
Vitamin B6 is one of the B vitamins, and thus an essential nutrient. The term refers to a group of six chemically similar compounds, i.e., "vitamers", which can be interconverted in biological systems. Its active form, pyridoxal 5′-phosphate, serves as a coenzyme in more than 140 enzyme reactions in amino acid, glucose, and lipid metabolism.
A prosthetic group is the non-amino acid component that is part of the structure of the heteroproteins or conjugated proteins, being tightly linked to the apoprotein.
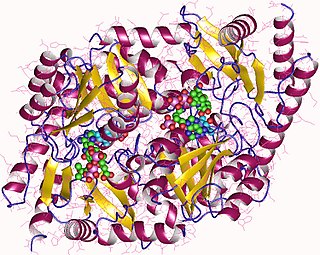
Aminolevulinic acid synthase (ALA synthase, ALAS, or delta-aminolevulinic acid synthase) is an enzyme (EC 2.3.1.37) that catalyzes the synthesis of δ-aminolevulinic acid (ALA) the first common precursor in the biosynthesis of all tetrapyrroles such as hemes, cobalamins and chlorophylls. The reaction is as follows:

Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent activities, corresponding to ~4% of all classified activities. The versatility of PLP arises from its ability to covalently bind the substrate, and then to act as an electrophilic catalyst, thereby stabilizing different types of carbanionic reaction intermediates.
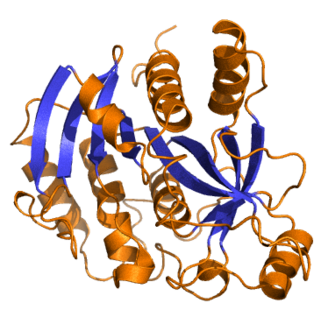
Purine nucleoside phosphorylase, PNP, PNPase or inosine phosphorylase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NP gene. It catalyzes the chemical reaction

Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological cell signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses. Lipid signaling is thought to be qualitatively different from other classical signaling paradigms because lipids can freely diffuse through membranes. One consequence of this is that lipid messengers cannot be stored in vesicles prior to release and so are often biosynthesized "on demand" at their intended site of action. As such, many lipid signaling molecules cannot circulate freely in solution but, rather, exist bound to special carrier proteins in serum.

Bisphosphoglycerate mutase is an enzyme expressed in erythrocytes and placental cells. It is responsible for the catalytic synthesis of 2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG) from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. BPGM also has a mutase and a phosphatase function, but these are much less active, in contrast to its glycolytic cousin, phosphoglycerate mutase (PGM), which favors these two functions, but can also catalyze the synthesis of 2,3-BPG to a lesser extent.

Pyridoxine 5′-phosphate oxidase is an enzyme, encoded by the PNPO gene, that catalyzes several reactions in the vitamin B6 metabolism pathway. Pyridoxine 5′-phosphate oxidase catalyzes the final, rate-limiting step in vitamin B6 metabolism, the biosynthesis of pyridoxal 5′-phosphate, the biologically active form of vitamin B6 which acts as an essential cofactor. Pyridoxine 5′-phosphate oxidase is a member of the enzyme class oxidases, or more specifically, oxidoreductases. These enzymes catalyze a simultaneous oxidation-reduction reaction. The substrate oxidase enzymes is hydroxylated by one oxygen atom of molecular oxygen. Concurrently, the other oxygen atom is reduced to water. Even though molecular oxygen is the electron acceptor in these enzymes' reactions, they are unique because oxygen does not appear in the oxidized product.
In enzymology, an erythrose-4-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.72) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxythreonine-4-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.262) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pyridoxal 4-dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.107) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
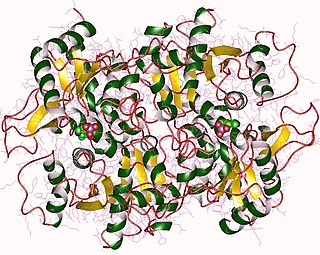
The enzyme threonine synthase (EC 4.2.3.1) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The primary biochemical reaction catalyzed by the enzyme adenosylcobalamin/α-ribazole phosphatase (formerly α-ribazole phosphatase) (EC 3.1.3.73) is
The enzyme dolichyl-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.51) catalyzes the reaction

In enzymology, a pyridoxine 5'-phosphate synthase (EC 2.6.99.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pyridoxamine-phosphate transaminase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a pyridoxal kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Lipid phosphate phosphohydrolase 1 also known as phosphatidic acid phosphatase 2a is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPAP2A gene.
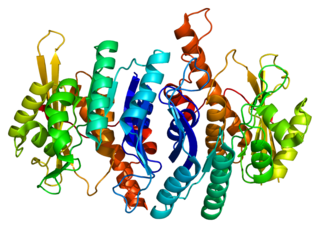
Pyridoxal kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PDXK gene.

Putative tyrosine-protein phosphatase TPTE is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TPTE gene.











