
Chongming District is northernmost district of the provincial-level municipality of Shanghai. Chongming consists of three low-lying inhabited alluvial islands at the mouth of the Yangtze north of the Shanghai peninsula: Chongming, Changxing, and Hengsha. Following its massive expansion in the 20th century, Chongming is now the 2nd-largest island administered by the People's Republic of China and the 2nd-largest in Greater China, after Hainan. Chongming does not, however, administer all of the island: owing to its continual expansion from sediment deposited by the Yangtze, it has merged with formerly separate islands and now includes Jiangsu province's pene-exclave townships of Haiyong and Qilong. Chongming proper covers an area of 1,411 km2 (545 sq mi) and had a population of 704 000 at the time of the Sixth National Census in 2010.

Hangzhou Bay Bridge is a long 35.7 km (22.2 mi) highway bridge with two separate cable-stayed portions, built across the mouth of Hangzhou Bay in the eastern coastal region of China. It connects the municipalities of Jiaxing and Ningbo in Zhejiang province.

Nantong is a prefecture-level city in southeastern Jiangsu province, China. Located on the northern bank of the Yangtze River, near the river mouth. Nantong is a vital river port bordering Yancheng to the north; Taizhou to the west; Suzhou, Wuxi and Shanghai to the south across the river; and the East China Sea to the east. Its population was 7,726,635 as of the 2020 census, 3,766,534 of whom lived in the built-up area made up of three urban districts.

Chongming, formerly known as Chungming, is an alluvial island at the mouth of the Yangtze River in eastern China covering 1,267 square kilometers (489 sq mi) as of 2010. Together with the islands Changxing and Hengsha, it forms Chongming District, the northernmost area of the provincial-level municipality of Shanghai. At the time of the 2010 Chinese census, its population was 660,000.

Qidong is a county-level city under the administration of the prefecture-level city of Nantong in southeastern Jiangsu province, China. It is located on the north side of the Yangtze River opposite Shanghai and forms a peninsula jutting out into the East China Sea. It has a population of 1.12 million.

Shanghai has an expansive grade-separated highway and expressway network consisting of 16 municipal express roads, 10 provincial-level expressways, and 8 national-level expressways. Three municipal expressways and four provincial-level expressways are also under construction.

Yangshan Port, formally the Yangshan Deep-Water Port, is a deep water port for container ships in Hangzhou Bay south of Shanghai. The port is part of the Maritime Silk Road. The port is built on the islands of Greater and Lesser Yangshan, part of the Zhoushan archipelago, with fill from land reclamation. Connected to Shanghai's Pudong New Area by the Donghai Bridge and forming part of the Port of Shanghai, the islands of Greater and Lesser Yangshan are administered separately as part of Zhejiang's Shengsi County.
The Chonghai Bridge is a proposed bridge to span the northern distributary at the mouth of the Yangtze River in the People's Republic of China. The bridge, along with the Chongqi Bridge and the Shanghai Yangtze River Tunnel and Bridge, is to connect the city of Shanghai with the north bank of the Yangtze in Jiangsu Province via Chongming Island.
Chongming-Qidong Yangtze River Bridge or the Chongqi Bridge, also called Chongqi Crossing Project, is a bridge across the north fork of the Yangtze River, near the river's mouth between Chongming Island of Shanghai and Qidong in Jiangsu Province. This bridge, along with the Shanghai Yangtze River Tunnel and Bridge to the south, forms the last crossing of the Yangtze River before the river empties into the East China Sea. The bridge carries the six-lane G40 Shanghai–Xi'an Expressway, part of the National Expressway Network of the People's Republic of China.

The Shanghai Yangtze River Tunnel and Bridge is a bridge–tunnel complex across the south fork of the Yangtze River near the river mouth in Shanghai. The tunnel connects the Pudong District of Shanghai on the south bank of the river with Changxing Island, while the bridge connects Changxing Island with Chongming Island. In combination with the Chongqi Bridge, which connects Chongming Island to the north bank of the Yangtze, the bridge–tunnel complex forms the final crossing of the Yangtze before it empties into the East China Sea.

