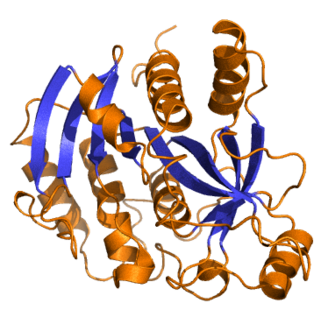
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase, PNP, PNPase or inosine phosphorylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NP gene. It catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an unspecific monooxygenase (EC 1.14.14.1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NADPH—hemoprotein reductase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
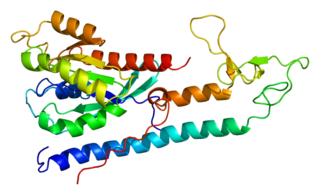
Ras-related protein Rab-3A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAB3A gene. It is involved in calcium-triggered exocytosis in neurons.

In enzymology, a succinate—CoA ligase (GDP-forming) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Rho GTPase-activating protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ARHGAP1 gene.
In enzymology, a nucleotide diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a GTP cyclohydrolase II (EC 3.5.4.25) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an ATP phosphoribosyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
See DGUOK for a more thorough description of the human deoxyguanosine kinase.

In enzymology, a guanylate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mannose-1-phosphate guanylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a mRNA guanylyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nucleoside-triphosphate-adenylate kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nucleoside-triphosphate-aldose-1-phosphate nucleotidyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
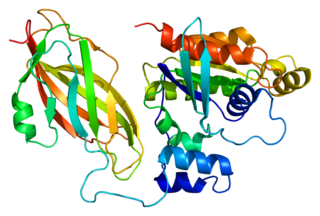
Rac2 is a small signaling G protein, and is a member of the Rac subfamily of the family Rho family of GTPases. It is encoded by the gene RAC2.

2,5-diamino-6-hydroxy-4-(5-phosphoribosylamino)pyrimidine is a metabolite in the purine metabolism, formed by the hydrolysis of GTP by GTP cyclohydrolase II. Alternatively two separate enzymes can carry out this reaction, initially GTP cyclohydrolase IIa hydrolyses the 8,9 bond to form 2-Amino-5-formylamino-6-(5-phospho-D-ribosylamino)pyrimidin-4(3H)-one, followed by de-formylation by 2-amino-5-formylamino-6-ribosylaminopyrimidin-4(3H)-one 5'-monophosphate deformylase. 2,5-diamino-6-hydroxy-4-(5-phosphoribosylamino)pyrimidine is deaminated by Diaminohydroxyphosphoribosylaminopyrimidine deaminase to form 5-amino-6-(5-phosphoribosylamino)uracil.
Sylvy Kornberg née Sylvia Ruth Levy (1917–1986) was an American biochemist who carried out research on DNA replication and polyphosphate synthesis. She discovered and characterized polyphosphate kinase (PPK), an enzyme that helps build long chains of phosphate groups called polyphosphate (PolyP) that play a variety of metabolic and regulatory functions. She worked closely with her husband and research partner, Arthur Kornberg, contributing greatly to the characterization of DNA polymerization that earned him the 1959 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.

Bernard Leonard (Bernie) Horecker (1914–2010) was an American biochemist known for work on the pentose phosphate pathway, and for cellular regulation in general.










