
The London Passenger Transport Board was the organisation responsible for local public transport in London and its environs from 1933 to 1948. In common with all London transport authorities from 1933 to 2000, the public name and brand was London Transport.
Dick, Kerr and Company was a locomotive and tramcar manufacturer based in Kilmarnock, Scotland and Preston, England.

The Portsdown and Horndean Light Railway was a tram service that ran initially from Cosham to Horndean in Hampshire, England.

The Rothesay tramway was a narrow gauge electric tramway on the Isle of Bute, Scotland. It opened in 1882 as a 4 ft gauge horse tramway, was converted to a 3 ft 6 in gauge electric tramway in 1902, and closed in 1936. It was the only public tramway to be built on a Scottish island.

The Taunton Tramway was an electric street tramway in Taunton, the county town of Somerset, England. It operated a fleet of six narrow gauge tramcars on a single route of 1.66 miles (2.67 km) between 1901 and 1921 when the tramway closed due to a dispute over the cost of electricity.
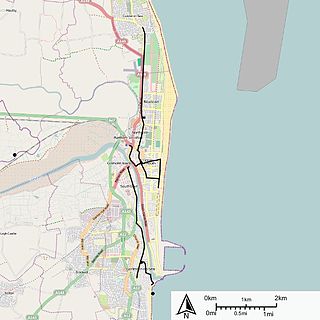
Great Yarmouth Corporation Tramways served the town of Great Yarmouth in Norfolk, England from 19 June 1902 until 14 December 1933.
Southend-on-Sea Corporation Transport was the overarching name given to the local municipal transport services provided to the town of Southend-on-Sea by the local council. Initially started as a tramway, although known officially as Southend-on-Sea Corporation Light Railway, the trams started operating on 19 July 1901 until the service was terminated on 8 April 1942. A trolleybus system was introduced in 16 October 1925, gradually replacing the tramway, before it closed on 28 October 1954. Motorbuses were first run by the Corporation in 1914, but two years later they withdrew the services. Buses did not return to the Corporation's service until 1932, eventually replacing the trams and trolleybuses. In 1974, the organisation was renamed Southend Transport, and after the Transport Act of 1985, it became involved in a bus war with rival Thamesway. The council sold Southend Transport to British Bus group in June 1993, which in turn was taken over by the Cowie group. Cowie was renamed Arriva in August 1998, with Southend Transport becoming Arriva serving Southend.

Northampton Corporation Tramways operated the tramway service in Northampton between 1901 and 1934.
The Worcester Electric Traction Company operated a tramway service in Worcester between 1904 and 1928.

Coventry Corporation Tramways operated a tramway service in Coventry, England, between 1912 and 1940.
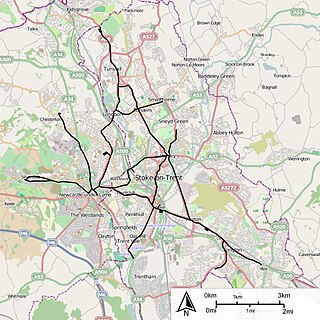
The Potteries Electric Traction Company operated a tramway service in The Potteries between 1899 and 1928.

Erith Urban District Council Tramways operated a passenger tramway service in Erith between 1905 and 1933.
Barking Town Urban District Council Light Railways operated a passenger tramway service in Barking between 1903 and 1929.
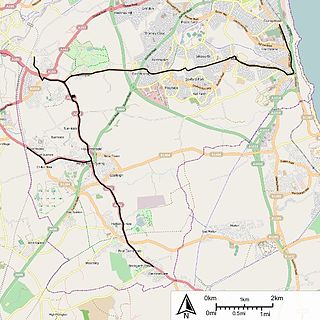
The Sunderland District Electric Tramways operated an electric tramway service from Grangetown to Easington Lane between 1905 and 1925.

South Shields Corporation Tramways operated an electric tramway service in South Shields between 1906 and 1946.

The Second International Tramways and Light Railways Exhibition was held in the Royal Agricultural Hall, Islington, London from 1 July 1902 - 12 July 1902

The First International Tramways and Light Railways Exhibition was held in the Royal Agricultural Hall, Islington, London from 30 June 1900 – 11 July 1900.

The Third International Electric Tramway and Railway Exhibition was held in the Royal Agricultural Hall, Islington, London from 3 July 1905 to 14 July 1905
Halifax Corporation Tramways operated a tramway service in Halifax, West Yorkshire, England between 1898 and 1939. After considering lifts and inclined planes to assist trams in negotiating the steep hills to the south of the town, they obtained permission to build a conventional system in 1897, and the first three routes opened in 1898. By 1905 there were 37 miles (60 km) of track and 96 tramcars, supplied by two manufacturers. In 1921, an additional route was added to the system, and the Corporation embarked on a programme of building their own tramcars, some of which replaced existing vehicles, while some extended the fleet. During the 1930s, the trams were gradually replaced by motor buses, either run by the Corporation or by private companies, and the last tram ran on 14 February 1939.

Stockport Corporation Tramways operated a tramway service in Stockport, England, between 1901 and 1951. It was preceded by a horse tramway from Levenshulme to Stockport, which opened in 1880, and was ultimately run by the Manchester Carriage and Tramways Company. A second independent horse tramway opened in 1890, running to Hazel Grove. In 1899 the Corporation bought the first line, electrified it, and leased it back to the operating company. Their powers to buy the Stockport and Hazel Grove Tramway, authorised by the same Act of Parliament, were not exercised until 1905.













