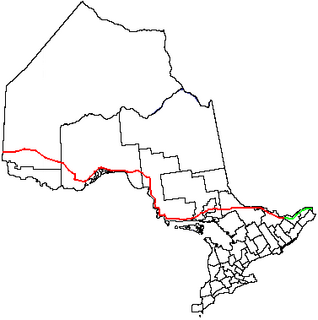
King's Highway 17, more commonly known as Highway 17, is a provincially maintained highway and the primary route of the Trans-Canada Highway through the Canadian province of Ontario. It begins at the Manitoba boundary, 50 km (31 mi) west of Kenora, and the main section ends where Highway 417 begins just west of Arnprior. A small disconnected signed section of the highway still remains within the Ottawa Region between County Road 29 and Grants Side Rd. This makes it Ontario's longest highway.

King's Highway 400, commonly referred to as Highway 400, historically as the Toronto–Barrie Highway, and colloquially as the 400, is a 400-series highway in the Canadian province of Ontario linking the city of Toronto in the urban and agricultural south of the province with the scenic and sparsely populated central and northern regions. The portion of the highway between Toronto and Lake Simcoe roughly traces the route of the Toronto Carrying-Place Trail, a historic trail between the Lower and Upper Great Lakes. North of Highway 12, in combination with Highway 69, it forms a branch of the Trans-Canada Highway (TCH), the Georgian Bay Route, and is part of the highest-capacity route from southern Ontario to the Canadian West, via a connection with the mainline of the TCH in Sudbury. The highway also serves as the primary route from Toronto to southern Georgian Bay and Muskoka, areas collectively known as cottage country. The highway is patrolled by the Ontario Provincial Police and has a speed limit of 100 km/h (62 mph), except for the section south of the 401, where the speed limit is 80 km/h (50 mph).
King's Highway 69, commonly referred to as Highway 69, is a major north–south highway in the central portion of the Canadian province of Ontario, linking the northern terminus of Highway 400 north of Parry Sound with the city of Greater Sudbury at Highway 17. It is part of the Trans-Canada Highway and the National Highway System.
King's Highway 27 is a short municipal highway in southern Ontario. Much of it is now cared for by the city of Toronto, York Region and Simcoe County. The Ministry of Transportation of Ontario was once responsible for the length of the route, when it ran through much of Southern Ontario. Now, only the southernmost 3 km (1.9 mi) from Dixon Road to Highway 427 is under provincial jurisdiction.
King's Highway 48, also known as Highway 48, is a provincially maintained highway in southern Ontario that extends from Major Mackenzie Drive in Markham, through Whitchurch-Stouffville and East Gwillimbury, to Highway 12 south-east of Beaverton. The route is generally rural and straight, passing near several communities within the Regional Municipality of York. The route is 65.2 kilometres (40.5 mi) long. Most part of the road has a speed limit of 80 km/h (50 mph), except within town limits, where the speed limit is reduced to 60 km/h (37 mph) or 50 km/h (31 mph).
King's Highway 2A, commonly referred to as Highway 2A, was the designation of five separate provincially maintained highways in the Canadian province of Ontario. Highway 2A was an alternate route to Highway 2 in Chatham, London and Cornwall; these routes were all eventually redesignated. Highway 2A was also a highway that extended from Windsor to Tilbury, which was redesignated as Highway 98 in 1938.

A county highway is a road in the United States and in the Canadian province of Ontario that is designated and/or maintained by the county highway department. Route numbering can be determined by each county alone, by mutual agreement among counties, or by a statewide pattern.
King's Highway 12, commonly referred to as Highway 12 and historically known as the Whitby and Sturgeon Bay Road, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The highway connects the eastern end of the Greater Toronto Area (GTA) with Kawartha Lakes, Orillia and Midland before ending at Highway 93. It forms the Central Ontario Route of the Trans-Canada Highway system from north of Sunderland to Coldwater. Highway 12 connects several small towns along its 146 km (91 mi) route, and bypasses a short distance from many others. It is signed as a north–south route between Whitby and Orillia, and as an east–west route from there to Midland. The rural portions of the highway feature a posted speed limit of 80 km/h (50 mph), often dropping to 50 km/h (31 mph) through built-up areas. The entire route is patrolled by the Ontario Provincial Police.

