Chemotaxis is the movement of an organism or entity in response to a chemical stimulus. Somatic cells, bacteria, and other single-cell or multicellular organisms direct their movements according to certain chemicals in their environment. This is important for bacteria to find food by swimming toward the highest concentration of food molecules, or to flee from poisons. In multicellular organisms, chemotaxis is critical to early development and development as well as in normal function and health. In addition, it has been recognized that mechanisms that allow chemotaxis in animals can be subverted during cancer metastasis. The aberrant chemotaxis of leukocytes and lymphocytes also contribute to inflammatory diseases such as atherosclerosis, asthma, and arthritis. Sub-cellular components, such as the polarity patch generated by mating yeast, may also display chemotactic behavior.

Signal transduction is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events. Most commonly, protein phosphorylation is catalyzed by protein kinases, ultimately resulting in a cellular response. Proteins responsible for detecting stimuli are generally termed receptors, although in some cases the term sensor is used. The changes elicited by ligand binding in a receptor give rise to a biochemical cascade, which is a chain of biochemical events known as a signaling pathway.
In biology, cell signaling is the process by which a cell interacts with itself, other cells and the environment. Cell signaling is a fundamental property of all cellular life in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Pectinesterase (EC 3.1.1.11; systematic name pectin pectylhydrolase) is a ubiquitous cell-wall-associated enzyme that presents several isoforms that facilitate plant cell wall modification and subsequent breakdown. It catalyzes the following reaction:
Demethylases are enzymes that remove methyl (CH3) groups from nucleic acids, proteins (particularly histones), and other molecules. Demethylases are important epigenetic proteins, as they are responsible for transcriptional regulation of the genome by controlling the methylation of DNA and histones, and by extension, the chromatin state at specific gene loci.

In enzymology, a protein-glutamate O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, glutamate racemase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme lysophospholipase (EC 3.1.1.5) catalyzes the reaction

In the field of molecular biology, a two-component regulatory system serves as a basic stimulus-response coupling mechanism to allow organisms to sense and respond to changes in many different environmental conditions. Two-component systems typically consist of a membrane-bound histidine kinase that senses a specific environmental stimulus and a corresponding response regulator that mediates the cellular response, mostly through differential expression of target genes. Although two-component signaling systems are found in all domains of life, they are most common by far in bacteria, particularly in Gram-negative and cyanobacteria; both histidine kinases and response regulators are among the largest gene families in bacteria. They are much less common in archaea and eukaryotes; although they do appear in yeasts, filamentous fungi, and slime molds, and are common in plants, two-component systems have been described as "conspicuously absent" from animals.

Histidine kinases (HK) are multifunctional, and in non-animal kingdoms, typically transmembrane, proteins of the transferase class of enzymes that play a role in signal transduction across the cellular membrane. The vast majority of HKs are homodimers that exhibit autokinase, phosphotransfer, and phosphatase activity. HKs can act as cellular receptors for signaling molecules in a way analogous to tyrosine kinase receptors (RTK). Multifunctional receptor molecules such as HKs and RTKs typically have portions on the outside of the cell that bind to hormone- or growth factor-like molecules, portions that span the cell membrane, and portions within the cell that contain the enzymatic activity. In addition to kinase activity, the intracellular domains typically have regions that bind to a secondary effector molecule or complex of molecules that further propagate signal transduction within the cell. Distinct from other classes of protein kinases, HKs are usually parts of a two-component signal transduction mechanisms in which HK transfers a phosphate group from ATP to a histidine residue within the kinase, and then to an aspartate residue on the receiver domain of a response regulator protein. More recently, the widespread existence of protein histidine phosphorylation distinct from that of two-component histidine kinases has been recognised in human cells. In marked contrast to Ser, Thr and Tyr phosphorylation, the analysis of phosphorylated Histidine using standard biochemical and mass spectrometric approaches is much more challenging, and special procedures and separation techniques are required for their preservation alongside classical Ser, Thr and Tyr phosphorylation on proteins isolated from human cells.

Serine/threonine-protein kinase D1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKD1 gene.

