Related Research Articles

Rhodium is a chemical element; it has symbol Rh and atomic number 45. It is a very rare, silvery-white, hard, corrosion-resistant transition metal. It is a noble metal and a member of the platinum group. It has only one naturally occurring isotope, which is 103Rh. Naturally occurring rhodium is usually found as a free metal or as an alloy with similar metals and rarely as a chemical compound in minerals such as bowieite and rhodplumsite. It is one of the rarest and most valuable precious metals.
Elastic properties describe the reversible deformation of a material to an applied stress. They are a subset of the material properties that provide a quantitative description of the characteristics of a material, like its strength.

Caesium hydroxide is a strong base containing the highly reactive alkali metal caesium, much like the other alkali metal hydroxides such as sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide. It is the strongest of the five alkali metal hydroxides. Fused Caesium hydroxide dissolves glass by attacking silica framework and it has applications in bringing glass samples into a solution for analytical purposes in commercial glass industry and defense waste processing facility. The melting process is carried out in a nickel or zirconium crucible. Caesium hydroxide fusion at 750°C produces complete dissolution of glass pellets.
The speed of sound in any chemical element in the fluid phase has one temperature-dependent value. In the solid phase, different types of sound wave may be propagated, each with its own speed: among these types of wave are longitudinal, transversal, and extensional.
This page shows the electron configurations of the neutral gaseous atoms in their ground states. For each atom the subshells are given first in concise form, then with all subshells written out, followed by the number of electrons per shell. For phosphorus as an example, the concise form is [Ne] 3s2 3p3. Here [Ne] refers to the core electrons which are the same as for the element neon (Ne), the last noble gas before phosphorus in the periodic table. The valence electrons are written explicitly for all atoms.
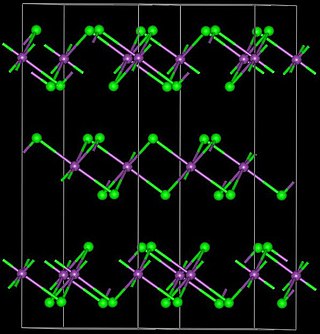
Yttrium(III) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula YBr3. It is a white solid. Anhydrous yttrium(III) bromide can be produced by reacting yttrium oxide or yttrium(III) bromide hydrate and ammonium bromide. The reaction proceeds via the intermediate (NH4)3YBr6. Another method is to react yttrium carbide (YC2) and elemental bromine. Yttrium(III) bromide can be reduced by yttrium metal to YBr or Y2Br3. It can react with osmium to produce Y4Br4Os.

Terbium(III) chloride (TbCl3) is a chemical compound. In the solid state TbCl3 has the YCl3 layer structure. Terbium(III) chloride frequently forms a hexahydrate.

Yttrium arsenide is an inorganic compound of yttrium and arsenic with the chemical formula YAs. It can be prepared by reacting yttrium and arsenic at high temperature. Some literature has done research on the eutectic system of it and zinc arsenide.
This page provides supplementary chemical data on calcium hydroxide.

Samarium(II) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula SmBr
2. It is a brown solid that is insoluble in most solvents but degrades readily in air.
Promethium compounds are compounds containing the element promethium, which normally take the +3 oxidation state. Promethium belongs to the cerium group of lanthanides and is chemically very similar to the neighboring elements. Because of its instability, chemical studies of promethium are incomplete. Even though a few compounds have been synthesized, they are not fully studied; in general, they tend to be pink or red in color. Treatment of acidic solutions containing Pm3+ ions with ammonia results in a gelatinous light-brown sediment of hydroxide, Pm(OH)3, which is insoluble in water. When dissolved in hydrochloric acid, a water-soluble yellow salt, PmCl3, is produced; similarly, when dissolved in nitric acid, a nitrate results, Pm(NO3)3. The latter is also well-soluble; when dried, it forms pink crystals, similar to Nd(NO3)3. The electron configuration for Pm3+ is [Xe] 4f4, and the color of the ion is pink. The ground state term symbol is 5I4. The sulfate is slightly soluble, like the other cerium group sulfates. Cell parameters have been calculated for its octahydrate; they lead to conclusion that the density of Pm2(SO4)3·8 H2O is 2.86 g/cm3. The oxalate, Pm2(C2O4)3·10 H2O, has the lowest solubility of all lanthanide oxalates.
References
- ↑ Schenkel, R.; Muller, W. (1977). "The electrical resistivity of 241Am metal". Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids. 38 (11): 1301–1305. Bibcode:1977JPCS...38.1301S. doi:10.1016/0022-3697(77)90033-6.
- ↑ Schenkel, R. (1977). "The electrical resistivity of 244Cm metal". Solid State Communications. 23 (6): 389–392. Bibcode:1977SSCom..23..389S. doi:10.1016/0038-1098(77)90239-3.
WEL
As quoted at http://www.webelements.com/ from these sources:
Contents
- G.W.C. Kaye and T. H. Laby in Tables of physical and chemical constants, Longman, London, UK, 15th edition, 1993.
- A.M. James and M.P. Lord in Macmillan's Chemical and Physical Data, Macmillan, London, UK, 1992.
- D.R. Lide, (ed.) in Chemical Rubber Company handbook of chemistry and physics, CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida, USA, 79th edition, 1998.
- J.A. Dean (ed) in Lange's Handbook of Chemistry, McGraw-Hill, New York, USA, 14th edition, 1992.
CRC
As quoted from various sources in an online version of:
- David R. Lide (ed), CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 84th Edition. CRC Press. Boca Raton, Florida, 2003; Section 12, Properties of Solids; Electrical Resistivity of Pure Metals
CR2
As quoted in an online version of:
- David R. Lide (ed), CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 84th Edition. CRC Press. Boca Raton, Florida, 2003; Section 4, Properties of the Elements and Inorganic Compounds; Physical Properties of the Rare Earth Metals
which further refers to:
- Beaudry, B. J. and Gschneidner, K.A., Jr., in Handbook on the Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths, Vol. 1, Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. and Eyring, L., Eds., North-Holland Physics, Amsterdam, 1978, 173.
- McEwen, K.A., in Handbook on the Physics and Chemistry of Rare Earths, Vol. 1, Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. and Eyring, L., Eds., North-Holland Physics, Amsterdam, 1978, 411.
LNG
As quoted from:
- J.A. Dean (ed), Lange's Handbook of Chemistry (15th Edition), McGraw-Hill, 1999; Section 4, Table 4.1 Electronic Configuration and Properties of the Elements