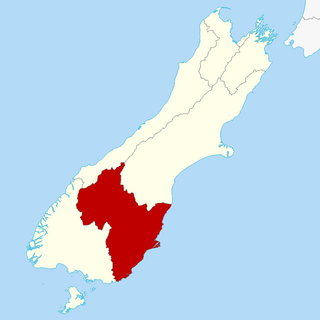
Canterbury is a region of New Zealand, located in the central-eastern South Island. The region covers an area of 44,503.88 square kilometres (17,183.04 sq mi), making it the largest region in the country by area. It is home to a population of 666,300.

The South Island is the largest of the three major islands of New Zealand in surface area, the other being the smaller but more populous North Island and sparsely populated Stewart Island. It is bordered to the north by Cook Strait, to the west by the Tasman Sea, to the south by the Foveaux Strait and Southern Ocean, and to the east by the Pacific Ocean. The South Island covers 150,437 square kilometres (58,084 sq mi), making it the world's 12th-largest island, constituting 56% of New Zealand's land area. At low altitudes, it has an oceanic climate.
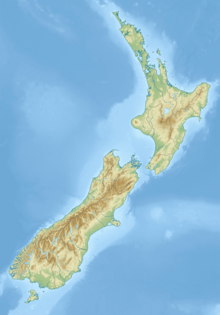
Otago is a region of New Zealand located in the southern half of the South Island administered by the Otago Regional Council. It has an area of approximately 32,000 square kilometres (12,000 sq mi), making it the country's second largest local government region. Its population was 254,600 in June 2023.

The Southern Alps are a mountain range extending along much of the length of New Zealand's South Island, reaching its greatest elevations near the range's western side. The name "Southern Alps" generally refers to the entire range, although separate names are given to many of the smaller ranges that form part of it.

The provinces of the Colony of New Zealand existed as a form of sub-national government. Initially established in 1846 when New Zealand was a Crown colony without responsible government, two provinces were first created. Each province had its own legislative council and governor. With the passing of the New Zealand Constitution Act 1852 the provinces were recreated around the six planned settlements or "colonies". By 1873 the number of provinces had increased to nine, but they had become less isolated from each other and demands for centralised government arose. In 1875 the New Zealand Parliament decided to abolish the provincial governments, and they came to an end in November 1876. They were superseded by counties, which were later replaced by territorial authorities.

North Otago is an area in New Zealand covers the area of the Otago region between Shag Point and the Waitaki River, and extends inland to the west as far as the village of Omarama.

Haast Pass / Tioripatea is a mountain pass in the Southern Alps of the South Island of New Zealand. Māori used the pass in pre-European times.

Waitaki District is a territorial authority district that is located in the Canterbury and Otago regions of the South Island of New Zealand. It straddles the traditional border between the two regions, the Waitaki River, and its seat is Oamaru.

Lake Ōhau is a lake in the Mackenzie Basin in the South Island of New Zealand. The Hopkins and Dobson rivers fed into the northern end of Lake Ōhau. These rivers have their headwaters in the Southern Alps. The lake's outflow is the Ōhau River, which travels from the southeast corner of Lake Ōhau and feeds into the Waitaki River hydroelectric project. The Barrier range dominate the western side of Lake Ōhau, while the Ben Ohau range dominates the eastern side of Lake Ōhau. At the northern end of the lake, in between the Hopkins and Dobson rivers, lies the Naumann Range of mountains.

The Hopkins River is in the central South Island of New Zealand. It flows south for 45 kilometres (28 mi) from the Southern Alps / Kā Tiritiri o te Moana into the northern end of Lake Ōhau in the Mackenzie Country.