The geography of Shanghai is characterised by its location on the Yangtze River Delta on China's east coast and its proximity to the Pacific Ocean via the East China Sea. The city is centred on the Huangpu River, a tributary of the Yangtze River, and extends outwards in all directions, with the suburbs and satellite towns reaching east to the East China Sea, north and west to Jiangsu province, and south to Zhejiang province over Hangzhou Bay.
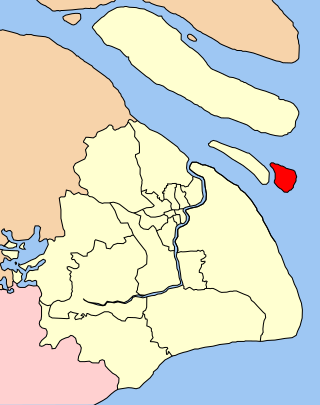
Hengsha is a low-lying alluvial island at the mouth of the Yangtze River in eastern China. Together with the islands of Chongming and Changxing, it forms Chongming District, the northernmost area of the provincial-level municipality of Shanghai. Its population was 33,400 in 2008.

The Chongming line is a rapid transit line on the Shanghai Metro that is part of the 2018–2023 Shanghai Metro plan. The Chongming line was previously treated as the last phase of Line 9, and was Line 19 until 2016, when it was renamed the Chongming line.

The bridges and tunnels across the Yangtze River carry rail and road traffic across China's longest and largest river and form a vital part of the country's transportation infrastructure. The river bisects China proper from west to east, and every major north–south bound highway and railway must cross the Yangtze. Large urban centers along the river such as Chongqing, Wuhan, and Nanjing also have urban mass transit rail lines crossing the Yangtze.

The Shenyang–Haikou Expressway, designated as G15 and commonly referred to as the Shenhai Expressway is an expressway in China that connects the cities of Shenyang, Liaoning, and Haikou, Hainan. When fully complete, it will be 3,710 km (2,310 mi) in length. One of its oldest portions is the Shenyang–Dalian Expressway, or Shenda Expressway is a 400 km (250 mi) expressway that connects Shenyang and Dalian, the two largest cities of China's Liaoning province.

Jiuduansha is a collection of four intertidal wetland shoals at the mouth of China's Yangtze River. They are administered as an island region of the municipality of Shanghai's Pudong New Area.
Haiyong is a town of Haimen District in Nantong, Jiangsu, China. Together with neighboring Qilong, it forms a pene-enclave of the province on Chongming Island, most of which belongs to the province-level municipality of Shanghai. Haiyong presently covers about 12.5 square kilometers (5 sq mi) and had a population of 5,004 during the year 2000 census.
Yonglongsha, sometimes translated as the Yonglong Shoal or Yonglong Sands, was a former island in the north channel of the Yangtze River to the north of Chongming in eastern China. It was also known as Yongfengsha and Hefengsha. Prior to its absorption by Chongming, it measured about 16 kilometers (9.9 mi) east to west but was very narrow, with an area of about 14 km2 (5.4 sq mi).
Qilong is a township of Qidong in eastern Jiangsu province. The land it occupies was formerly Yonglongsha, a separate island in the Yangtze River delta, but reclamation projects and natural deposition of sediment have joined it to Chongming Island, where it now forms a pene-enclave within Shanghai's Chongming County. Its population was 3436 at the time of the 2010 Chinese census. Qilong's name—literally "opening prosperity"—is a compound of contracted forms of its county and its former island.

Shanghai Suburban Railway (上海市域铁路) is a network of regional railways radiating or surrounding the city of Shanghai, China. It is a plan for the gradual implementation of a regional rail system across the metropolitan area. The system will eventually connect with Jiangsu Yangtze MIR and Hangzhou Greater Bay Area network.















