| Botlikh | |
|---|---|
| Botlix | |
| буйхалъи мицIцIи/bujxałi mic’c’i | |
| Pronunciation | [bujχaɬimits’ːi] |
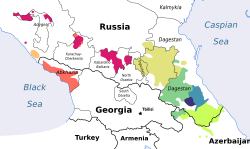
| Native to | North Caucasus |
| Region | Southwestern Dagestan [1] |
| Ethnicity | 3,788 Botlikh people (2020) |
Native speakers | 5,073 (2020 census) [2] c. 8,000 (2012) [3] |
Northeast Caucasian
| |
| Dialects |
|
| unwritten (transcribed using Cyrillic script) | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | bph |
| Glottolog | botl1242 |
| ELP | Botlikh |
 Botlikh | |
 Botlikh is classified as Definitely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger (2010) | |
Botlikh (also spelled Botlix) is an Andic language of the Northeast Caucasian language family spoken by the Botlikhs in the villages of Botlikh (Buikhe), Miarso and Ashino, as well as in Chontaul, Ankho and in Batlakhatli, [4] in southwestern Dagestan, Russia by approximately 5,000 people, according to the 2020 census. [2]