This article needs additional citations for verification .(March 2022) |
This article contains the rank insignia of the Hellenic Army (until 1973).
This article needs additional citations for verification .(March 2022) |
This article contains the rank insignia of the Hellenic Army (until 1973).
| Rank group | General / flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1829–1868) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Στρατηγός Stratigos | Ἀντιστράτηγος Antistratigos | Ὑποστράτηγος Ypostratigos | Συνταγματάρχης Syntagmatarchis | Ἀντισυνταγματάρχης Antisyntagmatarchis | Ταγματάρχης Tagmatarchis | Ὑποταγματάρχης Ypotagmatarchis | Ἐπιλοχαγός Epilochagós | Λοχαγός Lochagos | Πρωθυπολοχαγός Prothypolochagós [a] | Ὑπολοχαγός Ypolochagos | Ἀνθυπολοχαγός Anthypolochagos | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1868–1908) |  |  |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Στρατηγός Stratigos | Ἀντιστράτηγος Antistratigos | Ὑποστράτηγος Ypostratigos | Συνταγματάρχης Syntagmatarchis | Ἀντισυνταγματάρχης Antisyntagmatarchis | Ταγματάρχης Tagmatarchis | Ἐπιλοχαγός Epilochagós | Λοχαγός Lochagos | Ὑπολοχαγός Ypolochagós | Ἀνθυπολοχαγός Anthypolochagos | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1908–1936) |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Στρατάρχης [b] Stratarches | Στρατηγός Stratigos | Ἀντιστράτηγος Antistratigos | Ὑποστράτηγος Ypostratigos | Συνταγματάρχης Syntagmatarchis | Ἀντισυνταγματάρχης Antisyntagmatarchis | Ταγματάρχης Tagmatarchis | Λοχαγός Α΄ Τάξεως [c] | Λοχαγός Lochagos | Ὑπολοχαγός Ypolochagós | Ἀνθυπολοχαγός Anthypolochagos | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1936-1945) |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Στρατάρχης [d] Stratarches | Στρατηγός Stratigos | Ἀντιστράτηγος Antistratigos | Ὑποστράτηγος Ypostratigos | Συνταγματάρχης Syntagmatarchis | Ἀντισυνταγματάρχης Antisyntagmatarchis | Ταγματάρχης Tagmatarchis | Λοχαγός Lochagos | Ὑπολοχαγός Ypolochagós | Ἀνθυπολοχαγός Anthypolochagos | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1946–1959) |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Στρατάρχης [d] Stratarches | Στρατηγός Stratigos | Ἀντιστράτηγος Antistratigos | Ὑποστράτηγος Ypostratigos | Ταξίαρχος Taxiarchos | Συνταγματάρχης Syntagmatarchis | Ἀντισυνταγματάρχης Antisyntagmatarchis | Ταγματάρχης Tagmatarchis | Λοχαγός Lochagos | Ὑπολοχαγός Ypolochagós | Ἀνθυπολοχαγός Anthypolochagos | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1959–1970) |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Στρατάρχης [e] Stratarches | Στρατηγός Stratigos | Ἀντιστράτηγος Antistratigos | Ὑποστράτηγος Ypostratigos | Ταξίαρχος Taxiarchos | Συνταγματάρχης Syntagmatarchis | Ἀντισυνταγματάρχης Antisyntagmatarchis | Ταγματάρχης Tagmatarchis | Λοχαγός Lochagos | Ὑπολοχαγός Ypolochagós | Ἀνθυπολοχαγός Anthypolochagos | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1970–1973) |  |  |  |  |  |  |  |  | 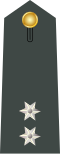 |  | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Στρατάρχης [f] Stratarches | Στρατηγός Stratigos | Ἀντιστράτηγος Antistratigos | Ὑποστράτηγος Ypostratigos | Ταξίαρχος Taxiarchos | Συνταγματάρχης Syntagmatarchis | Ἀντισυνταγματάρχης Antisyntagmatarchis | Ταγματάρχης Tagmatarchis | Λοχαγός Lochagos | Ὑπολοχαγός Ypolochagós | Ἀνθυπολοχαγός Anthypolochagos | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rank group | General / flag officers | Senior officers | Junior officers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (1829–1868) | No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ἀνθυπασπιστής Anthypaspistís | Ἐπιλοχίας Epilochías | Λοχίας Lochías | Δεκανέας Dekanéas | Ὑποδεκανέας Ypodekanéas | Στρατιώτης Stratiótis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1868–1924) |  | No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ἀνθυπασπιστής Anthypaspistís | Ἐπιλοχίας Epilochías | Λοχίας Lochías | Δεκανέας Dekanéas | Ὑποδεκανέας Ypodekanéas | Στρατιώτης Stratiótis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1912–1916) |  |  |  |  |  | No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ἀνθυπασπιστής Anthypaspistís | Ἐπιλοχίας Epilochías | Λοχίας Lochías | Δεκανέας Dekanéas | Ὑποδεκανέας Ypodekanéas | Στρατιώτης Stratiótis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1916–1924) |  |  |  |  |  | No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ἀνθυπασπιστής Anthypaspistís | Ἐπιλοχίας Epilochías | Λοχίας Lochías | Δεκανέας Dekanéas | Ὑποδεκανέας Ypodekanéas | Στρατιώτης Stratiótis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1936–1959) | No insignia | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ἀνθυπασπιστής Anthypaspistís | Ἐπιλοχίας Epilochías | Λοχίας Α΄ Lochías Á | Λοχίας Β΄ Lochías B́ | Δεκανέας Dekanéas | Στρατιώτης Stratiótis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1965–1970) [1] |  |  |  |  |  | No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ἀνθυπασπιστής Anthypaspistís | Ἐπιλοχίας Epilochías | Λοχίας Α΄ Lochías Á | Λοχίας Β΄ Lochías B́ | Δεκανέας Dekanéas | Στρατιώτης Stratiótis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1970–1973) |  |  | | No insignia | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ἀνθυπασπιστής Anthypaspistís | Ἐπιλοχίας Epilochías | Λοχίας Α΄ Lochías Á | Λοχίας Β΄ Lochías B́ | Δεκανέας Dekanéas | Στρατιώτης Stratiótis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rank group | Senior NCOs | Junior NCOs | Enlisted | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Royal Guard (Evzones) insignia during Paul's reign
 | |||||||
| 1947–1964 | |||||||