
In biochemistry, a phosphatase is an enzyme that uses water to cleave a phosphoric acid monoester into a phosphate ion and an alcohol. Because a phosphatase enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of its substrate, it is a subcategory of hydrolases. Phosphatase enzymes are essential to many biological functions, because phosphorylation and dephosphorylation serve diverse roles in cellular regulation and signaling. Whereas phosphatases remove phosphate groups from molecules, kinases catalyze the transfer of phosphate groups to molecules from ATP. Together, kinases and phosphatases direct a form of post-translational modification that is essential to the cell's regulatory network.

Apyrase is a calcium-activated plasma membrane-bound enzyme that catalyses the hydrolysis of ATP to yield AMP and inorganic phosphate. Two isoenzymes are found in commercial preparations from S. tuberosum. One with a higher ratio of substrate selectivity for ATP:ADP and another with no selectivity.
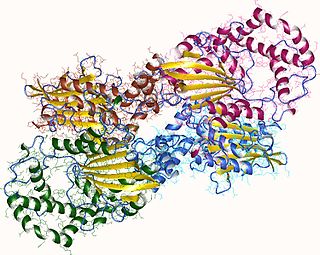
Acid phosphatase is an enzyme that frees attached phosphoryl groups from other molecules during digestion. It can be further classified as a phosphomonoesterase. It is stored in lysosomes and functions when these fuse with endosomes, which are acidified while they function; therefore, it has an acid pH optimum. This enzyme is present in many animal and plant species.

5′-Nucleotidase is an enzyme which catalyzes the phosphorylytic cleavage of 5′-nucleotides. Although originally found in snake venom, the activity of 5'nucleotidase has been described for bacteria and plant cells, and is widely distributed in vertebrate tissue. In mammalian cells the enzyme is predominantly located in the plasma membrane and its primary role is in the conversion of extracellular nucleotides, which are generally impermeable, to the corresponding nucleoside which can readily enter most cells. Consequently, the enzyme plays a key role in the metabolism of nucleotides.
A nucleotidase is a hydrolytic enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of a nucleotide into a nucleoside and a phosphate.

Thymidylate synthase (TS) is an enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) to deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP). Thymidine is one of the nucleotides in DNA. With inhibition of TS, an imbalance of deoxynucleotides and increased levels of dUMP arise. Both cause DNA damage.

In enzymology, a thymidylate synthase (FAD) (EC 2.1.1.148) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a FAD diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.18) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a guanosine-5'-triphosphate,3'-diphosphate diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.40) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a nucleoside-diphosphatase (EC 3.6.1.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a nucleoside-triphosphatase(NTPase) (EC 3.6.1.15) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme 2′,3′-cyclic-nucleotide 2'-phosphodiesterase (EC 3.1.4.16) catalyzes the reaction

The enzyme 3′(2′),5′-bisphosphate nucleotidase (EC 3.1.3.7) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme 3′-nucleotidase (EC 3.1.3.6) the reaction
The enzyme fructose-2,6-bisphosphate 6-phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.54) catalyzes the reaction

In enzymology, a ADP-ribosyl cyclase/cyclic ADP-ribose hydrolase (EC 3.2.2.6) is a bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

5′-nucleotidase (5′-NT), also known as ecto-5′-nucleotidase or CD73, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NT5E gene. CD73 commonly serves to convert AMP to adenosine.

Cytosolic 5'-nucleotidase 3 (NTC53), also known as cytosolic 5'-nucleotidase 3A, pyrimidine 5’-nucleotidase, and p56, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NT5C3, or NT5C3A, gene on chromosome 7.

5', 3'-nucleotidase, cytosolic, also known as 5'(3')-deoxyribonucleotidase, cytosolic type (cdN) or deoxy-5'-nucleotidase 1 (dNT-1), is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the NT5C gene on chromosome 17.

Fluorodeoxyuridylate, also known as FdUMP, 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridylate, and 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine 5'-monophosphate, is a molecule formed in vivo from 5-fluorouracil and 5-fluorodeoxyuridine.













