Hudson Strait in Nunavut links the Atlantic Ocean and the Labrador Sea to Hudson Bay in Canada. This strait lies between Baffin Island and Nunavik, with its eastern entrance marked by Cape Chidley in Newfoundland and Labrador and Nunavut and Resolution Island, off Baffin Island. The strait is about 750 km (470 mi) long with an average width of 125 km (78 mi), varying from 70 km (43 mi) at the eastern entrance to 240 km (150 mi) at Deception Bay.

Northern Canada, colloquially the North or the Territories, is the vast northernmost region of Canada, variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut. This area covers about 48 per cent of Canada's total land area, but has less than 0.5 per cent of Canada's population.

Arctic Bay is an Inuit hamlet located in the northern part of the Borden Peninsula on Baffin Island in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. Arctic Bay is located in the Eastern Time Zone although it is quite close to the time zone boundary. The predominant languages are Inuktitut and English. Arctic Bay is notable for being the birthplace of the former Premier of Nunavut and, as of 2021, the Commissioner of Nunavut, Eva Aariak. It is the northernmost public community in Canada not formed from forced relocation.

Cambridge Bay is a hamlet located on Victoria Island in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is the largest settlement on Victoria Island. Cambridge Bay is named for Prince Adolphus, Duke of Cambridge, while the traditional Inuinnaqtun name for the area is Ikaluktutiak or Iqaluktuuttiaq meaning "good fishing place".

Foxe Basin is a shallow oceanic basin north of Hudson Bay, in Nunavut, Canada, located between Baffin Island and the Melville Peninsula. For most of the year, it is blocked by sea ice and drift ice made up of multiple ice floes.
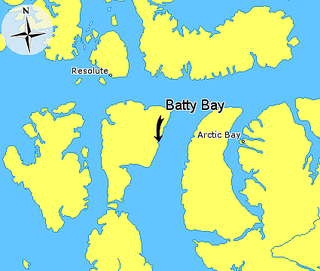
Batty Bay is a narrow bay in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is an arm of Prince Regent Inlet on the eastern side of Somerset Island.
Innetalling Island is an uninhabited island in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. Located in Hudson Bay's Omarolluk Sound, it is a member of the Belcher Islands group. It runs from Fairweather Sound at its northern end to Ridge Passage at its southern one. Fairweather Harbour is located on the north end of the island's east side.

Nunavut is the largest and northernmost territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the Nunavut Act and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act, which provided this territory to the Inuit for independent government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland was admitted in 1949.

Kuunajuk formerly Ellice River, for Edward Ellice, Jr., is a waterway in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. It rises close to the Back River between Lake Beechey and Pelly Lake, and flows northward into the Queen Maud Gulf. Its mouth opens between Campbell Bay and Gernon Bay. The land between the river and Sherman Inlet is generally flat and marshy. Muskox and barren-ground caribou frequent the area.
The Sheer Islands are Canadian arctic islands that are located in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. They are a Baffin Island offshore island group in Hudson Strait. The islands are situated approximately 1 mi (1.6 km) north of Cape Tanfield and form part of the north side of Itivirk Bay.

Hornaday River is a waterway located above the Arctic Circle on the mainland of Northern Canada.

Croker Bay is an Arctic waterway in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It lies off the southern coast of Devon Island in the eastern high Arctic. Like Maxwell Bay to the west, it is an arm of Lancaster Sound and Barrow Strait.
Macormick Bay is an Arctic waterway in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It lies off the southwestern coast of Devon Island in the eastern high Arctic. Like Baring Bay to the north, it is an arm of Wellington Channel.
Okse Bay is an Arctic waterway in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in Norwegian Bay by southwestern Ellesmere Island, east of Buckingham Island.
Rutherford Bay is an Arctic waterway in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located at the north end of Rice Strait, near the southern entrance of Kane Basin. Ellesmere Island is to the east.
Labyrinth Bay is an Arctic waterway in Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in southwestern Queen Maud Gulf off Nunavut's mainland.
Foggy Bay is an Arctic waterway in the Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in southwestern Queen Maud Gulf, off Nunavut's mainland.
Gernon Bay is an Arctic waterway in the Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located on the south side of the Queen Maud Gulf off Nunavut's mainland.

Dundas Harbour is an abandoned settlement in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located on Devon Island at the eastern shore of the waterway also named Dundas Harbour. Baffin Bay's Croker Bay is immediately to the west.
Gibson Bay is an arm of the Foxe Basin in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada. It is located on the northern coast of Foxe Peninsula, in western Baffin Island. The closest community is Cape Dorset, situated 123 km (76 mi) to the south, while Nuwata, a former settlement, is situated to the west. It is fed by the Kommanik River whose headwaters are at Kavivan Lake, 5 mi (8.0 km) to the southeast. Within the bay, there is a small island chain.