
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the gastrointestinal tract may include anemia, skin rashes, arthritis, inflammation of the eye, and fatigue. The skin rashes may be due to infections as well as pyoderma gangrenosum or erythema nodosum. Bowel obstruction may occur as a complication of chronic inflammation, and those with the disease are at greater risk of colon cancer and small bowel cancer.

Ulcerative colitis (UC) is one of the two types of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), with the other type being Crohn's disease. It is a long-term condition that results in inflammation and ulcers of the colon and rectum. The primary symptoms of active disease are abdominal pain and diarrhea mixed with blood (hematochezia). Weight loss, fever, and anemia may also occur. Often, symptoms come on slowly and can range from mild to severe. Symptoms typically occur intermittently with periods of no symptoms between flares. Complications may include abnormal dilation of the colon (megacolon), inflammation of the eye, joints, or liver, and colon cancer.

Defecation follows digestion, and is a necessary process by which organisms eliminate a solid, semisolid, or liquid waste material known as feces from the digestive tract via the anus or cloaca. The act has a variety of names ranging from the common, like pooping or crapping, to the technical, e.g. bowel movement, to the obscene (shitting), to the euphemistic, to the juvenile. The topic, usually avoided in polite company, can become the basis for some potty humor.

Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a "disorder of gut-brain interaction" characterized by a group of symptoms that commonly include abdominal pain, abdominal bloating and changes in the consistency of bowel movements. These symptoms may occur over a long time, sometimes for years. IBS can negatively affect quality of life and may result in missed school or work or reduced productivity at work. Disorders such as anxiety, major depression, and chronic fatigue syndrome are common among people with IBS.

Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of inflammatory conditions of the colon and small intestine, with Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis (UC) being the principal types. Crohn's disease affects the small intestine and large intestine, as well as the mouth, esophagus, stomach and the anus, whereas UC primarily affects the colon and the rectum.

Colitis is swelling or inflammation of the large intestine (colon). Colitis may be acute and self-limited or long-term. It broadly fits into the category of digestive diseases.
In medicine, the ileal pouch–anal anastomosis (IPAA), also known as restorative proctocolectomy (RPC), ileal-anal reservoir (IAR), an ileo-anal pouch, ileal-anal pullthrough, or sometimes referred to as a J-pouch, S-pouch, W-pouch, or a pelvic pouch, is an anastomosis of a reservoir pouch made from ileum to the anus, bypassing the former site of the colon in cases where the colon and rectum have been removed. The pouch retains and restores functionality of the anus, with stools passed under voluntary control of the person, preventing fecal incontinence and serving as an alternative to a total proctocolectomy with ileostomy.
Proctitis is an inflammation of the anus and the lining of the rectum, affecting only the last 6 inches of the rectum.
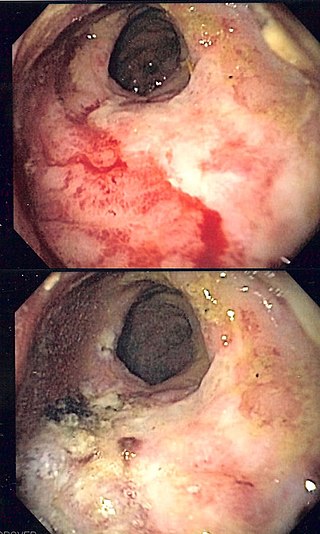
Radiation proctitis or radiation proctopathy is a condition characterized by damage to the rectum after exposure to x-rays or other ionizing radiation as a part of radiation therapy. Radiation proctopathy may occur as acute inflammation called "acute radiation proctitis" or with chronic changes characterized by radiation associated vascular ectasiae (RAVE) and chronic radiation proctopathy. Radiation proctitis most commonly occurs after pelvic radiation treatment for cancers such as cervical cancer, prostate cancer, bladder cancer, and rectal cancer. RAVE and chronic radiation proctopathy involves the lower intestine, primarily the sigmoid colon and the rectum, and was previously called chronic radiation proctitis, pelvic radiation disease and radiation enteropathy.

Ischemic colitis is a medical condition in which inflammation and injury of the large intestine result from inadequate blood supply. Although uncommon in the general population, ischemic colitis occurs with greater frequency in the elderly, and is the most common form of bowel ischemia. Causes of the reduced blood flow can include changes in the systemic circulation or local factors such as constriction of blood vessels or a blood clot. In most cases, no specific cause can be identified.

