Related Research Articles
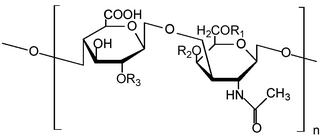
Chondroitin sulfate is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a chain of alternating sugars. It is usually found attached to proteins as part of a proteoglycan. A chondroitin chain can have over 100 individual sugars, each of which can be sulfated in variable positions and quantities. Chondroitin sulfate is an important structural component of cartilage, and provides much of its resistance to compression. Along with glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate has become a widely used dietary supplement for treatment of osteoarthritis, although large clinical trials failed to demonstrate any symptomatic benefit of chondroitin.

Dermatan sulfate is a glycosaminoglycan found mostly in skin, but also in blood vessels, heart valves, tendons, and lungs.

Arylsulfatase A is an enzyme that breaks down sulfatides, namely cerebroside 3-sulfate into cerebroside and sulfate. In humans, arylsulfatase A is encoded by the ARSA gene.
Cerebroside-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.8, arylsulfatase A, cerebroside sulfate sulfatase) is an enzyme with systematic name cerebroside-3-sulfate 3-sulfohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Steroid sulfatase (STS), or steryl-sulfatase, formerly known as arylsulfatase C, is a sulfatase enzyme involved in the metabolism of steroids. It is encoded by the STS gene.
Sulfatases EC 3.1.6.- are enzymes of the esterase class that catalyze the hydrolysis of sulfate esters. These may be found on a range of substrates, including steroids, carbohydrates and proteins. Sulfate esters may be formed from various alcohols and amines. In the latter case the resultant N-sulfates can also be termed sulfamates.

Arylsulfatase B is an enzyme associated with mucopolysaccharidosis VI.
Arylsulfatase (EC 3.1.6.1, sulfatase, nitrocatechol sulfatase, phenolsulfatase, phenylsulfatase, p-nitrophenyl sulfatase, arylsulfohydrolase, 4-methylumbelliferyl sulfatase, estrogen sulfatase) is a type of sulfatase enzyme with systematic name aryl-sulfate sulfohydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the GALNS gene.

N-acetylglucosamine-6-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.14, glucosamine (N-acetyl)-6-sulfatase, systematic name N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-6-sulfate 6-sulfohydrolase) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GNS gene. It is deficient in Sanfilippo Syndrome type IIId. It catalyses the hydrolysis of the 6-sulfate groups of the N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-sulfate units of heparan sulfate and keratan sulfate
In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfate sulfotransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a N-sulfoglucosamine sulfohydrolase (EC 3.10.1.1), otherwise known as SGSH, is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme chondro-4-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.9) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme chondro-6-sulfatase (EC 3.1.6.10) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme N-acetylgalactosamine-6-sulfatase catalyzes the chemical reaction of cleaving off the 6-sulfate groups of the N-acetyl-D-galactosamine 6-sulfate units of the macromolecule chondroitin sulfate and, similarly, of the D-galactose 6-sulfate units of the macromolecule keratan sulfate.
The enzyme N-sulfoglucosamine-3-sulfatase catalyzes cleaving off the 3-sulfate groups of the N-sulfo-D-glucosamine 3-O-sulfate units of heparin.
Glucuronylgalactosylproteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine:D-glucuronyl-(1->3)-beta-D-galactosyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Glucuronosyl-N-acetylgalactosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name UDP-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine:beta-D-glucuronosyl-(1->3)-N-acetyl-beta-D-galactosaminyl-proteoglycan 4-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase is an enzyme with systematic name 3'-phosphoadenylyl-sulfate:(dermatan)-4-O-sulfo-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine 6-O-sulfotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Dermatan 4-sulfotransferase is an enzyme with systematic name 3'-phospho-5'-adenylyl sulfate:(dermatan)-N-acetyl-D-galactosamine 4-sulfotransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
References
- ↑ Farooqui AA (October 1976). "The desulphation of hexosamine sulphates by arylsulphatase B". Experientia. 32 (10): 1242–4. doi:10.1007/BF01953071. PMID 976430. S2CID 26640171.
- ↑ Gorham SD, Cantz M (December 1978). "Arylsulphatase B, an exo-sulphatase for chondroitin 4-sulphate tetrasaccharide". Hoppe-Seyler's Zeitschrift für Physiologische Chemie. 359 (12): 1811–4. doi:10.1515/bchm2.1978.359.2.1811. PMID 738706.
- ↑ Tsuji M, Nakanishi Y, Habuchi H, Ishihara K, Suzuki S (April 1980). "The common identity of UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine 4-sulfatase, nitrocatechol sulfatase (arylsulfatase), and chondroitin 4-sulfatase". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 612 (2): 373–83. doi:10.1016/0005-2744(80)90120-5. PMID 7370276.