The Cree are a North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations.

Lake Winnipeg is an extremely large, relatively shallow 24,514-square-kilometre (9,465 sq mi) lake in North America, in the province of Manitoba, Canada. Its southern end is about 55 kilometres (34 mi) north of the city of Winnipeg. Lake Winnipeg is Canada's sixth-largest freshwater lake and the third-largest freshwater lake contained entirely within Canada, but it is relatively shallow excluding a narrow 36 m (118 ft) deep channel between the northern and southern basins. It is the eleventh-largest freshwater lake on Earth. The lake's east side has pristine boreal forests and rivers that were in 2018 inscribed as Pimachiowin Aki, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The lake is 416 km (258 mi) from north to south, with remote sandy beaches, large limestone cliffs, and many bat caves in some areas. Manitoba Hydro uses the lake as one of the largest reservoirs in the world. There are many islands, most of them undeveloped.

Lawrence Hargrave, MRAeS, was a British-born Australian engineer, explorer, astronomer, inventor and aeronautical pioneer.

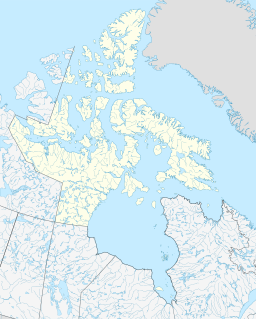
Somerset Island is a large, uninhabited island of the Arctic Archipelago, that is part of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. The island is separated from Cornwallis Island and Devon Island to the north by the Parry Channel, from Baffin Island to the east by Prince Regent Inlet, from the Boothia Peninsula to the south by Bellot Strait, and from Prince of Wales Island to the west by Peel Sound. It has an area of 24,786 km2 (9,570 sq mi), making it the 46th largest island in the world and Canada's twelfth largest island.

King's Highway 17, more commonly known as Highway 17, is a provincially maintained highway and the primary route of the Trans-Canada Highway through the Canadian province of Ontario. It begins at the Manitoba boundary, 50 km (31 mi) west of Kenora, and the main section ends where Highway 417 begins just west of Arnprior. A small disconnected signed section of the highway still remains within the Ottawa Region between County Road 29 and Grants Side Road. This makes it Ontario's longest highway.

Stanwell Park is a coastal village and northern suburb of Wollongong, New South Wales, Australia. It is the northernmost point of the Illawarra coastal strip and lies south of Sydney's Royal National Park. It is situated in a small valley between Bald Hill to the north, Stanwell Tops to the west and Mount Mitchell to the south. It has two lagoons from the village's two creeks, Stanwell and Hargrave Creeks and a beach running between headlands. Stanwell Park and the surrounding suburbs are colloquially referred to by its postcode 2508.
Fall River is a suburban community located in Nova Scotia, Canada within the Halifax Regional Municipality. It is located north-northeast of the Bedford Basin, northeast of Bedford and Lower Sackville and north of Waverley.

Shuswap Lake is a lake located in the southern interior of British Columbia, Canada that drains via the Little Shuswap River into Little Shuswap Lake. Little Shuswap Lake is the source of the South Thompson River, a branch of the Thompson River, a tributary of the Fraser River. It is at the heart of a region known as the Columbia Shuswap or "the Shuswap", noted for its recreational lakeshore communities including the city of Salmon Arm. The name "Shuswap" is derived from the Shuswap or Secwepemc First Nations people, the most northern of the Interior Salish peoples, whose territory includes the Shuswap. The Shuswap call themselves /ʃǝxwépmǝx/ in their own language, which is called /ʃǝxwepmǝxtʃín/.

Thunder Bay—Superior North is a federal electoral district in Ontario, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada since 1976.

Trunk 2 is part of the Canadian province of Nova Scotia's system of Trunk Highways. The route runs from Halifax to Fort Lawrence on the New Brunswick border. Until the 1960s, Trunk 2 was the Halifax area's most important highway link to other provinces, and was part of a longer Interprovincial Highway 2 which ended in Windsor, Ontario. The controlled access Highway 102 and Highway 104 now carry most arterial traffic in the area, while Trunk 2 serves regional and local traffic.

The Burdekin Falls Dam, also known as the Burdekin Dam, is a concrete gravity dam with an uncontrolled spillway across the Burdekin River, located south west of Ayr, and Home Hill in the Shire of Burdekin, North Queensland, Australia. Built for the purpose of irrigation, the reservoir is called Lake Dalrymple. Burdekin Falls Dam is managed by SunWater. Water from the reservoir is also used to replenish downstream aquifers.
Creswell Bay is an Arctic waterway in Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is an arm of western Prince Regent Inlet in eastern Somerset Island. Its northeastern landmark, Fury Point, is approximately 100 km (62 mi) west of Baffin Island.

Fort Ross is an abandoned former trading post on Somerset Island, in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada. Founded in 1937, it was the last trading post to be established by the Hudson's Bay Company. It was operational for only eleven years, being abandoned in 1948, as severe ice conditions in the surrounding waters made the site hard to reach and economically unviable.

Stanwell-Fletcher Lake is the largest lake on Somerset Island, the tenth-largest island of the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The lake, along with most of Somerset Island, is located within the Qikiqtaaluk Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut.
Theodora Stanwell-Fletcher was an American naturalist and writer. She is best known for her book Driftwood Valley (1946) which won the John Burroughs Medal for distinguished writing in natural history in 1948. She was recognized as a Distinguished Daughter of Pennsylvania and elected to the Society of Woman Geographers.