King's Highway 93, commonly referred to as Highway 93, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. Located entirely within Simcoe County, the highway extends 23.9 kilometres (14.9 mi) from an interchange with Highway 400 in Springwater, just south of the community of Hillsdale, to an intersection with Highway 12 at the town limits of Midland. The route follows the historic Penetanguishene Road, an early colonization road which served to connect Lake Simcoe with Georgian Bay, thus providing an overland route from Lake Huron to Lake Ontario via Yonge Street.
King's Highway 35, also known as Highway 35, is a provincial highway in the Canadian province of Ontario, linking Highway 401 with Peterborough, Kawartha Lakes, and Algonquin Park. The highway travels from west of Newcastle, through Lindsay and the Kawarthas and into Haliburton before terminating at Highway 60 to the west of Algonquin Park. The winding course of the highway, combined with the picturesque views offered along its length, have led some to declare it the most scenic highway in Ontario.
King's Highway 15, commonly referred to as Highway 15, is a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. It travels north from an interchange with Highway 401 in Kingston to Highway 7 in Carleton Place, a distance of 114.7 kilometres (71.3 mi). In addition to Kingston and Carleton Place, the highway provides access to the Eastern Ontario communities of Joyceville, Seeley's Bay, Morton, Elgin, Crosby, Portland, Lombardy and Franktown. Prior to 1998, Highway 15 continued north from Carleton Place, passed Almonte and through Pakenham, to Highway 17 in Arnprior.
King's Highway 38, commonly referred to as Highway 38, was a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The 66.9-kilometre (41.6 mi) road connected Highway 2 and Highway 401 in Kingston with Highway 7 west of Perth. It was designated in 1934 and remained relatively unchanged throughout its existence, aside from some minor diversions and a rerouting through Kingston as a result of the construction of Highway 401 in the mid-1950s. At the beginning of 1998, the entire highway was transferred to the municipalities of Frontenac County through which it travelled: Kingston, South Frontenac and Central Frontenac. Today the former highway is named Road 38 and Gardiners Road, but is still referred to as Highway 38 by locals.
King's Highway 46, commonly referred to as Highway 46, was a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario that connected Highway 7 with Highway 48 in Victoria County. The route existed between 1937 and 1997, after which it was decommissioned and transferred to the county. In 2001, Victoria County amalgamated into the city of Kawartha Lakes, and the road became known as Kawartha Lakes Road 46. It is 25.7 kilometres (16.0 mi) long, passing through the villages of Woodville, Argyle and Bolsover.
King's Highway 121, commonly referred to as Highway 121, was a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario that connected several communities in the cottage country region of Central Ontario on the southern edge of the Canadian Shield. Between Fenelon Falls and Minden, Highway 121 served as an alternative route to Highway 35, which was severely congested during summer weekends. From Minden, the highway branched east to Haliburton Village and thereafter followed the present route of Highway 118 to Highway 28 in Paudash.
Secondary Highway 503, commonly referred to as Highway 503, was a provincially maintained secondary highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The 116.8 km (72.6 mi) route existed between 1956 and 1998. Between 1956 and 1963, the highway stretched from Kirkfield to Sebright, and then along the Monck Road from Sebright to Kinmount, entirely within Victoria County. In 1964, the route was extended to Highway 121 in Tory Hill along the route of Highway 500 through the counties of Peterborough and Haliburton. In 1998, the route was transferred to the various counties in which it resided. Today it is known as Kawartha Lakes City Road 6 and 45, Peterborough County Road 503 and Haliburton County Road 503.
Secondary Highway 649, commonly referred to as Highway 649, was a provincially maintained secondary highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. Now known as Kawartha Lakes Road 49, and locally as East Street North in Bobcaygeon, it is a municipally-maintained class-3 roadway located mostly along the boundary between the city of Kawartha Lakes and Peterborough County. The 18-kilometre-long (11 mi) route begins in Bobcaygeon at a junction with former Highway 36, and proceeds north along the boundary between Kawartha Lakes and Peterborough County to a junction with former Highway 121 just south of Kinmount.
King's Highway 36, commonly referred to as Highway 36, was a provincially maintained highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. The highway connected Highway 7 and Highway 35 in Lindsay with Highway 28 in Burleigh Falls, providing access to recreational cottages along the northern shore of several of the Kawartha lakes as well as to multiple communities, including Bobcaygeon. Today it is known as Kawartha Lakes City Road 36 and Peterborough County Road 36.
Ontario Highway 549, commonly referred to as Highway 549, was a provincially maintained secondary highway in the Canadian province of Ontario. This highway connected former Highway 17 in Whitefish to Lake Panache. The route was assumed along with many other secondary highways in 1956 and remained unchanged until the early 1980s, when it was decommissioned as a provincial highway and transferred to the newly formed Regional Municipality of Sudbury. Today it is known as Greater Sudbury Road 10.








