A phosphodiesterase (PDE) is an enzyme that breaks a phosphodiester bond. Usually, phosphodiesterase refers to cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases, which have great clinical significance and are described below. However, there are many other families of phosphodiesterases, including phospholipases C and D, autotaxin, sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, DNases, RNases, and restriction endonucleases, as well as numerous less-well-characterized small-molecule phosphodiesterases.
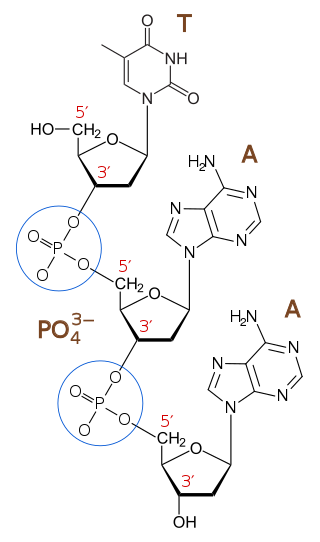
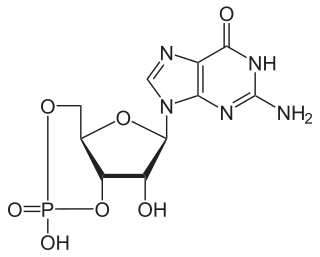
In chemistry, a phosphodiester bond occurs when exactly two of the hydroxyl groups in phosphoric acid react with hydroxyl groups on other molecules to form two ester bonds. The "bond" involves this linkage C−O−PO−2O−C. Discussion of phosphodiesters is dominated by their prevalence in DNA and RNA, but phosphodiesters occur in other biomolecules, e.g. acyl carrier proteins.
An esterase is a hydrolase enzyme that splits esters into an acid and an alcohol in a chemical reaction with water called hydrolysis.

3′,5′-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterases (EC 3.1.4.17) are a family of phosphodiesterases. Generally, these enzymes hydrolyze a nucleoside 3′,5′-cyclic phosphate to a nucleoside 5′-phosphate:
Phosphodiesterase 1, PDE1, EC 3.1.4.1, systematic name oligonucleotide 5′-nucleotidohydrolase) is a phosphodiesterase enzyme also known as calcium- and calmodulin-dependent phosphodiesterase. It is one of the 11 families of phosphodiesterase (PDE1-PDE11). Phosphodiesterase 1 has three subtypes, PDE1A, PDE1B and PDE1C which divide further into various isoforms. The various isoforms exhibit different affinities for cAMP and cGMP.
The enzyme 2′,3′-cyclic-nucleotide 2'-phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.16) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme 3′,5′-cyclic-GMP phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.35) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme [acyl-carrier-protein] phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.14) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme alkylglycerophosphoethanolamine phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.39) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme CMP-N-acylneuraminate phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.40) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme dolichylphosphate-glucose phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.48) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme dolichylphosphate-mannose phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.49) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme glucose-1-phospho-D-mannosylglycoprotein phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.51) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme glycerol-1,2-cyclic-phosphate 2-phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.42) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme glycerophosphocholine phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.2) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme glycerophosphoinositol glycerophosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.44) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme glycerophosphoinositol inositolphosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.43) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphodiester α-N-acetylglucosaminidase (EC 3.1.4.45) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme serine-ethanolaminephosphate phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.13) catalyzes the reaction

Nucleotide pyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase (NPP) is a class of dimeric enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of phosphate diester bonds. NPP belongs to the alkaline phosphatase (AP) superfamily of enzymes. Humans express seven known NPP isoforms, some of which prefer nucleotide substrates, some of which prefer phospholipid substrates, and others of which prefer substrates that have not yet been determined. In eukaryotes, most NPPs are located in the cell membrane and hydrolyze extracellular phosphate diesters to affect a wide variety of biological processes. Bacterial NPP is thought to localize to the periplasm.




