Traditional religion in Serbia
| Part of a series on |
| Christianity |
|---|
 |
|
| Part of a series on |
| Serbs |
|---|
 |
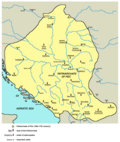
Eastern Orthodoxy is the primary Christian denomination in Serbia, representing 81% of the population as of 2022, [1] followed traditionally by the majority of Serbs, and also Romanians and Vlachs, Montenegrins, Macedonians and Bulgarians living in Serbia. The dominant Eastern Orthodox church in Serbia is the Serbian Orthodox Church. Also, the Romanian Orthodox Church has its own Diocese of Dacia Felix that operates among Orthodox Romanians in Serbian Banat and the Timok Valley.