Sir John Franklin was a British Royal Navy officer and Arctic explorer. After serving in wars against Napoleonic France and the United States, he led two expeditions into the Canadian Arctic and through the islands of the Arctic Archipelago, in 1819 and 1825, and served as Lieutenant-Governor of Van Diemen's Land from 1839 to 1843. During his third and final expedition, an attempt to traverse the Northwest Passage in 1845, Franklin's ships became icebound off King William Island in what is now Nunavut, where he died in June 1847. The icebound ships were abandoned ten months later and the entire crew died from causes such as starvation, hypothermia, and scurvy.

HMS Erebus was a Hecla-class bomb vessel constructed by the Royal Navy in Pembroke dockyard, Wales, in 1826. The vessel was the second in the Royal Navy named after Erebus, the personification of darkness in Greek mythology.

Melville Island is an uninhabited member of the Queen Elizabeth Islands of the Arctic Archipelago. With an area of 42,149 km2 (16,274 sq mi), it is the 33rd largest island in the world and Canada's eighth largest island.
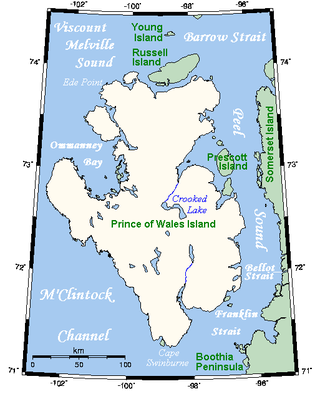
Prince of Wales Island is an Arctic island in Nunavut, Canada. One of the larger members of the Arctic Archipelago, it lies between Victoria Island and Somerset Island and is south of the Queen Elizabeth Islands.

Admiral Sir Edward Belcher was a British naval officer, hydrographer, and explorer. Born in Nova Scotia, he was the great-grandson of Jonathan Belcher, who served as a colonial governor of Massachusetts, New Hampshire, and New Jersey.

Henry Asbjørn Larsen was a Norwegian-Canadian Arctic explorer. Larsen was born on a small island, Herføl, south of Fredrikstad in Norway. Like his hero, Roald Amundsen, he became a seaman. Larsen immigrated to Canada, and became a British subject in 1927. In 1928, he joined the Royal Canadian Mounted Police (RCMP).

Cornwall Island is a small, uninhabited island in the high Arctic region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. It is near the geometric centre of the Queen Elizabeth Islands. To the north, it is separated from Amund Ringnes Island by Hendriksen Strait. To the south, it is separated from Devon Island by Belcher Channel. It is the largest of six islands in Norwegian Bay, west of Ellesmere Island.

Joseph-René Bellot was a French naval officer and Arctic explorer.
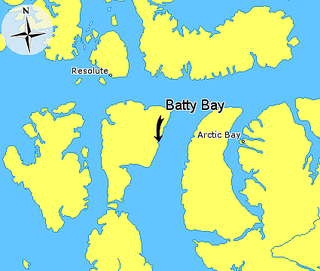
Batty Bay is a narrow bay in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is an arm of Prince Regent Inlet on the eastern side of Somerset Island.

HMS Terror was a specialised warship and a newly developed bomb vessel constructed for the Royal Navy in 1813. She participated in several battles of the War of 1812, including the Battle of Baltimore with the bombardment of Fort McHenry. She was converted into a polar exploration ship two decades later, and participated in George Back's Arctic expedition of 1836–1837, the successful Ross expedition to the Antarctic of 1839 to 1843, and Sir John Franklin's ill-fated attempt to force the Northwest Passage in 1845, during which she was lost with all hands along with HMS Erebus.
Beechey Island is an island located in the Arctic Archipelago of Nunavut, Canada, in Wellington Channel. It is separated from the southwest corner of Devon Island by Barrow Strait. Other features include Wellington Channel, Erebus Harbour, and Terror Bay.

Francis Rawdon Moira Crozier was an Irish officer of the Royal Navy and polar explorer who participated in six expeditions to the Arctic and Antarctic. In 1843, he became a Fellow of the Royal Society for his scientific work during his multiple expeditions. Later, he was second-in-command to Sir John Franklin and captain of HMS Terror during the Franklin expedition to discover the Northwest Passage, which ended with the loss of all 129 crewmen in mysterious circumstances.

Sir Edward Augustus Inglefield was a Royal Navy officer who led one of the searches for the missing Arctic explorer John Franklin during the 1850s. In doing so, his expedition charted previously unexplored areas along the northern Canadian coastline, including Baffin Bay, Smith Sound and Lancaster Sound.

The British Arctic Expedition of 1875–1876, led by Sir George Nares, was sent by the British Admiralty to attempt to reach the North Pole via Smith Sound on the west coast of Greenland.

Murchison Promontory, a cape (promontory) in the northern Canadian Arctic, is the northernmost mainland point of the Americas and of Canada. Located 1,087 nautical miles from the North Pole, it is 64 km (40 mi) farther north than Point Barrow, Alaska, the northernmost point of all U.S. territory.

Franklin's lost expedition was a failed British voyage of Arctic exploration led by Captain Sir John Franklin that departed England in 1845 aboard two ships, HMS Erebus and HMS Terror, and was assigned to traverse the last unnavigated sections of the Northwest Passage in the Canadian Arctic and to record magnetic data to help determine whether a better understanding could aid navigation. The expedition met with disaster after both ships and their crews, a total of 129 officers and men, became icebound in Victoria Strait near King William Island in what is today the Canadian territory of Nunavut. After being icebound for more than a year Erebus and Terror were abandoned in April 1848, by which point two dozen men, including Franklin, had died. The survivors, now led by Franklin's second-in-command, Francis Crozier, and Erebus's captain, James Fitzjames, set out for the Canadian mainland and disappeared, presumably having perished.
Lowther Island lies within the Arctic Archipelago in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of northern Canada's territory of Nunavut. It is one of the mid-channel islands in the western sector of Barrow Strait. Bathurst Island and Cornwallis Island are to the north, while Prince of Wales Island is to the south. The island is clustered within a group of uninhabited islands. It is 15.5 mi (24.9 km) northeast of Young Island, separated by the Kettle Passage, a shipping route, and 13 mi (21 km) southeast of Garrett Island, separated by Hayes Channel.

HMS Alert was a 17-gun wooden screw sloop of the Cruizer class of the Royal Navy, launched in 1856 and broken up in 1894. She was the eleventh ship of the Royal Navy to bear the name, and was noted for her Arctic exploration work; in 1876 she reached a record latitude of 82° North. Alert briefly served with the US Navy, and ended her career with the Canadian Marine Service as a lighthouse tender and buoy ship.

The McClure Arctic expedition, one of many attempts to find the missing Franklin expedition, was significant for being the first to successfully discover and transit the Northwest Passage, which it accomplished by both boat and sledging.

Vice-Admiral William John Samuel Pullen was a Royal Navy officer who was the first European to sail along the north coast of Alaska from the Bering Strait to the Mackenzie River in Canada. His 1849 journey was one of the many unsuccessful expeditions to rescue Sir John Franklin and explore the Northwest Passage.