This is a list of properties and districts in Illinois that are on the National Register of Historic Places. There are over 1,800 in total. Of these, 85 are National Historic Landmarks. There are listings in all of the state's 102 counties.

The Hinson Mounds (8Cr180) comprise an archeological site in Collier County, Florida near Miles City. It is located three miles northeast of Miles City. The mounds were estimated to have been used for burial from 400 - 900 AD, and they were part of the Glades culture. Excavation of the mounds, which were found on a hardwood hammock island, has produced evidence of prehistoric Native American occupation.

The Portavant Mound is an archaeological site on Snead Island within the Emerson Point Preserve, just west of Palmetto, Florida. On December 23, 1994, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places.

The Birnirk Site is an archaeological site near Barrow, Alaska. It includes sixteen prehistoric mounds which have yielded evidence of very early Birnirk and Thule culture. It is the type site of the Birnirk culture, and was designated a National Historic Landmark in 1962 for its archaeological importance in understanding prehistoric Arctic cultures.

Silver Mound is a sandstone hill in Wisconsin where American Indians quarried quartzite for stone tools. Tools made from Silver Mound's quartzite have been found as far away as Kentucky. The oldest have been dated to around 11,000 years ago, so they provide clues about the first people in Wisconsin. Silver Mound Archeological District was declared a National Historic Landmark in 2006.

Calumet County Park Group is an archaeological site in Calumet County, Wisconsin, United States. It consists of six effigy mounds of panthers and other water spirits and it is located at the top of the Niagara Escarpment where overlook Lake Winnebago. The group is located within the Calumet County Park approximately 2 miles northwest of Stockbridge. The mounds are consistent with other mound groups found at the peak of the Niagara Escarpment along the eastern shore of Lake Winnebago, including the High Cliff Mounds. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1997.

Deprato Mounds, also known as the Ferriday Mounds, is a multi-mound archaeological site located in Concordia Parish, Louisiana. The site shows occupation from the Troyville period to the Middle Coles Creek period. The largest mound at the site has been dated by radiocarbon analysis and decorated pottery to about 600 CE.

Cranberry Creek Archeological District, also known as Cranberry Creek Mound Group, is an ancient American Indian burial mound site from circa AD 100–800 near New Miner, Wisconsin, United States. It is three miles east of Necedah National Wildlife Refuge in Juneau County. It is part of the "effigy mound culture" of native peoples in Wisconsin, who practiced the "respectful burial of their dead".

The Gee's Slough Group of Indian Mounds, located along the Lemonweir River just outside of New Lisbon, Wisconsin, is listed on the US National Register of Historic Places. The New Lisbon area was a winter gathering place for the Woodland Culture Indians who are considered the ancestors to the Ho-Chunk (Winnebago) tribe.
The Schilling Archeological District is a prehistoric Native American archaeological site on private property on Lower Grey Cloud Island in Cottage Grove, Minnesota, United States. It consists of a habitation site and mound group with artifacts that date from the Early Woodland Period to the Late Prehistoric Period. It was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1978 for having state-level significance in the theme of archaeology. It was nominated for its rare Early Woodland component, Middle Mississippian cultural influences, and potential to show climatic adaptations over time.
Indian Fish Trap State Preserve, also known as the Indian Fish Weir, is a historic site located near the Amana Colonies in rural Iowa County, Iowa. The fish weir is an array of rocks in a V-shaped formation in the Iowa River. It is the only structure of this kind in Iowa. It is not known when the fish weir was built, possibly in either the Late Prehistoric period or Early Historic period. Glacial boulders from a nearby bluff were probably used to construct it. Each wing of the dam is about 155 feet (47 m) in length. The fish were thought to be herded toward the vertex of the "V" where they would be easier to net or spear. They were then placed into an adjacent holding pool. Early pioneers discovered the weir, and it was included on a General Land Office map in the 1840s. Archaeologist Charles R. Keyes wrote about the weir in 1925.
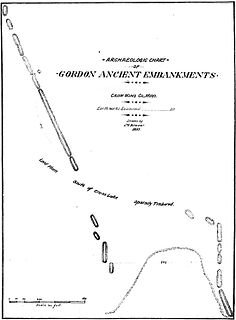
The Gordon–Schaust Site is a prehistoric Native American archaeological site in Crosslake, Minnesota, United States. It comprises two separate but nearly parallel groups of linear mounds, undated but well preserved. The site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974 for having state-level significance in the theme of archaeology.

The Fort Flatmouth Mounds form a prehistoric Native American archaeological site in Mission Township, Minnesota, United States. It consists of nine mounds grouped in a rough ellipse and a few additional mounds in close proximity. Early Euro-American settlers assumed the enclosure was built as a fort, hence the name, but it was more likely religious in nature. The site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973 for having state-level significance in the theme of archaeology. It was nominated for its information potential as a unique site in a region whose numerous mound and village sites indicate a long span of indigenous occupation.
The Four Mounds Site is a historic site located in Dubuque, Iowa, United States. It is made up of a row of four conical burial mounds on a blufftop that overlooks the Mississippi River. They are prehistoric in their origin. The site was individually listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2000. It was included as a contributing property in the Four Mounds Estate Historic District in 2002.
Fort Juelson, designated 21OT198 in the state archaeological inventory, is a historic site located east of Underwood, Minnesota, United States. An earthen fort was built at this hilltop in July 1876 after rumors of Indian attacks in Foxhome, French, and Fergus Falls following the Battle of Little Bighorn in Montana. Many settlers left the area. Charles A. Dollner, a local merchant, suggested the rest of the people band together and build the fortification under leadership of two American Civil War veterans, Hans Juelson and Berge O. Lee. The scare proved to be a hoax, and the fort was never used for defensive purposes. Remnants of the sod barricade are still on the site.
Morrison Mounds is a historic site located north of Battle Lake, Minnesota, United States. It consists of 22 Indian burial mounds that were built beginning in 800 B.C. There are 20 conical mounds, one flat-topped mound, and one elongated mound near Otter Tail Lake. This site has the oldest radiocarbon date for any mound group in the state of Minnesota. However, its construction is similar to other mound groups in the area which suggests they are all from the same social group that built them over a period of time. Similarities include a central burial pit, logs over the burial pit, and the possibility of partial cremation on-site. The site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1973.
The Orwell Site, designated 21OT7 in the state archaeological inventory, is a historic site located near Fergus Falls, Minnesota, United States. It consists of twelve Middle or Late Woodland period burial mounds, four of which are enclosed by an earthwork. They were built from about A.D. 350-600. They share similarities with the mounds found at Fort Juelson, also in Otter Tail County, with their central burial chamber. The site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1974.
The Rosenstock Village Site is a historic site located in Frederick County, Maryland, United States, near the city of Frederick. It contains the remains of a Late Woodland Village situated on a bluff overlooking the Monocacy River. The village was occupied between A.D. 1335 and A.D. 1400, based on artifact analysis and radiocarbon dating. It is similar to the Montgomery Complex, which is a cultural complex made up of Late Woodland sites located on the Potomac River. The site was excavated in 1979 and from 1990 to 1992, and estimates suggest that 93% of the site remains undisturbed. They uncovered a large oval area surrounded by pits, a large sheet midden area, and what are believed to be two sweatlodges. The excavations have yielded a trove of artifacts and animal remains. The site was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 2018.