoria Island and Somerset Island and is south of the Queen Elizabeth Islands.

Bathurst Island is one of the Queen Elizabeth Islands in Nunavut, Canada. It is a member of the Arctic Archipelago. The area of the island is estimated at 16,042 km2 (6,194 sq mi), 115 to 117 mi long and from 63 mi (101 km) to 72 mi (116 km) to 92.9 mi (149.5 km) wide, making it Canada's 13th largest island. It is located between Devon Island and Cornwallis Island in the east, and Melville Island in the west. Four small islands of Cameron, Vanier, Massey and Alexander lie in its northwest.

Admiral Sir Edward Belcher was a British naval officer, hydrographer, and explorer. Born in Nova Scotia, he was the great-grandson of Jonathan Belcher, who served as a colonial governor of Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and New Jersey.

Melville Peninsula is a large peninsula in the Canadian Arctic north of Hudson Bay. To the east is Foxe Basin and to the west the Gulf of Boothia. To the north the Fury and Hecla Strait separates it from Baffin Island. To the south Repulse Bay and Frozen Strait separate it from Southampton Island at the north end of Hudson Bay. On the southwest it is connected to the mainland by the Rae Isthmus, named after the Arctic explorer John Rae.

Boothia Peninsula is a large peninsula in Nunavut's northern Canadian Arctic, south of Somerset Island. The northern part, Murchison Promontory, is the northernmost point of mainland Canada.

The Gulf of Boothia is a body of water in Nunavut, Canada. Administratively it is divided between the Kitikmeot Region on the west and the Qikiqtaaluk Region on the east. It merges north into Prince Regent Inlet, the two forming a single bay with different names for its parts. It is surrounded by, clockwise, Baffin Island, Fury and Hecla Strait, the Melville Peninsula, the Canadian mainland, and the Boothia Peninsula. The south end is Committee Bay, northwest of which are the Simpson Peninsula and Pelly Bay. On the west side of the gulf at 70°18′N91°42′W, north of Pelly Bay and Thom Bay, is Eden Bay, which should not be confused with a bay of the same name in the Qikiqtaaluk Region.
Dundas Island is a member of the Queen Elizabeth Islands and the Arctic Archipelago in the territory of Nunavut. It is an irregularly shaped island located between Devon Island and Baillie-Hamilton Island. The smaller Margaret Island is 1 km (0.62 mi) to the east of Dundas.
The Spicer Islands are an uninhabited island group located in Foxe Basin, within Qikiqtaaluk Region, in the Canadian territory of Nunavut. The Melville Peninsula is to the west, Prince Charles Island to the east, Rowley Island to the north. The two main islands are North Spicer Island and South Spicer Island. They are very low-lying and swampy.
Sabine Island is an uninhabited island located in Nunavut's Qikiqtaaluk Region within the northern Canadian Arctic. It is in eastern Gulf of Boothia's Committee Bay, south of Wales Island and west of the mainland's Melville Peninsula.
Honeyman Island is an irregularly shaped, uninhabited island in Nunavut, Canada. It is located in the Qikiqtaaluk Region's side of the Gulf of Boothia within Committee Bay. It is west of the mainland's Melville Peninsula.
Hecla and Griper Bay is an Arctic waterway. Located in the Hazen Strait, it is a large inlet in the north of Melville Island, Canada. It is split between the Northwest Territories and Nunavut. The bay takes its name from Arctic explorer William Edward Parry's ships HMS Hecla and HMS Griper.
Weatherall Bay is an Arctic waterway in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in the Byam Martin Channel, northeast of Melville Island. Domett Point is at its mouth.
Eden Bay is an Arctic waterway in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Located off northern Melville Island's Sabine Peninsula, the bay is an arm of Byam Martin Channel. Sherard Bay is to the south.
Eldridge Bay is an Arctic waterway located mainly in the Qikiqtaaluk Region or Nunavut but with a small portion in the southwest corner of the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories. Lying off the coast of Melville Island's Sabine Peninsula, the bay is an arm of Hecla and Griper Bay. To the south lies Sabine Bay.
Sabine Bay is an Arctic waterway mainly in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, but partly in the Inuvik Region, Northwest Territories, Canada. Located off northern Melville Island's Sabine Peninsula, the bay is an arm of Hecla and Griper Bay. Eldridge Bay is to the north.

The McClure Arctic expedition, one of many attempts to find the missing Franklin expedition, was significant for being the first to successfully discover and transit the Northwest Passage, which it accomplished by both boat and sledging.
Marie Bay is a fjord on the Northwest tip of Melville Island. Marie Bay lies on the part of Melville Island that is in the Northwest Territories while the eastern part of the island is in Nunavut.

Homfray Channel is a deep water channel, reaching depths of 731 meters, located between East Redonda and the mainland coast of British Columbia, Canada.