Related Research Articles
The Library of Congress Classification (LCC) is a system of library classification developed by the Library of Congress in the United States, which can be used for shelving books in a library. LCC is mainly used by large research and academic libraries, while most public libraries and small academic libraries used the Dewey Decimal Classification system. The classification was developed by James Hanson, with assistance from Charles Martel, in 1897, while they were working at the Library of Congress. It was designed specifically for the purposes and collection of the Library of Congress to replace the fixed location system developed by Thomas Jefferson.

Physical geography is one of the three main branches of geography. Physical geography is the branch of natural science which deals with the processes and patterns in the natural environment such as the atmosphere, hydrosphere, biosphere, and geosphere. This focus is in contrast with the branch of human geography, which focuses on the built environment, and technical geography, which focuses on using, studying, and creating tools to obtain, analyze, interpret, and understand spatial information. The three branches have significant overlap, however.

The Universal Decimal Classification (UDC) is a bibliographic and library classification representing the systematic arrangement of all branches of human knowledge organized as a coherent system in which knowledge fields are related and inter-linked. The UDC is an analytico-synthetic and faceted classification system featuring detailed vocabulary and syntax that enables powerful content indexing and information retrieval in large collections. Since 1991, the UDC has been owned and managed by the UDC Consortium, a non-profit international association of publishers with headquarters in The Hague, Netherlands.
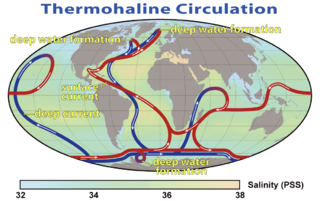
Oceanography, also known as oceanology, sea science, ocean science, and marine science, is the scientific study of the oceans. It is an Earth science, which covers a wide range of topics, including ecosystem dynamics; ocean currents, waves, and geophysical fluid dynamics; plate tectonics and seabed geology; and fluxes of various chemical substances and physical properties within the ocean and across its boundaries. These diverse topics reflect multiple disciplines that oceanographers utilize to glean further knowledge of the world ocean, including astronomy, biology, chemistry, geography, geology, hydrology, meteorology and physics. Paleoceanography studies the history of the oceans in the geologic past. An oceanographer is a person who studies many matters concerned with oceans, including marine geology, physics, chemistry, and biology.

An ecoregion is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural communities and species. The biodiversity of flora, fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation . Ecoregions are also known as "ecozones", although that term may also refer to biogeographic realms.

A bioregion is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a biogeographic realm, but larger than an ecoregion or an ecosystem, and is defined along watershed and hydrological boundaries. People are counted as an integral part of the definition of a bioregion.

An academic discipline or field of study is a branch of knowledge, taught and researched as part of higher education. A scholar's discipline is commonly defined by the university faculties and learned societies to which they belong and the academic journals in which they publish research.
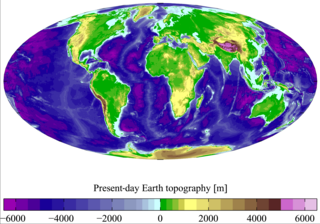
Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.
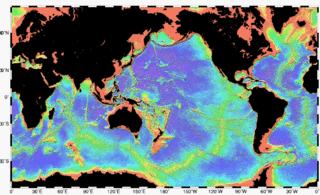
Bathymetry is the study of underwater depth of ocean floors, lake floors, or river floors. In other words, bathymetry is the underwater equivalent to hypsometry or topography. The first recorded evidence of water depth measurements are from Ancient Egypt over 3000 years ago. Bathymetric charts, are typically produced to support safety of surface or sub-surface navigation, and usually show seafloor relief or terrain as contour lines and selected depths (soundings), and typically also provide surface navigational information. Bathymetric maps may also use a Digital Terrain Model and artificial illumination techniques to illustrate the depths being portrayed. The global bathymetry is sometimes combined with topography data to yield a global relief model. Paleobathymetry is the study of past underwater depths.

The North Pacific Gyre (NPG) or North Pacific Subtropical Gyre (NPSG), located in the northern Pacific Ocean, is one of the five major oceanic gyres. This gyre covers most of the northern Pacific Ocean. It is the largest ecosystem on Earth, located between the equator and 50° N latitude, and comprising 20 million square kilometers. The gyre has a clockwise circular pattern and is formed by four prevailing ocean currents: the North Pacific Current to the north, the California Current to the east, the North Equatorial Current to the south, and the Kuroshio Current to the west. It is the site of an unusually intense collection of human-created marine debris, known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch.
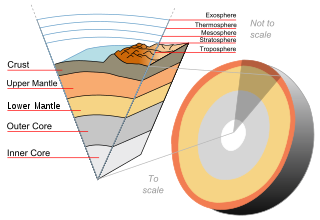
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Earth science:
Class V: Naval science is a classification used by the Library of Congress Classification system. This article outlines the subclasses of Class V.
Class T: Technology is a classification used by the Library of Congress Classification system. This page outlines the subclasses of Class T.

Earth science or geoscience includes all fields of natural science related to the planet Earth. This is a branch of science dealing with the physical, chemical, and biological complex constitutions and synergistic linkages of Earth's four spheres: the biosphere, hydrosphere/cryosphere, atmosphere, and geosphere. Earth science can be considered to be a branch of planetary science but with a much older history.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to social science:
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to natural science:

The Institute of Arctic and Alpine Research (INSTAAR) is a scientific institute that is part of the University of Colorado Boulder. Its research mission is to "[develop] scientific knowledge of physical and biogeochemical environmental processes at local, regional and global scales, and appl[y] this knowledge to improve society's awareness and understanding of natural and anthropogenic environmental change."
References
- ↑ "Library of Congress Classification Outline: CLASS G - GEOGRAPHY. ANTHROPOLOGY. RECREATION" (PDF). Library of Congress. 2019-04-29. Retrieved 2019-04-29.
- ↑ "Library of Congress Classification Full Text: Class G - Geography. Anthropology. Recreation" (PDF). Library of Congress. 2019-05-01. Retrieved 2019-05-01.