In planetary nomenclature, a fossa is a long, narrow depression (trough) on the surface of an extraterrestrial body, such as a planet or moon. The term, which means "ditch" or "trench" in Latin, is not a geological term as such but a descriptor term used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) and the International Astronomical Union (IAU) for topographic features whose geology or geomorphology is uncertain due to lack of data or knowledge of the exact processes that formed them. Fossae are believed to be the result of a number of geological processes, such as faulting or subsidence. Many fossae on Mars are probably graben.

Hecates Tholus is a Martian volcano, notable for results from the European Space Agency's Mars Express mission which indicate a major eruption took place 350 million years ago. The eruption created a caldera 10 km in diameter on the volcano's western flank.

Elysium, located in the Elysium and Cebrenia quadrangles, is the second largest volcanic region on Mars, after Tharsis. The region includes the volcanoes Hecates Tholus, Elysium Mons and Albor Tholus. The province is centered roughly on Elysium Mons at 24.7°N 150°E. Elysium Planitia is a broad plain to the south of Elysium, centered at 3.0°N 154.7°E. Another large volcano, Apollinaris Mons, lies south of Elysium Planitia and is not part of the province. Besides having large volcanoes, Elysium has several areas with long trenches, called fossa or fossae (plural) on Mars. They include the Cerberus Fossae, Elysium Fossae, Galaxias Fossae, Hephaestus Fossae, Hyblaeus Fossae, Stygis Fossae and Zephyrus Fossae.

Elysium Mons is a volcano on Mars located in the volcanic province Elysium, at 25.02°N 147.21°E, in the Martian eastern hemisphere. It stands about 12.6 km (41,000 ft) above its base, and about 14.1 km (46,000 ft) above the Martian datum, making it the third tallest Martian mountain in terms of relief and the fourth highest in elevation. Its diameter is about 240 km (150 mi), with a summit caldera about 14 km (8.7 mi) across. It is flanked by the smaller volcanoes Hecates Tholus to the northeast, and Albor Tholus to the southeast.

Albor Tholus is an extinct volcano in the volcanic province Elysium on Mars. It lies south of the neighbouring volcanoes Elysium Mons and Hecates Tholus. Albor Tholus is 4.5 kilometres high and has a diameter of 160 km at its base. Its large caldera, having a diameter of 30 km and a depth of 3 km, is deep compared to calderas on the Earth. The elevation of the lowest level of the caldera is the same as the base of the volcano; however, the original lower slopes of Albor Tholus may have been covered by lava flows from its larger neighbor, Elysium Mons. Evaluations by the Mars probe Mars Express found that the volcanoes of the Elysium region were active over long periods.
In planetary nomenclature, a tholus is a small domical mountain or hill. The word is from the Greek θόλος, tholos, which means a circular building with a conical or vaulted roof. The Romans transliterated the word into the Latin tholus, which means cupola or dome. In 1973, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) adopted tholus as one of a number of official descriptor terms for topographic features on Mars and other planets and satellites. One justification for using neutral Latin or Greek descriptors was that it allowed features to be named and described before their geology or geomorphology could be determined. For example, many tholi appear to be volcanic in origin, but the term does not imply a specific geologic origin. Currently, the IAU recognizes 56 descriptor terms. Tholi are present on Venus, Mars, asteroid 4 Vesta, dwarf planet Ceres, and on Jupiter's moon Io.

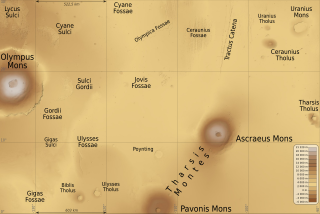
Biblis Tholus is an extinct Martian volcano located at 2.55°N 235.62°E, one of two volcanoes near the center of the Tharsis volcanism. Along with Ulysses Tholus, it is almost midway between Olympus Mons and the Tharsis Montes. Biblis Tholus lies in the Tharsis quadrangle. It is approximately 170 kilometers (110 mi) long and 100 kilometers (62 mi) wide, rising about 3 kilometers (1.9 mi) from its surroundings.
Volcanic activity, or volcanism, has played a significant role in the geologic evolution of Mars. Scientists have known since the Mariner 9 mission in 1972 that volcanic features cover large portions of the Martian surface. These features include extensive lava flows, vast lava plains, and the largest known volcanoes in the Solar System. Martian volcanic features range in age from Noachian to late Amazonian, indicating that the planet has been volcanically active throughout its history, and some speculate it probably still is so today. Both Earth and Mars are large, differentiated planets built from similar chondritic materials. Many of the same magmatic processes that occur on Earth also occurred on Mars, and both planets are similar enough compositionally that the same names can be applied to their igneous rocks and minerals.

Tharsis Tholus is an intermediate-sized shield volcano located in the eastern Tharsis region of the planet Mars. The volcano was discovered by the Mariner 9 spacecraft in 1972 and originally given the informal name Volcano 7. In 1973, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) officially designated it Tharsis Tholus. In planetary geology, tholus is the term for a small domical mountain, usually a volcano.

The Tharsis quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Tharsis quadrangle is also referred to as MC-9 . The name Tharsis refers to a land mentioned in the Bible. It may be at the location of the old town of Tartessus at the mouth of Guadalquivir.

Ulysses Tholus is a Martian volcano. It is located in the Tharsis quadrangle at 2.89° north latitude and 121.55° west longitude. It is 58 km across and is named after a classical albedo feature. Ulysses Tholus is immediately east and slightly north of another volcano, Biblis Tholus. The name of the mountain itself was changed on September 19, 2007. The former terminology, Ulysses Patera, now applies only to the central caldera, whereas formerly it had applied to the whole edifice. Tholus describes a volcanic edifice somewhat smaller than would be implied by mons.

Ceraunius Tholus is a volcano on Mars located in the Tharsis quadrangle at 24.25° north latitude and 262.75° east longitude, part of the Uranius group of volcanoes. It is 130 kilometres (81 mi) across, approximately 8,500 metres (27,887 ft) high and is named after a classical albedo feature name.

Uranius Tholus is a volcano on Mars located in the Tharsis quadrangle at 26.52° north latitude and 262.43° east longitude. It is 61.4 kilometres (38 mi) across with an elevation of 4,290 metres (14,075 ft) and was named after a classical albedo feature name.

The Ulysses Fossae are a group of troughs in the Tharsis quadrangle of Mars at 10.06° north latitude and 123.07° west longitude. They were named after an albedo feature name. The area contains pitted cones called Ulysses Colles which were interpreted to be possible Martian equivalents to terrestrial cinder cones.
The Uranius group of volcanoes is located on planet Mars in the northeast part of Tharsis and includes Uranius Mons, Ceraunius Tholus, and Uranius Tholus. Along with the Tharsis Montes to the southwest, they form part of a linear chain of volcanoes in the Tharsis region.

Lockyer is a crater in the Elysium quadrangle of Mars. It was named after Norman Lockyer, a British astronomer (1836-1920). Lockyer is surrounded by relatively smooth plains, where there are few craters. It is east of Elysium Mons and Hecates Tholus, two large volcanoes. It is south of the larger crater Adams and the Phlegra Montes.

Chatturat is an impact crater on Mars. It was named by the IAU in 1991 after the Chatturat District, Chaiyaphum Province, Thailand.















