
Melbourne tram route 5 is operated by Yarra Trams on the Melbourne tram network from Melbourne University to Malvern. The 12.6-kilometre (7.8 mi) route is operated out of Malvern depot with Z and D1 class trams.

Melbourne tram route 96 is operated by Yarra Trams on the Melbourne tram network from Brunswick East to St Kilda Beach. The 13.9 kilometre route is operated out of Southbank depot with C2 and E class trams.

Melbourne tram route 75 is operated by Yarra Trams on the Melbourne tram network from Vermont South to Central Pier. The 22.8 kilometre route is operated out of Camberwell depot with A and B class trams. It is the longest route on the network.

Melbourne tram route 109 is operated by Yarra Trams on the Melbourne tram network from Box Hill to Port Melbourne. The 19.3 kilometre route is operated out of Kew depot with A and C class trams.

Melbourne tram route 59 is operated by Yarra Trams on the Melbourne tram network from Airport West to Flinders Street station. The 14.7 kilometre route is operated out of Essendon depot with Z and B class trams.

Norwich railway station is the northern terminus of the Great Eastern Main Line in the East of England, serving the city of Norwich, Norfolk. It is 114 miles 77 chains (185.0 km) down the main line from London Liverpool Street, the western terminus.

The Sydney tramway network served the inner suburbs of Sydney, Australia, from 1879 until 1961. In its heyday, it was the largest in Australia, the second largest in the Commonwealth of Nations, and one of the largest in the world. The network was heavily worked, with about 1,600 cars in service at any one time at its peak during the 1930s . Patronage peaked in 1945 at 405 million passenger journeys. Its maximum street trackage totalled 291 km in 1923.
The Edinburgh Suburban and Southside Junction Railway was a railway company that built an east-west railway on the southern margin of Edinburgh, Scotland, primarily to facilitate the operation of heavy goods and mineral traffic across the city. The line opened in 1884. Although its route was rural at the time, suburban development quickly caught up and passenger carryings on the line were buoyant; the passenger service operated on a circular basis through Edinburgh Waverley railway station.
Lowestoft Corporation Tramways was the operator of the electric tramway system that served Lowestoft from 22 July 1903 until 8 May 1931.

The Perth tramway network served Perth, the capital city of Western Australia, from 1899 until 1958. The network was initially run by a private company but was taken over by the state government in 1913. From a single line along Hay Street, the network expanded north as far as Osborne Park, east as far as Welshpool, south as far as Como, and west as far as Claremont. The tramways were gradually replaced by buses after World War II.

Ipswich Corporation Tramways was an electric tramway system that served the town of Ipswich in Suffolk from 23 November 1903 until 26 July 1926.
Colchester Corporation Tramways served the town of Colchester in Essex from 28 July 1904 until 8 December 1929.
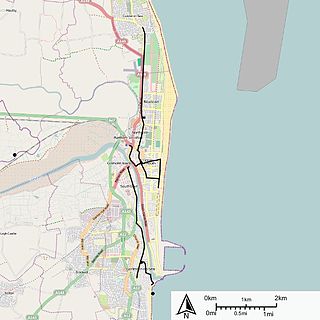
Great Yarmouth Corporation Tramways served the town of Great Yarmouth in Norfolk, England from 19 June 1902 until 14 December 1933.
Southend-on-Sea Corporation Tramways served the town of Southend-on-Sea in Essex from 19 July 1901 until 8 April 1942.

Bournemouth Corporation Tramways served the town of Bournemouth in Dorset from 23 July 1902 until 8 April 1936.

The City of Oxford and District Tramway Company and its successor the City of Oxford Electric Traction Company operated a horse-drawn passenger tramway service in Oxford between 1881 and 1914. The tramway was unusual for having a track gauge of only 4 feet (1.219 m).

Cambridge Street Tramways operated a horse-drawn tramway service in Cambridge, England, between 1880 and 1914.
The Melbourne tram network began in 1884 with the construction of the Fairfield Horse Tramway. However, the purpose of the line was to increase land prices in the area, and it soon closed during the depression in 1890. The first genuine attempt to construct a tramway network was the construction of the Richmond cable tram line by the Melbourne Tramway & Omnibus Company in 1885. Over the next few years, 16 more cable tram lines were constructed, as well as numerous other horse tramways. The depression of the early 1890s slowed further expansion of the cable network. The first electric tram line was the Box Hill and Doncaster tramway which opened in 1889. This was a pioneering line in what was then the countryside and thus didn't receive much patronage. It closed in 1896. The next attempt at an electric tramway was Victorian Railways' St Kilda to Brighton line, which opened in 1906. Later that year, the North Melbourne Electric Tramway & Lighting Company opened lines to Essendon and Maribyrnong. Many local councils formed their own tramway trusts and built tramways within their own constituency. The most successful of these was the Prahran & Malvern Tramways Trust.
Trams existed in Sri Lanka's capital Colombo from 1899 to 1960.















