
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are one class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic, antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to treat infections. They should be distinguished from virucides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural virucides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees.
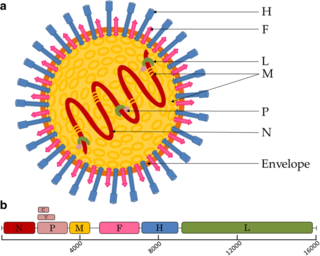
Paramyxoviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Mononegavirales. Vertebrates serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this family include measles, mumps, and respiratory tract infections. The family has four subfamilies, 17 genera, and 78 species, three genera of which are unassigned to a subfamily.

Influenza hemagglutinin (HA) or haemagglutinin[p] is a homotrimeric glycoprotein found on the surface of influenza viruses and is integral to its infectivity.

Orthomyxoviridae is a family of negative-sense RNA viruses. It includes seven genera: Alphainfluenzavirus, Betainfluenzavirus, Gammainfluenzavirus, Deltainfluenzavirus, Isavirus, Thogotovirus, and Quaranjavirus. The first four genera contain viruses that cause influenza in birds and mammals, including humans. Isaviruses infect salmon; the thogotoviruses are arboviruses, infecting vertebrates and invertebrates. The Quaranjaviruses are also arboviruses, infecting vertebrates (birds) and invertebrates (arthropods).
Antigenic drift is a kind of genetic variation in viruses, arising from the accumulation of mutations in the virus genes that code for virus-surface proteins that host antibodies recognize. This results in a new strain of virus particles that is not effectively inhibited by the antibodies that prevented infection by previous strains. This makes it easier for the changed virus to spread throughout a partially immune population. Antigenic drift occurs in both influenza A and influenza B viruses.

Measles morbillivirus(MeV), also called measles virus (MV), is a single-stranded, negative-sense, enveloped, non-segmented RNA virus of the genus Morbillivirus within the family Paramyxoviridae. It is the cause of measles. Humans are the natural hosts of the virus; no animal reservoirs are known to exist.
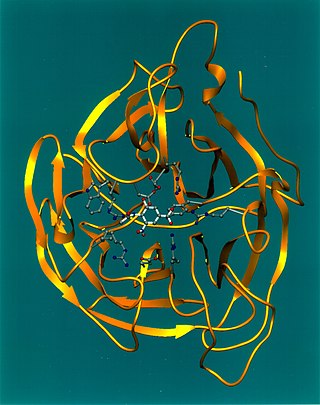
Exo-α-sialidase is a glycoside hydrolase that cleaves the glycosidic linkages of neuraminic acids:
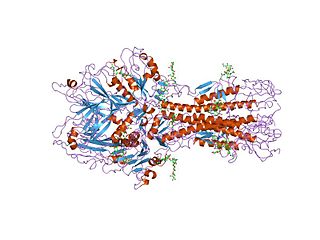
Hemagglutinin esterase (HEs) is a glycoprotein that certain enveloped viruses possess and use as an invading mechanism. HEs helps in the attachment and destruction of certain sialic acid receptors that are found on the host cell surface. Viruses that possess HEs include influenza C virus, toroviruses, and coronaviruses of the subgenus Embecovirus. HEs is a dimer transmembrane protein consisting of two monomers, each monomer is made of three domains. The three domains are: membrane fusion, esterase, and receptor binding domains.

H5N1 genetic structure is the molecular structure of the H5N1 virus's RNA.

In structural biology, a beta-propeller (β-propeller) is a type of all-β protein architecture characterized by 4 to 8 highly symmetrical blade-shaped beta sheets arranged toroidally around a central axis. Together the beta-sheets form a funnel-like active site.
Antigenic variation or antigenic alteration refers to the mechanism by which an infectious agent such as a protozoan, bacterium or virus alters the proteins or carbohydrates on its surface and thus avoids a host immune response, making it one of the mechanisms of antigenic escape. It is related to phase variation. Antigenic variation not only enables the pathogen to avoid the immune response in its current host, but also allows re-infection of previously infected hosts. Immunity to re-infection is based on recognition of the antigens carried by the pathogen, which are "remembered" by the acquired immune response. If the pathogen's dominant antigen can be altered, the pathogen can then evade the host's acquired immune system. Antigenic variation can occur by altering a variety of surface molecules including proteins and carbohydrates. Antigenic variation can result from gene conversion, site-specific DNA inversions, hypermutation, or recombination of sequence cassettes. The result is that even a clonal population of pathogens expresses a heterogeneous phenotype. Many of the proteins known to show antigenic or phase variation are related to virulence.

