
Biogen Inc. is an American multinational biotechnology company based in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States specializing in the discovery, development, and delivery of therapies for the treatment of neurological diseases to patients worldwide. Biogen operates in Argentina, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, Hungary, India, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Netherlands, Poland, Sweden, and Switzerland.

Donepezil, sold under the brand name Aricept among others, is a medication used to treat dementia of the Alzheimer's type. It appears to result in a small benefit in mental function and ability to function. Use, however, has not been shown to change the progression of the disease. Treatment should be stopped if no benefit is seen. It is taken by mouth or via a transdermal patch.
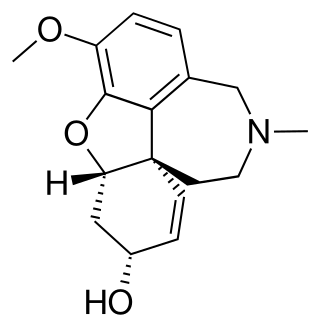
Galantamine is used for the treatment of cognitive decline in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease and various other memory impairments. It is an alkaloid extracted from the bulbs and flowers of Galanthus nivalis, Galanthus caucasicus, Galanthus woronowii, and other members of the family Amaryllidaceae, such as Narcissus (daffodil), Leucojum aestivum (snowflake), and Lycoris including Lycoris radiata. It can also be produced synthetically.
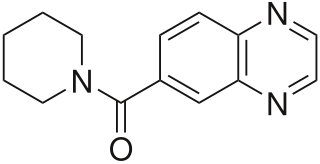
Ampakines or AMPAkines are a subgroup of AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulators with a benzamide or closely related chemical structure. They are also known as "CX compounds". Ampakines take their name from the AMPA receptor (AMPAR), a type of ionotropic glutamate receptor with which the ampakines interact and act as positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) of. Although all ampakines are AMPAR PAMs, not all AMPAR PAMs are ampakines.

CX717 is an ampakine compound created by Christopher Marrs and Gary Rogers in 1996 at Cortex Pharmaceuticals. It affects the neurotransmitter glutamate, with trials showing the drug improves cognitive functioning and memory.

CX-516 is an ampakine and nootropic that acts as an AMPA receptor positive allosteric modulator and had been undergoing development by a collaboration between Cortex, Shire, and Servier. It was studied as a potential treatment for Alzheimer's disease under the brand name Ampalex, and was also being examined as a treatment for ADHD.

Latrepirdine is an antihistamine drug which has been used clinically in Russia since 1983.

Intepirdine (INN; developmental codes SB-742457, RVT-101) is a selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist with potential cognition, memory, and learning-enhancing effects. It was under development by GlaxoSmithKline for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease and demonstrated some preliminary efficacy in phase II clinical trials. GSK chose not to continue development and sold the rights to Axovant Sciences for $5 million in December 2014.

Basmisanil is a highly selective inverse agonist/negative allosteric modulator of α5 subunit-containing GABAA receptors which is under development by Roche for the treatment of cognitive impairment associated with Down syndrome. As of June 2016, it is no longer studied. It is studied with schizophrenia patients.

Pesampator is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the AMPA receptor (AMPAR), an ionotropic glutamate receptor, which is under development by Pfizer for the treatment of cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia. It was also under development for the treatment of age-related sensorineural hearing loss, but development for this indication was terminated due to insufficient effectiveness. As of July 2018, pesampator is in phase II clinical trials for cognitive symptoms in schizophrenia.

Mibampator is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the AMPA receptor (AMPAR), an ionotropic glutamate receptor, which was under development by Eli Lilly for the treatment of agitation/aggression in Alzheimer's disease but was never marketed. It reached phase II clinical trials prior to the discontinuation of its development.

Tulrampator is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the AMPA receptor (AMPAR), an ionotropic glutamate receptor, which is under development by RespireRx Pharmaceuticals and Servier for the treatment of major depressive disorder, Alzheimer's disease, dementia, and mild cognitive impairment. Tulrampator was in phase II clinical trial for depression, but failed to show superiority over placebo. There are also phase II clinical trials for Alzheimer's disease and phase I trials for dementia and mild cognitive impairment.

Zuranolone, sold under the brand name Zurzuvae, is a medication used for the treatment of postpartum depression. It is taken by mouth.
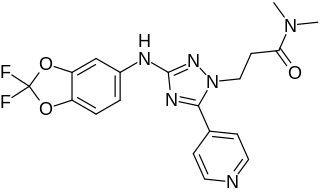
JNJ-39393406 is an experimental medication which is under development by Janssen Pharmaceutica, a division of Johnson & Johnson, for the treatment of depressive disorders and smoking withdrawal. It acts as a selective positive allosteric modulator of the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR). It does not act on the α4β2 or α3β4 nAChRs or the serotonin 5-HT3 receptor, and does not interact with a panel of 62 other receptors and enzymes. The drug has been found to lower the agonist and nicotine threshold for activation of the α7 nAChR by 10- to 20-fold and to increase the maximum agonist response of the α7 nAChR by 17- to 20-fold.

Phenserine is a synthetic drug which has been investigated as a medication to treat Alzheimer's disease (AD), as the drug exhibits neuroprotective and neurotrophic effects.

Mevidalen (developmental code name LY-3154207) is a dopaminergic drug which is under development for the treatment of Lewy body disease, including those with Parkinson's disease. It acts as a selective positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of the dopamine D1 receptor. The drug is orally active and crosses the blood–brain barrier. It is a tetrahydroisoquinoline and is a close analogue of DETQ, another D1 receptor PAM. Mevidalen has been found to have wakefulness-promoting effects in sleep-deprived humans. Side effects of mevidalen have been reported to include increased heart rate and blood pressure, insomnia, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, anxiety, nervousness, fatigue, headaches, palpitations, and contact dermatitis, as well as falls in those with dementia. As of March 2022, mevidalen is in phase 2 clinical trials for the treatment of Lewy body disease. Besides for movement disorders and dementia, D1 receptor PAMs like mevidalen might have value in the treatment of certain neuropsychiatric disorders, such as depression, excessive somnolence, and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
KarXT is an investigational oral dual-drug fixed-dose combination of xanomeline and trospium. It is undergoing a phase 3 clinical trial for the treatment of schizophrenia. Xanomeline is a functionally preferring muscarinic M4 and M1 receptor agonist that readily passes into the central nervous system (CNS) to stimulate these receptors in key areas of the brain. Trospium is a non-selective muscarinic antagonist that does not cross into the CNS and reduces peripheral cholinergic side effects associated with xanomeline.

Darigabat is a GABAergic medication which is under development for the treatment of photosensitive epilepsy, focal onset seizures, panic disorder, and other anxiety disorders. It was also under development for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder and chronic lower back pain, but development for these indications was discontinued. It is taken via oral administration.
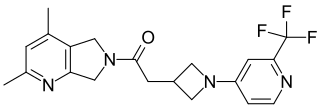
Emraclidine is an investigational antipsychotic for the treatment of both schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s disease psychosis developed by Cerevel Therapeutics. As of February 2023, it is in phase II of clinical trial. Emraclidine is a positive allosteric modulator that selectively targets the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor M4 subtype. The M4 receptor subtype is expressed in the striatum of the brain, which plays a key role in regulating acetylcholine and dopamine levels. An imbalance of these neurotransmitters has been linked to psychotic symptoms in schizophrenia. Unlike other muscarinic receptors, M4 receptor subtypes are selectively expressed in the striatum and activation of these receptors has been shown to indirectly regulate dopamine levels without blocking D2/D3 receptors, which may lead to unwanted motor side effects seen in current antipsychotics.

















