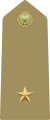
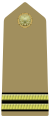
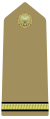
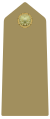
A private is a soldier, usually with the lowest rank in many armies. Soldiers with the rank of private may be conscripts or they may be professional (career) soldiers.
Corporal is a military rank in use by the armed forces of many countries. It is also a police rank in some police services. The rank is usually the lowest ranking non-commissioned officer. In some militaries, the rank of corporal nominally corresponds to commanding a section or squad of soldiers.

Epaulette is a type of ornamental shoulder piece or decoration used as insignia of rank by armed forces and other organizations. Flexible metal epaulettes are referred to as shoulder scales.
The chart below shows the current enlisted rank insignia of the United States Army, with seniority, and pay grade, increasing from right to left. The enlisted ranks of corporal (E-4) and higher are considered non-commissioned officers (NCOs). The rank of specialist is also in pay grade E-4, but does not hold non-commissioned officer status; it is common that a soldier may never hold the rank of corporal, and instead be promoted from specialist to sergeant, attaining junior NCO status at that time.

Modern Russian military ranks trace their roots to the Table of Ranks established by Peter the Great. Most of the rank names were borrowed from existing German/Prussian, French, English, Dutch, and Polish ranks upon the formation of the Russian regular army in the late 17th century.
Officer candidate or officer aspirant (OA) is a rank in some militaries of the world that is an appointed position while a person is in training to become an officer. More often than not, an officer candidate was a civilian who applied to join the military directly as an officer. Officer candidates are, therefore, not considered of the same status as enlisted personnel.
The military ranks of Finland are the military insignia used by the Finnish Defence Forces. The ranks incorporate features from the Swedish, German, and Russian armed forces. In addition, the system has some typically Finnish characteristics that are mostly due to the personnel structure of the Finnish Defence Forces. The ranks have official names in Finnish and Swedish languages and official English translations. The Swedish forms are used in all Swedish-language communications in Finland, e.g. in Swedish-speaking units of the Finnish Defence Force. The system of ranks in the Swedish Armed Forces is slightly different.
Before Unification as the Canadian Armed Forces in 1968, the Canadian military had three distinct services: the Royal Canadian Navy, the Royal Canadian Air Force, and the Canadian Army. All three services had a Regular (full-time) component and a reserve (part-time) component. The rank structure for these services were based on the services of the British military, the Royal Navy, the Royal Air Force, and the British Army. The change to a "Canadian" rank structure meant that many of the traditional (British) rank titles and insignia were removed or changed.

The ranks in the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) reflect an individual's level in the military.
United States Army commissioned officers rank insignia in use today.

The United States Marine Corps (USMC) prescribes several types of military uniform to distinguish its service members from other armed services, depending on the situation.
The Singapore Armed Forces (SAF) has five rank schemes for active and reservist personnel, with a sixth for the auxiliaries of the SAF Volunteer Corps. The SAF has a unique rank structure as an integrated force, ranks are the same in the Singapore Army, the Republic of Singapore Navy (RSN), the Republic of Singapore Air Force (RSAF), and the Digital and Intelligence Service (DIS).

The Italian military rank of maresciallo is classified as a "sub-officer" and is the highest rank of non-commissioned officer in the Italian Armed Forces. It is higher than the rank of sergeant but lower than that of ensign/second lieutenant. There are from three to five grades within the rank, according to the different branches of the armed forces. The rank is achieved through merit or attending the Scuola Allievi Marescialli. Marshal is an intermediate rank of the armed forces which is currently granted to NCOs with the training and technical competence to carry out specialised executive roles, and to command smaller and technically complex units.
A new law approved in July 2008 changed the military ranks of Venezuela, principally with regard to names, functions and commanding regulation of the armed forces. The law was sanctioned by Venezuela's National Assembly.
Present Estonian system of rank insignia is a direct descendant of various systems used in the past in the Estonian Defence Forces. Some of the grades trace their name back to the period of World Wars, for instance, the rank of aspirant literally means an officer in training in military academies or voluntaries, serving as temporary officers.
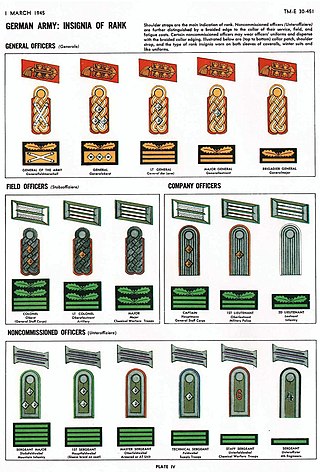
The Heer as the German army and part of the Wehrmacht inherited its uniforms and rank structure from the Reichsheer of the Weimar Republic (1921–1935). There were few alterations and adjustments made as the army grew from a limited peacetime defense force of 100,000 men to a war-fighting force of several million men.
The rank insignia of the federal armed forces of the Federal Republic of Germany indicate rank and branch of service in the German Army, German Air Force, or the German Navy.

The Czech military ranks are the military insignia used by the Army of the Czech Republic. The ranks are common for all its forces. They are displayed on the beret or a service hat, as well as on the chest of the battledress. On the display uniform, the rank insignia is worn on epaulettes and a head cover, and differs slightly in the Air Force, where it is displayed against a dark blue fabric, instead of the khaki fabric, common for the rest of the forces. For all the forces, the ranks also have the same name.
The Military ranks of the Kingdom of Italy were the military insignia used by the Italian Armed Forces when Italy was the Kingdom of Italy (1861–1946). During the World Wars, the Carabinieri, as the then-most senior corps of the Army, wore similar insignia to those used by the rest of the service.
The military ranks of the German Empire were the ranks used by the military of the German Empire. It inherited the various traditions and military ranks of its constituent states.