Murine respirovirus, formerly Sendai virus (SeV) and previously also known as murine parainfluenza virus type 1 or hemagglutinating virus of Japan (HVJ), is an enveloped, 150-200 nm–diameter, negative sense, single-stranded RNA virus of the family Paramyxoviridae. It typically infects rodents and it is not pathogenic for humans or domestic animals
Cyanovirin-N (CV-N) is a protein produced by the cyanobacterium Nostoc ellipsosporum that displays virucidal activity against several viruses, including human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). A cyanobacterial protein called cyanovirin-N (CV-N) has strong anti-human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) neutralizing properties. The virucidal activity of CV-N is mediated through specific high-affinity interactions with the viral surface envelope glycoproteins gp120 and gp41, as well as to high-mannose oligosaccharides found on the HIV envelope. In addition, CV-N is active against rhinoviruses, human parainfluenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus, and enteric viruses. The virucidal activity of CV-N against influenza virus is directed towards viral haemagglutinin.

Viral neuraminidase is a type of neuraminidase found on the surface of influenza viruses that enables the virus to be released from the host cell. Neuraminidases are enzymes that cleave sialic acid groups from glycoproteins. Neuraminidase inhibitors are antiviral agents that inhibit influenza viral neuraminidase activity and are of major importance in the control of influenza.

In molecular biology, hemagglutinins are receptor-binding membrane fusion glycoproteins produced by viruses in the Paramyxoviridae family. Hemagglutinins are responsible for binding to receptors on red blood cells to initiate viral attachment and infection. The agglutination of red cells occurs when antibodies on one cell bind to those on others, causing amorphous aggregates of clumped cells.
Measles hemagglutinin is a hemagglutinin produced by measles virus.
Parainfluenza hemagglutinin-neuraminidase is a type of hemagglutinin-neuraminidase produced by parainfluenza.

George Keble Hirst, M.D. was an American virologist and science administrator who was among the first to study the molecular biology and genetics of animal viruses, especially influenza virus. He directed the Public Health Research Institute in New York City (1956–1981), and was also the founding editor-in-chief of Virology, the first English-language journal to focus on viruses. He is particularly known for inventing the hemagglutination assay, a simple method for quantifying viruses, and adapting it into the hemagglutination inhibition assay, which measures virus-specific antibodies in serum. He was the first to discover that viruses can contain enzymes, and the first to propose that virus genomes can consist of discontinuous segments. The New York Times described him as "a pioneer in molecular virology."
Neuraminidase inhibitors inhibit enzymatic activity of the enzyme neuraminidase (sialidase). These type of inhibitors have been introduced as anti-influenza drugs as they prevent the virus from exiting infected cells and thus stop further spreading of the virus. Neuraminidase inhibitors for human neuraminidase (hNEU) have the potential to be useful drugs as the enzyme plays a role in several signaling pathways in cells and is implicated in diseases such as diabetes and cancer.
Bat mumps orthorubulavirus, formerly Bat mumps rubulavirus (BMV), is a member of genus Orthorubulavirus, family Paramyxoviridae, and order Mononegavirales. Paramyxoviridae viruses were first isolated from bats using heminested PCR with degenerate primers. This process was then followed by Sanger sequencing. A specific location of this virus is not known because it was isolated from bats worldwide. Although multiple paramyxoviridae viruses have been isolated worldwide, BMV specifically has not been isolated thus far. However, BMV was detected in African fruit bats, but no infectious form has been isolated to date. It is known that BMV is transmitted through saliva in the respiratory system of bats. While the virus was considered its own species for a few years, phylogenetic analysis has since shown that it is a member of Mumps orthorubulavirus.