In the anatomy of humans and homologous primates, the descending colon is the part of the colon extending from the left colic flexure to the level of the iliac crest. The function of the descending colon in the digestive system is to store the remains of digested food that will be emptied into the rectum.
Proctocolectomy is the surgical removal of the entire large colon and rectum from the human body, leaving the patients small intestine disconnected from their anus. It is a major surgery that is performed by colon and rectal surgeons, however some portions of the surgery, specifically the colectomy may be performed by general surgeons. It was first performed in 1978 and since that time, medical advancements have led to the surgery being less invasive with great improvements in patient outcomes. The procedure is most commonly indicated for severe forms of inflammatory bowel disease such as ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. It is also the treatment of choice for patients with Familial Adenomatous Polyposis.
Stercoral ulcer is an ulcer of the colon due to pressure and irritation resulting from severe, prolonged constipation due to a large bowel obstruction, damage to the autonomic nervous system, or stercoral colitis. It is most commonly located in the sigmoid colon and rectum. Prolonged constipation leads to production of fecaliths, leading to possible progression into a fecaloma. These hard lumps irritate the rectum and lead to the formation of these ulcers. It results in fresh bleeding per rectum. These ulcers may be seen on imaging, such as a CT scan but are more commonly identified using endoscopy, usually a colonoscopy. Treatment modalities can include both surgical and non-surgical techniques.

Pancolitis, in its most general sense, refers to inflammation of the entire colon. This can be caused by a variety of things. Pancolitis or universal colitis is frequently used in a more specific fashion to denote a very severe form of ulcerative colitis. This form of ulcerative colitis is spread throughout the entire large intestine including the right colon, the left colon, the transverse colon, descending colon, and the rectum. A diagnosis can be made using a number of techniques but the most accurate method is direct visualization via a colonoscopy. Symptoms are similar to those of ulcerative colitis but more severe and affect the entire large intestine. Patients with ulcerative colitis generally exhibit symptoms including rectal bleeding as a result of ulcers, pain in the abdominal region, inflammation in varying degrees, and diarrhea. Pancolitis patients exhibit these symptoms and may also experience fatigue, fever, and night sweats. Due to the loss of function in the large intestine patients may lose large amounts of weight from being unable to procure nutrients from food. In other cases the blood loss from ulcers can result in anemia which can be treated with iron supplements. Additionally, due to the chronic nature of most cases of pancolitis, patients have a higher chance of developing colon cancer.
Rectal discharge is intermittent or continuous expression of liquid from the anus. Normal rectal mucus is needed for proper excretion of waste. Otherwise, this is closely related to types of fecal incontinence but the term rectal discharge does not necessarily imply degrees of incontinence. Types of fecal incontinence that produce a liquid leakage could be thought of as a type of rectal discharge.

Cuffitis is inflammation at the anal transition zone or "cuff" created as a result of ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA). It is considered a variant form of ulcerative colitis that occurs in the rectal cuff. Cuffitis is a common complication of IPAA, particularly when a stapled anastomosis without mucosectomy procedure has been used.

Colonic ulcer can occur at any age, in children however they are rare. Most common symptoms are abdominal pain and hematochezia.
Checkpoint inhibitor induced colitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the colon (colitis), which is caused by cancer immunotherapy. Symptoms typically consist of diarrhea, abdominal pain and rectal bleeding. Less commonly, nausea and vomiting may occur, which may suggest the present of gastroenteritis. The severity of diarrhea and colitis are graded based on the frequency of bowel movements and symptoms of colitis, respectively.

Segmental colitis associated with diverticulosis (SCAD) is a condition characterized by localized inflammation in the colon, which spares the rectum and is associated with multiple sac-like protrusions or pouches in the wall of the colon (diverticulosis). Unlike diverticulitis, SCAD involves inflammation of the colon between diverticula, while sparing the diverticular orifices. SCAD may lead to abdominal pain, especially in the left lower quadrant, intermittent rectal bleeding and chronic diarrhea.
Ralph John Nicholls, FRCS (Eng), EBSQ is a retired British colorectal surgeon, Emeritus Consultant Surgeon at St Mark’s Hospital London and Professor of Colorectal Surgery, Imperial College London.












