Related Research Articles

Finno-Ugric is a traditional linguistic grouping of all languages in the Uralic language family except for the Samoyedic languages. Its once commonly accepted status as a subfamily of Uralic is based on criteria formulated in the 19th century and is criticized by some contemporary linguists such as Tapani Salminen and Ante Aikio. The three most spoken Uralic languages, Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian, are all included in Finno-Ugric.

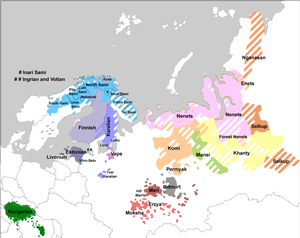
The Uralic languages, sometimes called the Uralian languages, are spoken predominantly in Europe and North Asia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian. Other languages with speakers above 100,000 are Erzya, Moksha, Mari, Udmurt and Komi spoken in the European parts of the Russian Federation. Still smaller minority languages are Sámi languages of the northern Fennoscandia; other members of the Finnic languages, ranging from Livonian in northern Latvia to Karelian in northwesternmost Russia; and the Samoyedic languages, Mansi and Khanty spoken in Western Siberia.

Ural-Altaic, Uralo-Altaic, Uraltaic, or Turanic is a linguistic convergence zone and abandoned language-family proposal uniting the Uralic and the Altaic languages. It is now generally agreed that even the Altaic languages do not share a common descent: the similarities between Turkic, Mongolic and Tungusic are better explained by diffusion and borrowing. Just as in Altaic, the internal structure of the Uralic family has been debated since the family was first proposed. Doubts about the validity of most or all of the proposed higher-order Uralic branchings are becoming more common. The term continues to be used for the central Eurasian typological, grammatical and lexical convergence zone.

The Mari are a Finno-Ugric people in Eastern Europe, who have traditionally lived along the Volga and Kama rivers in Russia. Almost half of Maris today live in the Mari El republic, with significant populations in the Bashkortostan and Tatarstan republics. In the past, the Mari have also been known as the Cheremisa or the Cheremis people in Russian and the Çirmeş in Tatar.

Mordvins is an official term used in the Russian Federation to refer both to Erzyas and Mokshas since 1928.
Udmurt may refer to:

Jumala, Jumal or Jumo (Mari) means "god" in the Finnic languages and those of the Volga Finns, both the Christian God and any other deity of any religion. The word is thought to have been the name of a sky god of the ancient Finnic-speaking peoples. Jumala as a god of the sky is associated with the related Estonian Jumal, Mari Jumo and is thought to stem from an ancient tradition of the Finno-Ugric peoples.

Chud or Chude is a term historically applied in the early East Slavic annals to several Baltic Finnic peoples in the area of what is now Estonia, Karelia and Northwestern Russia. It has also been used to refer to other Finno-Ugric peoples.

The Finno-Samic languages are a hypothetical subgroup of the Uralic family, and are made up of 22 languages classified into either the Sami languages, which are spoken by the Sami people who inhabit the Sápmi region of northern Fennoscandia, or Finnic languages, which include the major languages Finnish and Estonian. The grouping is not universally recognized as valid.
Udmurtia is a federal subject of Russia. The largest ethnic group in the area are the Udmurts, who have vibrant folk song traditions. Musical contests as well as ceremonial and ritual music are an important part of the music of Udmurtia. Every year since 1958 the capital Izhevsk has been hosting a traditional musical festival dedicated to the birthday of Tchaikovsky.

The Estonian Wikipedia is the Estonian version of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia, started on 24 August 2002. As of December 2024, the edition has about 249,000 articles.
Paul Ariste was an Estonian linguist renowned for his studies of the Finno-Ugric languages, Yiddish and Baltic Romani language.
Elements of a Proto-Uralic religion can be recovered from reconstructions of the Proto-Uralic language.

The Permians are the peoples who speak the Permic languages, a branch of the Uralic language family, and include Komis, Udmurts, and Besermyans.

Nõva is a village in Lääne-Nigula Parish Lääne County, on the northwestern coast of Estonia. It was the administrative centre of Nõva Parish. Nõva had a population of 136 as of 2010.
Uralic neopaganism encompasses contemporary movements which have been reviving or revitalising the ethnic religions of the various peoples who speak Uralic languages. The movement has taken place since the 1980s and 1990s, after the collapse of the Soviet Union and alongside the ethnonational and cultural reawakening of the Finnic peoples of Russia, the Estonians and the Finns. In fact, Neopagan movements in Finland and Estonia have much older roots, dating from the early 20th century.

The Finnic or Fennic peoples, sometimes simply called Finns, are the nations who speak languages traditionally classified in the Finnic language family, and which are thought to have originated in the region of the Volga River. The largest Finnic peoples by population are the Finns, the Estonians, the Mordvins (800,000), the Mari (570,000), the Udmurts (550,000), the Komis (330,000) and the Sami (100,000).

Ruuben Kaalep is an Estonian politician, poet and a far-right philosopher. He has been member of XIV Riigikogu. He is a founder of the Conservative People's Party of Estonia's youth organization Sinine Äratus. Since 2012, he is a member of Estonian Conservative People's Party.

World Congress of Finno-Ugric Peoples is the representative forum of Finno-Ugric and Samoyedic peoples. The forum is not related to any government or political party. The goals of the forum is to "develop and protect national identity, cultures and languages of Finno-Ugric peoples, to promote cooperation between Finno-Ugric peoples, to discuss topical issues and to identify solutions, and to realise the right of Finno-Ugric peoples to self-determination in accordance with international norms and principles".
Ethnofuturism is an artistic and philosophic movement originating from Estonia that has gone through different phases. During its initial phase from 1989 to 1994, it was an avant-garde artistic movement with emphasis on futurism and characterized by parody, absurdity and provocative statements. In the second phase, starting with the First Ethnofuturist Manifesto in 1994, the focus shifted to the ethnic elements, foregrounding folklore, borealism and the issues of the Finno-Ugric peoples.
References
- ↑ Sikk, Rein (May 27, 2009). "Udmurdid lõid soome-ugri ühistehiskeele". Eesti Päevaleht. Retrieved 14 January 2022.
- ↑ Ville Ropponen (ed.): Volga-antologia. Turku 2010. ISBN 978-952-5500-75-2