Sir Edward Sabine was an Irish astronomer, geophysicist, ornithologist, explorer, soldier and the 30th president of the Royal Society.

Sabine's gull also known as the fork-tailed gull or xeme, is a small gull. It is the only species placed in the genus Xema. It breeds in colonies on coasts and tundra, laying two or three spotted olive-brown eggs in a ground nest lined with grass. Sabine's gull is pelagic outside the breeding season. It takes a wide variety of mainly animal food, and will eat any suitable small prey.

Sabine Lake is a bay on the Gulf coasts of Texas and Louisiana, located approximately 90 miles (140 km) east of Houston and 160 miles (260 km) west of Baton Rouge, adjoining the city of Port Arthur. The lake is formed by the confluence of the Neches and Sabine Rivers and connects to the Gulf of Mexico through Sabine Pass. It forms part of the Texas–Louisiana border, falling within Jefferson and Orange Counties in Texas and Cameron Parish, Louisiana.

Renfrew—Nipissing—Pembroke is a federal electoral district in Ontario, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons since 1979.
Nipissing was a federal electoral district that was represented in the House of Commons of Canada from 1896 to 2004. It was located in the northeastern part of Ontario, Canada.

Foxe Basin is a shallow oceanic basin north of Hudson Bay, in Nunavut, Canada, located between Baffin Island and the Melville Peninsula. For most of the year, it is blocked by sea ice and drift ice made up of multiple ice floes.
An EPPO code, formerly known as a Bayer code, is an encoded identifier that is used by the European and Mediterranean Plant Protection Organization (EPPO), in a system designed to uniquely identify organisms – namely plants, pests and pathogens – that are important to agriculture and crop protection. EPPO codes are a core component of a database of names, both scientific and vernacular. Although originally started by the Bayer Corporation, the official list of codes is now maintained by EPPO.
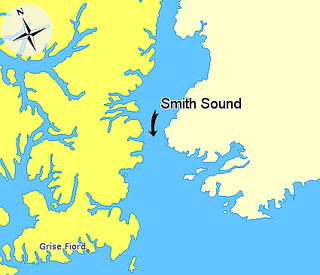
Smith Sound is an Arctic sea passage between Greenland and Nunavut's northernmost island, Ellesmere Island. It links Baffin Bay with Kane Basin and forms part of the Nares Strait. On the Canadian side it extends from Cape Sabine in the north to Cape Isabella in the south.
Sabine Channel Provincial Park, also known as Sabine Channel Marine Provincial Park, is a provincial park in British Columbia, Canada, in the waters surrounding Jervis Island in Sabine Channel, which separates Texada Island, to the north, from Lasqueti Island, which lies to the south. Established in 2001, the park is approximately 2,254 hectares in size.
Cape Sabine is a land point on Pim Island, off the eastern shores of the Johan Peninsula, Ellesmere Island, in the Smith Sound, Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada.
Sabine Glacier is a glacier terminating at the sea between Wennersgaard Point and Cape Kater on the northwest coast of Graham Land, Antarctica.

Pim Island is an uninhabited island located off the eastern coast of Ellesmere Island, part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. Located within the Arctic Archipelago, it is a part of the Queen Elizabeth Islands.
Cocked Hat Island, located off the eastern coast of Ellesmere Island, is a part of the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. The island is located within the Arctic Archipelago, and is a part of the Queen Elizabeth Islands.
Sabine Island is an uninhabited island located in Nunavut's Qikiqtaaluk Region within the northern Canadian Arctic. It is in eastern Gulf of Boothia's Committee Bay, south of Wales Island and west of the mainland's Melville Peninsula.
Hecla and Griper Bay is an Arctic waterway. Located in the Hazen Strait, it is a large inlet in the north of Melville Island, Canada. It is split between the Northwest Territories and Nunavut. The bay takes its name from Arctic explorer William Edward Parry's ships HMS Hecla and HMS Griper.
Herschel Bay is an Arctic waterway in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in Nares Strait, west of Smith Sound. Ellesmere Island is to the east, while Cape Sabine on Pim Island is to the northeast.
Sherard Bay is an Arctic waterway in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Located off northern Melville Island's Sabine Peninsula, the bay is an arm of Byam Martin Channel. Eden Bay and Weatherall Bay are nearby.
Eden Bay is an Arctic waterway in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Located off northern Melville Island's Sabine Peninsula, the bay is an arm of Byam Martin Channel. Sherard Bay is to the south.
Eldridge Bay is an Arctic waterway located mainly in the Qikiqtaaluk Region or Nunavut but with a small portion in the southwest corner of the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories. Lying off the coast of Melville Island's Sabine Peninsula, the bay is an arm of Hecla and Griper Bay. To the south lies Sabine Bay.
Sabine Bay is an Arctic waterway mainly in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, but partly in the Inuvik Region, Northwest Territories, Canada. Located off northern Melville Island's Sabine Peninsula, the bay is an arm of Hecla and Griper Bay. Eldridge Bay is to the north.