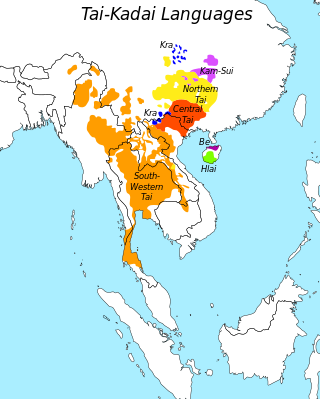
The term Kra–Dai peoples or Kra–Dai-speaking peoples refers collectively to the ethnic groups of southern China and Southeast Asia, stretching from Hainan to Northeast India and from southern Sichuan to Laos, Thailand and parts of Vietnam, who not only speak languages belonging to the Kra–Dai language family, but also share similar traditions, culture and ancestry.
The autonomous regions are one of four types of province-level divisions of China. Like Chinese provinces, an autonomous region has its own local government, but under the law of the People's Republic of China, an autonomous region has more legislative rights, such as the right to "formulate self-government regulations and other separate regulations." An autonomous region is the highest level of minority autonomous entity in China, which has a comparably higher population of a particular minority ethnic group.

Adenophora is a genus of flowering plants in the family Campanulaceae, the bellflowers. Plants of this genus are known commonly as ladybells. Most of the species in the genus are native to eastern Asia, with a few in Europe. Many are endemic to either China or Siberia.
Villages, formally village-level divisions in China, serve as a fundamental organizational unit for its rural population. Basic local divisions like neighborhoods and communities are not informal, but have defined boundaries and designated heads. In 2000, China's densely populated villages had a population greater than 500 million and covered more than 2 million square kilometers, or more than 20% of China's total area. By 2020, all incorporated villages had road access, the last village to be connected being a remote village in Sichuan province's Butuo County.
The 10th National Games of the People's Republic of China was a multi-sport event that was held in Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province, from 12–23 October 2005.

Southwestern China is a region in the south of the People's Republic of China.

Autonomous prefectures are one type of autonomous administrative divisions of China, existing at the prefectural level, with either ethnic minorities forming over 50% of the population or being the historic home of significant minorities. Autonomous prefectures are mostly majority Han Chinese by population. The official name of an autonomous prefecture includes the most significant minority in that region, sometimes two, rarely three. For example, a Kazakh prefecture may be called Kazak Zizhizhou. Like all other prefectural level divisions, autonomous prefectures are divided into county level divisions. There is one exception: Ili Kazak Autonomous Prefecture contains two prefectures of its own. Under the Constitution of the People's Republic of China, autonomous prefectures cannot be abolished.
The Rau people, also known as Lao, were an ethnic group of ancient China. Their descendants are the Zhuang, Buyei, Tày–Nùng and other Kra–Dai-speaking peoples.
Townships, formally township-level divisions, are the basic level of political divisions in the People's Republic of China. They are similar to municipalities and communes in other countries and in turn may contain village committees and villages. In 1995 there were 29,648 townships and 17,570 towns in China which included the territories held by the Republic of China and claimed by the PRC.

Biston panterinaria is a moth of the family Geometridae. It is found in China, India, Nepal, Sikkim, Vietnam and Thailand.

The 9th National Games of China was a multi-sport event that was held in Guangzhou, Guangdong Province, China from 11–25 November 2001.
The history of the administrative divisions of China after 1949 refers to the administrative divisions under the People's Republic of China. In 1949, the communist forces initially held scattered fragments of China at the start of the Chinese Civil War. By late 1949, they controlled the majority of mainland China, forcing the Republic of China government to relocate to Taiwan.
Eupoecilia amphimnesta is a species of moth of the family Tortricidae. It is found in China, Taiwan, India, Japan, Korea, Mongolia, Russia and Europe.

Guangxi, officially the Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, is an autonomous region of the People's Republic of China, located in South China and bordering Vietnam and the Gulf of Tonkin. Formerly a province, Guangxi became an autonomous region in 1958. Its current capital is Nanning.









