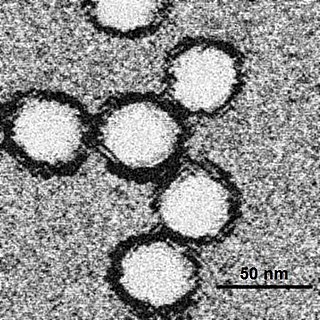
Arbovirus is an informal name used to refer to any viruses that are transmitted by arthropod vectors. The word arbovirus is an acronym. The word tibovirus is sometimes used to more specifically describe viruses transmitted by ticks, a superorder within the arthropods. Arboviruses can affect both animals, including humans, and plants. In humans, symptoms of arbovirus infection generally occur 3–15 days after exposure to the virus and last 3 or 4 days. The most common clinical features of infection are fever, headache, and malaise, but encephalitis and hemorrhagic fever may also occur.
La Crosse encephalitis is an encephalitis caused by an arbovirus which has a mosquito vector.
Togaviridae is a family of viruses. Humans, mammals, birds, and mosquitoes serve as natural hosts. There are currently 32 species in this family, divided among 2 genera. Diseases associated with this family include: Alphaviruses: arthritis, encephalitis; Rubiviruses: rubella.
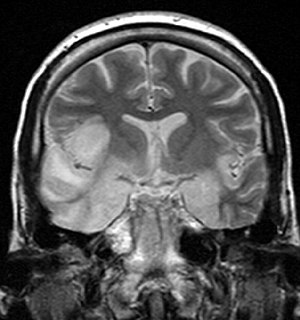
Murray Valley encephalitis virus (MVEV) is a zoonotic flavivirus endemic to northern Australia and Papua New Guinea. It is the causal agent of Murray Valley encephalitis. In humans it can cause permanent neurological disease or death. MVEV is related to Kunjin virus which has a similar ecology but a lower morbidity rate. Although the arbovirus is endemic to Northern Australia, it has occasionally spread to the southern states during times of heavy rainfall during the summer monsoon season via seasonal flooding of the Murray-Darling river system. These outbreaks can be "...decades apart, with no or very few cases identified in between".
California encephalitis orthobunyavirus or California encephalitis virus was discovered in Kern County, California and causes encephalitis in humans. Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain that can cause minor symptoms, such as headaches, to more severe symptoms such as seizures. Mosquitoes serve as its carrier and for this reason this virus is known as an arbovirus.
Viral encephalitis is a type of encephalitis caused by a virus.

Culex is a genus of mosquitoes, several species of which serve as vectors of one or more important diseases of birds, humans, and other animals. The diseases they vector include arbovirus infections such as West Nile virus, Japanese encephalitis, or St. Louis encephalitis, but also filariasis and avian malaria. They occur worldwide except for the extreme northern parts of the temperate zone, and are the most common form of mosquito encountered in some major US cities such as Los Angeles.
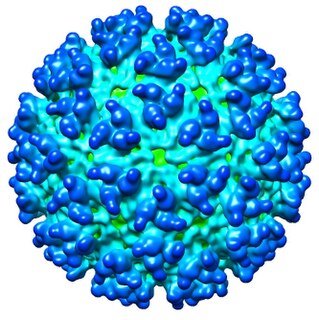
The Western equine encephalomyelitis virus is the causative agent of relatively uncommon viral disease Western equine encephalomyelitis (WEE). An Alphavirus of the family Togaviridae, the WEE virus is an arbovirus transmitted by mosquitoes of the genera Culex and Culiseta. WEE is a recombinant virus between two other alphaviruses, an ancestral Sindbis virus-like virus, and an ancestral Eastern equine encephalitis virus-like virus. There have been under 700 confirmed cases in the U.S. since 1964. This virus contains an envelope that is made up of glycoproteins and nucleic acids. The virus is transmitted to people and horses by bites from infected mosquitoes and birds during wet, summer months.
The National Institute of Virology, Pune is an Indian virology research institute, and one of the Translational science cells part of Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). It was previously known as 'Virus Research Center' and was founded in collaboration with the Rockefeller Foundation. It has been designated as a WHO H5 reference Laboratory for SE Asia region
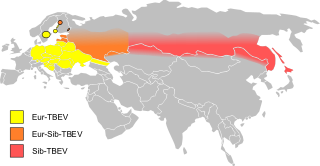
Powassan encephalitis, caused by the Powassan virus (POWV), a flavivirus also known as the deer tick virus, is a form of arbovirus infection that results from tick bites. It can occur as a co-infection with Lyme disease since both are transmitted to humans by the same species of tick. There has been a surge in the number of cases and geographic range in the last decade. In the United States, cases have been recorded in the northeast. The disease was first isolated from the brain of a boy who died of encephalitis in Powassan, Ontario, in 1958. The disease is a zoonosis, an animal disease, usually found in rodents and ticks, with spillover transmission to humans. The virus is antigenically related to the Far Eastern tick-borne encephalitis viruses.
Arbovirus is a shortened name given to viruses that are transmitted by arthropods, or arthropod-borne viruses.
Toscana virus (TOSV) is an arbovirus belonging to Bunyavirales, an order of negative-stranded, enveloped RNA viruses. The virus can be transmitted to humans by the bite of an infected sandfly of the genus Phlebotomus. Toscana is not normally associated with disease, as indicated by high seroprevalence rates in endemic areas, but in common with other sandfly transmitted viruses such as Naples virus and Sicilian virus, infection may result in Pappataci fever, an illness with mild fever, headache and myalgia. In serious cases that go undiagnosed, acute meningitis, meningoencephalitis and encephalitis may occur. There is no specific treatment for infection, so treatment is supportive, reducing the severity of symptoms until the immune system has cleared the infection.
Sleeping sickness may refer to:
Kunjin virus (KUNV) is a zoonotic virus of the family Flaviviridae and the genus Flavivirus. It is a subtype of West Nile Virus endemic to Oceania.
Usutu virus (USUV) first identified in South Africa in 1959, is an emerging zoonotic arbovirus of concern because of its pathogenicity to humans and its similarity in ecology with other emerging arboviruses such as West Nile Virus. USUV is a flavivirus belonging to the Japanese encephalitis complex.
Jamestown Canyon encephalitis is an infectious disease cause by the Jamestown Canyon virus, an orthobunyavirus of the California serogroup. It is mainly spread during the summer by different mosquito species in the United States and Canada.
Aedes mitchellae mosquitoes were originally collected in southern Georgia and Florida in 1905 by entomologist Harrison Gray Dyar, Jr. The species' range extends through the coastal plains from the southeastern United States, north to New York and west to New Mexico with the greatest abundance in the Atlantic and Gulf coastal plains.
The Keystone virus is a mosquito-borne virus which can infect mammals. It was first discovered in animals in the Florida area, where it is spread in part by local species of Aedes mosquitoes. In 1964, a case of human infection, producing minor symptoms of a rash and fever, was circumstantially diagnosed. Conclusive laboratory demonstration of the virus in humans was first obtained and reported in 2018.