
A knot is an intentional complication in cordage which may be practical or decorative, or both. Practical knots are classified by function, including hitches, bends, loop knots, and splices: a hitch fastens a rope to another object; a bend fastens two ends of a rope to each another; a loop knot is any knot creating a loop; and splice denotes any multi-strand knot, including bends and loops. A knot may also refer, in the strictest sense, to a stopper or knob at the end of a rope to keep that end from slipping through a grommet or eye. Knots have excited interest since ancient times for their practical uses, as well as their topological intricacy, studied in the area of mathematics known as knot theory.

The bowline is an ancient and simple knot used to form a fixed loop at the end of a rope. It has the virtues of being both easy to tie and untie; most notably, it is easy to untie after being subjected to a load. The bowline is sometimes referred to as king of the knots because of its importance. Along with the sheet bend and the clove hitch, the bowline is often considered one of the most essential knots.

The constrictor knot is one of the most effective binding knots. Simple and secure, it is a harsh knot that can be difficult or impossible to untie once tightened. It is made similarly to a clove hitch but with one end passed under the other, forming an overhand knot under a riding turn. The double constrictor knot is an even more robust variation that features two riding turns.

A shank is a type of knot that is used to shorten a rope or take up slack, such as the sheepshank. The sheepshank knot is not stable. It will fall apart under too much load or too little load.

The trucker's hitch is a compound knot commonly used for securing loads on trucks or trailers. The general arrangement, using loops and turns in the rope itself to form a crude block and tackle, has long been used to tension lines and is known by multiple names. Knot author Geoffrey Budworth claims the knot can be traced back to the days when carters and hawkers used horse-drawn conveyances to move their wares from place to place.

The marlinespike hitch is a temporary knot used to attach a rod to a rope in order to form a handle. This allows more tension than could be produced comfortably by gripping the rope with the hands alone. It is useful when tightening knots and for other purposes in ropework.

The taut-line hitch is an adjustable loop knot for use on lines under tension. It is useful when the length of a line will need to be periodically adjusted in order to maintain tension. It is made by tying a rolling hitch around the standing part after passing around an anchor object. Tension is maintained by sliding the hitch to adjust the size of the loop, thus changing the effective length of the standing part without retying the knot.
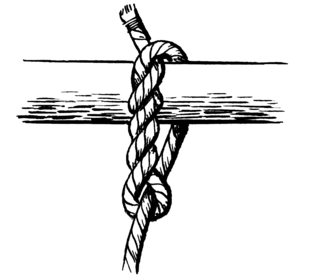
The timber hitch is a knot used to attach a single length of rope to a cylindrical object. Secure while tension is maintained, it is easily untied even after heavy loading.

A zeppelin bend is an end-to-end joining knot formed by two symmetrically interlinked overhand knots. It is stable, secure, and highly resistant to jamming. It is also resistant to the effects of slack shaking and cyclic loading.

A fireman's chair knot is a knot tied in the bight forming two adjustable, lockable loops. The knot consists of a handcuff knot finished with a locking half hitch around each loop. The loops remain adjustable until the half hitches are tightened.

The Highwayman’s hitch is a quick-release draw hitch used for temporarily securing a load that will need to be released easily and cleanly. The hitch can be untied with a tug of the working end, even when under tension. The highwayman's hitch can be tied in the middle of a rope, and so the working end does not need to be passed around the anchor when tying or releasing.
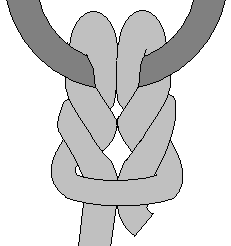
The Cat's paw is a knot used for connecting a rope to an object. It is very similar to the cow hitch except there is an additional twist on each side of the bight, making it less prone to slipping.
The cat's-paw is the common hook hitch for slings. It is the same basic form as the bale sling hitch but has additional twists. Brady says "two or three altogether," and Steel, who mentioned the name in 1794, says "three twists." It is the best of all sling hitches and is often recommended for a slippery rope. But no hitch can slip when tied in a slings since it has no ends. All that is needed is a hitch that cannot jam, and this requirement the cat's-paw fills admirably. The knot spills instantly when removed from the hook. It is the hitch always used for heavy lifts.

The Munter hitch, also known as the Italian hitch, mezzo barcaiolo or the crossing hitch, is a simple adjustable knot, commonly used by climbers, cavers, and rescuers to control friction in a life-lining or belay system. To climbers, this hitch is also known as HMS, the abbreviation for the German term Halbmastwurfsicherung, meaning half clove hitch belay. This technique can be used with a special "pear-shaped" HMS locking carabiner, or any locking carabiner wide enough to take two turns of the rope.

The Bachmann hitch is a friction hitch, named after the Austrian alpinist Franz Bachmann. It is useful when the friction hitch needs to be reset quickly or often or made to be self-tending as in crevasse and self-rescue.

A Prusik is a friction hitch or knot used to attach a loop of cord around a rope, applied in climbing, canyoneering, mountaineering, caving, rope rescue, ziplining, and by arborists. The term Prusik is a name for both the loops of cord used to tie the hitch and the hitch itself, and the verb is "to prusik" or "prusiking". More casually, the term is used for any friction hitch or device that can grab a rope. Due to the pronunciation, the word is often misspelled Prussik, Prussick, or Prussic.

The halter hitch is a type of knot used to connect a rope to an object. As the name implies, an animal's lead rope, attached to its halter, may be tied to a post or hitching rail with this knot. The benefit of the halter hitch is that it can be easily released by pulling on one end of the rope, even if it is under tension. Some sources show the knot being finished with the free end running through the slipped loop to prevent it from working loose or being untied by a clever animal, still allowing easy but not instant untying.

In knot tying, a bight is a curved section or slack part between the two ends of a rope, string, or yarn. A knot that can be tied using only the bight of a rope, without access to the ends, is described as in the bight. The term "bight" is also used in a more specific way when describing Turk's head knots, indicating how many repetitions of braiding are made in the circuit of a given knot.

The harness knot is a general purpose bend knot used to join two ropes together. The knot can be tied under tension and will not capsize.

The tumble hitch is a "slip-free", quick-release hitch knot used for temporarily securing a rope such that it can be released easily to be completely free of the hitched-to object. The hitch might be able to be released with a tug of the working end, even when under tension; but the workings depend upon materials and forces; note that in some cases, "under tension" will amount to simply being tied and the line itself giving significant tension by weight. The tumble hitch is tied in the bight.
























