Indore is the most populous and the largest city in the Indian state of Madhya Pradesh. It serves as the headquarters of both Indore District and Indore Division. It is also considered as an education hub of the state and first city to have campuses of both the Indian Institute of Technology and the Indian Institute of Management. Located on the southern edge of Malwa Plateau, at an average altitude of 550 meters (1,800 ft) above sea level, it has the highest elevation among major cities of Central India. The city is 190 km (120 mi) west of the state capital of Bhopal. Indore had a census-estimated 2011 population of 1,994,397 and 2,170,295. The city is distributed over a land area of just 530 square kilometres (200 sq mi), making Indore the most densely populated major city in the central province. It comes under Tier 2 cities in India.

The Gondi (Gōndi) or Gond people are a Dravidian ethnic group spread over the states of Madhya Pradesh, eastern Maharashtra (Vidarbha), Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar and Orissa.

Madhya Bharat, also known as Malwa Union, was an Indian state in west-central India, created on 28 May 1948 from twenty-five princely states which until 1947 had been part of the Central India Agency, with Jiwajirao Scindia as its Rajpramukh.

Gonda district is one of the districts of Uttar Pradesh, India. The city of Gonda is the district headquarters, and also the administrative centre for the Devipatan Division.
The administrative divisions of India are subnational administrative units of India; they compose a nested hierarchy of country subdivisions. Indian states and territories frequently use different local titles for the same level of subdivision.
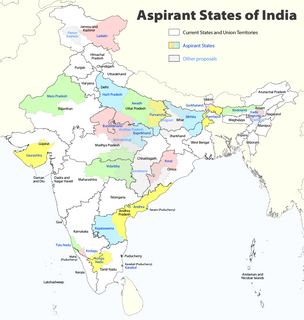
The creation of new states and territories in India is a power reserved solely for the Parliament of India. Parliament can do so by announcing new states, separating territory from an existing state or by merging two or more states or parts thereof. In addition to the existing twenty nine states and seven union territories some new states and territories of India have been proposed to be established over time.

Rapid improvements are being made in augmenting drinking water supply and sanitation in India, due to concerted efforts by the various levels of government and communities at improving coverage. The level of investment in water and sanitation, albeit low by international standards, has increased in size during the 2000s. For example, in 1980 rural sanitation coverage was estimated at 1% and reached 95% in 2018. Also, the share of Indians with access to improved sources of water has increased significantly from 72% in 1990 to 88% in 2008. At the same time, local government institutions in charge of operating and maintaining the infrastructure are seen as weak and lack the financial resources to carry out their functions. In addition, only two Indian cities have continuous water supply and according to an estimate from 2018 about 8% of Indians still lack access to improved sanitation facilities. A study by Water Aid estimated as many as 10 million Indians, or 5 percent of Indians living in urban areas, live without adequate sanitation. India comes in first place globally for having the greatest number of urban-dwelling inhabitants living without sanitation. India tops the urban sanitation crisis, has the largest amount of urban dwellers without sanitation, and the most open defecators(urban) with over 5 million people.

Telephone numbers in India are administered under the National Numbering Plan of 2003 by the Department of Telecommunications. The numbering plan was last updated in 2015. The International Telecommunication Union has assigned the country calling code "91" to India.
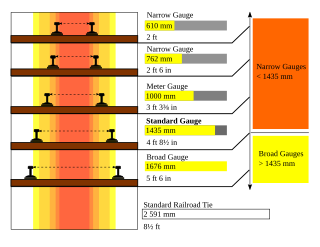
Project Unigauge, started in early 1990s, is an ongoing effort by Indian Railways to convert all rail gauges in India to 1,676 mm broad gauge.

The following outline is provided as an overview of, and topical guide to, India:
Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs (MoHUA), Government of India, is the apex body for formulation and administration of the rules and regulations and laws relating to the housing and urban development in India. The ministry was under the charge of Venkaiah Naidu and was given to Hardeep Singh Puri when Naidu was elected Vice President of India. The Ministry became independent from Ministry of Housing and Urban Poverty Alleviation in 2004, but was re-merged with it in 2017.

Indian Institutes of Information Technology (IIITs) are a group of institutes of higher education in India, focused on information technology. Five of them are established, funded and managed by the Ministry of Human Resource Development. The rest are set up on the public-private partnership (PPP) model.

This page gives a list of the territories of the dioceses of the Catholic Church in India.

Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (SBA) or Swachh Bharat Mission (SBM) is a nation-wide campaign in India for the period 2014 to 2019 that aims to clean up the streets, roads and infrastructure of India's cities, towns, and rural areas. The campaign's official name is in Hindi and translates to "Clean India Mission" in English. The objectives of Swachh Bharat include eliminating open defecation through the construction of household-owned and community-owned toilets and establishing an accountable mechanism of monitoring toilet use. Run by the Government of India, the mission aims to achieve an "open-defecation free" (ODF) India by 2 October 2019, the 150th anniversary of the birth of Mahatma Gandhi, by constructing 90 million toilets in rural India at a projected cost of ₹1.96 lakh crore. The mission will also contribute to India reaching Sustainable Development Goal 6, established by the UN in 2015.

The 2004–05 Ranji Trophy was the 71st season of the Ranji Trophy. Railways defeated Punjab on first innings lead in the final.

Vivek Yadav is an 2008 IAS Cadre officer, currently serving as the District Collector and Magistrate of Vizianagaram district in Andhra Pradesh.
"Ho Halla" is an Indore Swachhta Anthem song for Swachh Survekshan 2017, sung by Shaan, composed by Rishikesh Pandey and conceived by Parikipandla Narahari. The purpose of the song was to encourage the city of Indore to achieve the highest levels of cleanliness. It became very popular in Indore with residents using the track as their caller tunes.