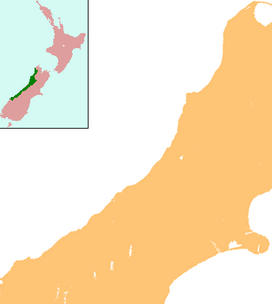
Aoraki / Mount Cook is the highest mountain in New Zealand. Its height, as of 2014, is listed as 3,724 metres. It is situated in the Southern Alps, the mountain range that runs the length of the South Island. A popular tourist destination, it is also a favourite challenge for mountain climbers. Aoraki / Mount Cook consists of three summits: from south to north, the Low Peak, the Middle Peak and the High Peak. The summits lie slightly south and east of the main divide of the Southern Alps, with the Tasman Glacier to the east and the Hooker Glacier to the southwest. Mount Cook is ranked 10th in the world by topographic isolation.

Mount Everest, known locally as Sagarmatha or Qomolangma, is Earth's highest mountain above sea level, located in the Mahalangur Himal sub-range of the Himalayas. The China–Nepal border runs across its summit point. Its elevation of 8,848.86 m was most recently established in 2020 by the Chinese and Nepali authorities.

Mount Kosciuszko is mainland Australia's highest mountain, at 2,228 metres (7,310 ft) above sea level. It is located on the Main Range of the Snowy Mountains in Kosciuszko National Park, part of the Australian Alps National Parks and Reserves, in New South Wales, Australia, and is located west of Crackenback and close to Jindabyne, near the border with Victoria. Mount Kosciuszko is ranked 35th by topographic isolation.

Denali is the highest mountain peak in North America, with a summit elevation of 20,310 feet (6,190 m) above sea level. It is the tallest mountain in the world from base-to-peak on land, measuring 18,000 ft (5,500 m), with a topographic prominence of 20,194 feet (6,155 m) and a topographic isolation of 4,621.1 miles (7,436.9 km), Denali is the third most prominent and third-most isolated peak on Earth, after Mount Everest and Aconcagua. Located in the Alaska Range in the interior of the U.S. state of Alaska, Denali is the centerpiece of Denali National Park and Preserve.

Vinson Massif is a large mountain massif in Antarctica that is 21 km (13 mi) long and 13 km (8 mi) wide and lies within the Sentinel Range of the Ellsworth Mountains. It overlooks the Ronne Ice Shelf near the base of the Antarctic Peninsula. The massif is located about 1,200 kilometres (750 mi) from the South Pole. Vinson Massif was discovered in January 1958 by U.S. Navy aircraft. In 1961, the Vinson Massif was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN), after Carl G. Vinson, United States congressman from the state of Georgia, for his support for Antarctic exploration. On November 1, 2006, US-ACAN declared Mount Vinson and Vinson Massif to be separate entities. Vinson Massif lies within the unrecognised Chilean claim under the Antarctic Treaty System.

Lhotse is the fourth-highest mountain on Earth, after Mount Everest, K2, and Kangchenjunga. At an elevation of 8,516 metres (27,940 ft) above sea level, the main summit is on the border between Tibet Autonomous Region of China and the Khumbu region of Nepal.

The Matterhorn is a mountain of the Alps, straddling the main watershed and border between Italy and Switzerland. It is a large, near-symmetric pyramidal peak in the extended Monte Rosa area of the Pennine Alps, whose summit is 4,478 metres (14,692 ft) above sea level, making it one of the highest summits in the Alps and Europe. The four steep faces, rising above the surrounding glaciers, face the four compass points and are split by the Hörnli, Furggen, Leone/Lion, and Zmutt ridges. The mountain overlooks the Swiss town of Zermatt, in the canton of Valais, to the northeast; and the Italian town of Breuil-Cervinia in the Aosta Valley to the south. Just east of the Matterhorn is Theodul Pass, the main passage between the two valleys on its north and south sides, which has been a trade route since the Roman Era.

Cho Oyu is the sixth-highest mountain in the world at 8,188 metres (26,864 ft) above sea level. Cho Oyu means "Turquoise Goddess" in Tibetan. The mountain is the westernmost major peak of the Khumbu sub-section of the Mahalangur Himalaya 20 km west of Mount Everest. The mountain stands on the China–Nepal border, between the Tibet Autonomous Region and Koshi Province.

Kamet is the second-highest mountain in the Garhwal region of Uttarakhand, India, after Nanda Devi. It is the 29th highest mountain in the world. It lies in the Chamoli District of Uttarakhand. Its appearance resembles a giant pyramid topped by a flat summit area with two peaks.

Mount Aspiring / Tititea is New Zealand's 23rd-highest mountain. The peak's altitude of 3,033 metres (9,951 ft) makes it the country's highest outside the Aoraki / Mount Cook region.

Diadem Peak is a peak located in the Sunwapta River Valley of Jasper National Park, Canada. Diadem Peak is essentially the high point of a ridge leading down from the slightly higher Mount Woolley. This peak was the first 11,000er north of the Columbia Icefield to be climbed and one of the few peaks in the Canadian Rockies to be climbed before 1900.

Changtse is a mountain situated between the Main Rongbuk and East Rongbuk Glaciers in Tibet Autonomous Region, China, immediately north of Mount Everest. It is connected to Mount Everest via the North Col.

Toubkal, also Jbel Toubkal or Jebel Toubkal, is a mountain in southwestern Morocco, located in the Toubkal National Park. At 4,167 m (13,671 ft), it is the highest peak in Morocco, the Atlas Mountains, North Africa and the Arab world. Located 63 km (39 mi) south of the city of Marrakesh, and visible from it, Toubkal is an ultra prominent peak, the highest for over 2,000 km (1,200 mi). Toubkal is ranked 27th by topographic isolation.
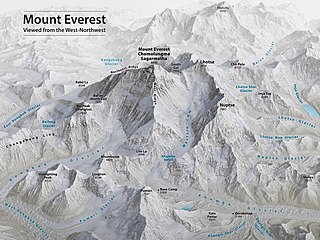
Mount Everest is the world's highest mountain, with a peak at 8,849 metres (29,031.7 ft) above sea level. It is situated in the Himalayan range of Solukhumbu district, Nepal.

Emmeline Freda Du Faur was an Australian mountaineer, credited as the first woman to climb New Zealand's tallest mountain, Aoraki / Mount Cook. Du Faur was a leading amateur climber of her day. She was the first female high mountaineer known to be active in New Zealand, although she never lived there.

Mount Woolsey is located in the Bighorn Mountains in the U.S. state of Wyoming. The peak is the third highest in the range after Cloud Peak, which is only 1.3 miles (2.1 km) to the south, and the summit is located in the Cloud Peak Wilderness of Bighorn National Forest. Black Tooth Mountain, the second highest mountain in the Bighorns, is an adjacent summit only .20 mi (0.32 km) to the northwest. Mount Woolsey is on a knife-like ridge known as an arête and is connected to both Black Tooth Mountain and Cloud Peak by this ridge. Along the arête is another mountain peak known as The Innominate. A small glacier lies below the arête to the southeast of Mount Woolsey.
The 1951 British Mount Everest reconnaissance expedition ran between 27 August 1951 and 21 November 1951 with Eric Shipton as leader.

Hochstetter Dome is a 2,827-metre-elevation (9,275-foot) mountain in New Zealand.

Mount Green is a 2,837-metre-elevation (9,308-foot) mountain in New Zealand.

Haeckel Peak is a 2,965-metre-elevation (9,728-foot) mountain in the Canterbury Region of New Zealand.