The Dobson River is a river in the South Island of New Zealand. It flows south between the Neumann and Ohau ranges for 45 kilometres (28 mi) from its source to the east of Mount Hopkins, in the Southern Alps, before joining with the Hopkins River, close to the latter's entry into the northern end of Lake Ōhau in the Mackenzie Country. The river flows over wide shingle beds, and has no rapids of interest to whitewater enthusiasts. It was named by Julius von Haast in the 1860s for his father-in-law, Edward Dobson, who was the Canterbury Provincial Engineer. The Māori name, also given as Otao in some works, means "driftwood," and has also been applied to the Hopkins River into which the Dobson/Ōtaao flows.
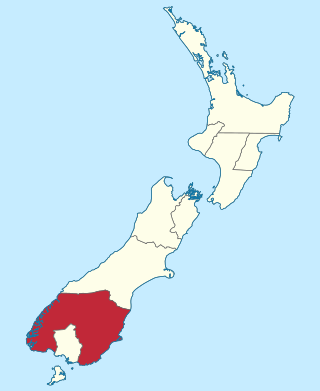
The Otago Province was a province of New Zealand until the abolition of provincial government in 1876. The capital of the province was Dunedin. Southland Province split from Otago in 1861, but became part of the province again in 1870.

Mount Adams is a mountain in the West Coast region of New Zealand's South Island. The summit is roughly 19 km south of Harihari and reaches 2,208 metres (7,244 ft) in height.
The South Canterbury Rugby Football Union (SCRFU) is a rugby province based in the central South Island city of Timaru, New Zealand. The South Canterbury team play at Fraser Park located in Timaru.

South Canterbury is the area of the Canterbury Region of the South Island of New Zealand bounded by the Rangitata River in the north and the Waitaki River to the south. The Pacific Ocean and ridge of the Southern Alps form natural boundaries to the east and west respectively. Though the exact boundaries of the region have never been formalised, the term is used for a variety of government agencies and other entities. It is one of four traditional sub-regions of Canterbury, along with Mid Canterbury, North Canterbury, and Christchurch city.

Otago is a rural residential locality in the local government areas (LGA) of Brighton and Clarence in the Hobart LGA region of Tasmania. The locality is about 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) south of the town of Brighton. The 2016 census recorded a population of 554 for the state suburb of Otago. It is a suburb of Hobart, located on the shores of Otago Bay.
Mount Misery or Misery Mountain may refer to:

The Mathias River is a river of the Canterbury region of New Zealand's South Island. It flows from its origins in three rivers in the Southern Alps. Of these, the North Mathias River is the longest, flowing predominantly southwards from its source northeast of Mount Williams. After 18 kilometres (11 mi) its waters combine with those of the West Mathias River, which flows predominantly southwest for 13 kilometres (8 mi) from its sources 10 kilometres (6 mi) west of Mount Williams. The South Mathias River, a tributary of the West Mathias River, is a 6-kilometre (4 mi) long easterly-flowing river which meets the West Mathias 5 kilometres (3 mi) from its confluence with the North Mathias.
Big Bay, also known as Awarua Bay, is a deep indentation in the southwestern coast of New Zealand's South Island, 40 kilometres north of Milford Sound and immediately to the north of Martins Bay. The bay is eight kilometres in width, and extends eight kilometres into the South Island, making an almost square indentation in the island's coastline. Its northern end is Awarua Point. Immediately beyond Long Reef, the rocky point at the southern end, is the mouth of the Hollyford River and Martins Bay. Big Bay has a sandy beach named Three Mile Beach. The Awarua River enters the bay at the northern end of the beach.

The South Island, with an area of 150,437 km2 (58,084 sq mi), is the largest landmass of New Zealand; it contains about one-quarter of the New Zealand population and is the world's 12th-largest island. It is divided along its length by the Southern Alps, the highest peak of which is Aoraki / Mount Cook at 3,724 metres (12,218 ft), making it 9th-highest island, with the high Kaikōura Ranges to the northeast. There are eighteen peaks of more than 3,000 metres (9,800 ft) in the South Island. The east side of the island is home to the Canterbury Plains while the West Coast is famous for its rough coastlines such as Fiordland, a very high proportion of native bush, and Fox and Franz Josef Glaciers. The dramatic landscape of the South Island has made it a popular location for the production of several films, including The Lord of the Rings trilogy and The Chronicles of Narnia: The Lion, the Witch and the Wardrobe. It lies at similar latitudes to Tasmania, and parts of Patagonia in South America.