Protein kinase C eta type is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCH gene.

Ras GTPase-activating protein-binding protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the G3BP1 gene.

Protein phosphorylation is a reversible post-translational modification of proteins in which an amino acid residue is phosphorylated by a protein kinase by the addition of a covalently bound phosphate group. Phosphorylation alters the structural conformation of a protein, causing it to become activated, deactivated, or otherwise modifying its function. Approximately 13,000 human proteins have sites that are phosphorylated.
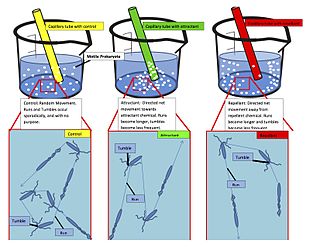
The methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins are a family of transmembrane receptors that mediate chemotactic response in certain enteric bacteria, such as Salmonella enterica enterica and Escherichia coli. These methyl-accepting chemotaxis receptors are one of the first components in the sensory excitation and adaptation responses in bacteria, which act to alter swimming behaviour upon detection of specific chemicals. Use of the MCP allows bacteria to detect concentrations of molecules in the extracellular matrix so that the bacteria may smooth swim or tumble accordingly. If the bacterium detects rising levels of attractants (nutrients) or declining levels of repellents (toxins), the bacterium will continue swimming forward, or smooth swimming. If the bacterium detects declining levels of attractants or rising levels of repellents, the bacterium will tumble and re-orient itself in a new direction. In this manner, a bacterium may swim towards nutrients and away from toxins

A response regulator is a protein that mediates a cell's response to changes in its environment as part of a two-component regulatory system. Response regulators are coupled to specific histidine kinases which serve as sensors of environmental changes. Response regulators and histidine kinases are two of the most common gene families in bacteria, where two-component signaling systems are very common; they also appear much more rarely in the genomes of some archaea, yeasts, filamentous fungi, and plants. Two-component systems are not found in metazoans.
In molecular biology, the HAMP domain is an approximately 50-amino acid alpha-helical region that forms a dimeric, four-helical coiled coil. It is found in bacterial sensor and chemotaxis proteins and in eukaryotic histidine kinases. The bacterial proteins are usually integral membrane proteins and part of a two-component signal transduction pathway. One or several copies of the HAMP domain can be found in association with other domains, such as the histidine kinase domain, the bacterial chemotaxis sensory transducer domain, the PAS repeat, the EAL domain, the GGDEF domain, the protein phosphatase 2C-like domain, the guanylate cyclase domain, or the response regulatory domain. In its most common setting, the HAMP domain transmits conformational changes in periplasmic ligand-binding domains to cytoplasmic signalling kinase and methyl-acceptor domains and thus regulates the phosphorylation or methylation activity of homodimeric receptors.

Tyrosine phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate (PO43−) group to the amino acid tyrosine on a protein. It is one of the main types of protein phosphorylation. This transfer is made possible through enzymes called tyrosine kinases. Tyrosine phosphorylation is a key step in signal transduction and the regulation of enzymatic activity.

Histidine phosphotransfer domains and histidine phosphotransferases are protein domains involved in the "phosphorelay" form of two-component regulatory systems. These proteins possess a phosphorylatable histidine residue and are responsible for transferring a phosphoryl group from an aspartate residue on an intermediate "receiver" domain, typically part of a hybrid histidine kinase, to an aspartate on a final response regulator.
Michael Eisenbach is an Israeli biochemist who specializes in the navigation mechanisms of bacterial and sperm cells. He is a professor emeritus at the Weizmann Institute of Science, Department of Biomolecular Sciences, Rehovot, Israel. He discovered that sperm cells (spermatozoa) of mammals are actively guided to the egg. This opened the research field of mammalian sperm navigation. He demonstrated that the active navigation entails chemotaxis and thermotaxis. He made seminal contributions to the understanding of these two processes at the molecular, physiological and behavioural levels, as well as contributing to our understanding of the molecular mechanism of bacterial chemotaxis.















