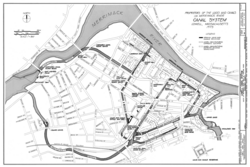

Completed in 1796, the Pawtucket Canal was originally built as a transportation canal to circumvent the Pawtucket Falls of the Merrimack River in East Chelmsford, Massachusetts. In the early 1820s it became a major component of the Lowell power canal system. with the founding of the textile industry at what became Lowell. [1]

Pawtucket Falls is a waterfall on the Merrimack River at Lowell, Massachusetts. The waterfall and rapids below it drop a total of 32 feet in a little under a mile, and was an important fishing ground for the Pennacook Indians in pre-colonial times.

The Merrimack River is a 117-mile-long (188 km) river in the northeastern United States. It rises at the confluence of the Pemigewasset and Winnipesaukee rivers in Franklin, New Hampshire, flows southward into Massachusetts, and then flows northeast until it empties into the Gulf of Maine at Newburyport. From Pawtucket Falls in Lowell, Massachusetts, onward, the Massachusetts–New Hampshire border is roughly calculated as the line three miles north of the river.

Chelmsford is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts in the United States. As of the 2010 United States Census, the town's population was 33,802. Only 48.4% are male and the median age of residents in Chelmsford is 39.2 years old. It is located 24 miles (39 km) northwest of Boston and, bordering on the city of Lowell, is part of the Greater Lowell metropolitan area. Besides Lowell on its northeast, Chelmsford is surrounded by four towns: Tyngsborough to the north, Billerica to the southeast, Carlisle to the south, and Westford to the west. Chelmsford is bordered by two sizable rivers: the Merrimack River to the north, and the Concord River to the east.
Contents
The Pawtucket Falls are a mile long series of falls and rapids over which the Merrimack River drops 32 feet. The falls hampered the shipment of inland goods, mostly lumber, to the mouth of the Merrimack and Newburyport, Massachusetts. Newburyport was then one of the largest shipbuilding centers in New England, and a steady supply of wood from New Hampshire was critical to its industry.

Lumber or timber is a type of wood that has been processed into beams and planks, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for structural purposes but has many other uses as well.

Newburyport is a small coastal, scenic, and historic city in Essex County, Massachusetts, United States, 35 miles (56 km) northeast of Boston. The population was 17,416 at the 2010 census. A historic seaport with a vibrant tourism industry, Newburyport includes part of Plum Island. The mooring, winter storage and maintenance of recreational boats, motor and sail, still contribute a large part of the city's income. A Coast Guard station oversees boating activity, especially in the sometimes dangerous tidal currents of the Merrimack River.

Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to before recorded history.
The original canal was built by wealthy Boston merchants who formed a limited liability corporation called the Proprietors of Locks and Canals, one of the first of its kind in the United States. However, within a decade of its construction the Middlesex Canal was completed, connecting the Merrimack directly with Boston, Massachusetts. Bringing goods directly to Boston was more advantageous for merchants, and the Pawtucket Canal fell out of favor for inland transport.

Limited liability is where a person's financial liability is limited to a fixed sum, most commonly the value of a person's investment in a company or partnership. If a company with limited liability is sued, then the claimants are suing the company, not its owners or investors. A shareholder in a limited company is not personally liable for any of the debts of the company, other than for the amount already invested in the company and for any unpaid amount on the shares in the company, if any. The same is true for the members of a limited liability partnership and the limited partners in a limited partnership. By contrast, sole proprietors and partners in general partnerships are each liable for all the debts of the business.
The Proprietors of Locks and Canals on the Merrimack River is a limited liability corporation founded on June 27, 1792, making it one of the oldest corporations in the United States. Its named incorporators were Dudley Atkins Tyng, William Coombs, Joseph Tyler, Nicholas Johnson, and Joshua Carter.

The United States of America (USA), commonly known as the United States or America, is a country comprising 50 states, a federal district, five major self-governing territories, and various possessions. At 3.8 million square miles, the United States is the world's third or fourth largest country by total area and is slightly smaller than the entire continent of Europe's 3.9 million square miles. With a population of over 327 million people, the U.S. is the third most populous country. The capital is Washington, D.C., and the largest city by population is New York City. Forty-eight states and the capital's federal district are contiguous in North America between Canada and Mexico. The State of Alaska is in the northwest corner of North America, bordered by Canada to the east and across the Bering Strait from Russia to the west. The State of Hawaii is an archipelago in the mid-Pacific Ocean. The U.S. territories are scattered about the Pacific Ocean and the Caribbean Sea, stretching across nine official time zones. The extremely diverse geography, climate, and wildlife of the United States make it one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries.
The investors in the Boston Manufacturing Company having successfully built upon Francis Cabot Lowell and Paul Moody's work in building a successfully integrated cotton mill at Waltham, Massachusetts on the Charles River were looking for a site that offered more waterpower and the Pawtucket Falls offered what they needed. In 1821 they bought the Proprietors of Locks and Canals and with it the water rights of the Merrimack River upstream from the Pawtucket Falls. The Pawtucket Canal was deepened to become a power canal, and the first of 5.6 miles of canals in the soon to be named City of Lowell, Massachusetts. The first canal built off the Pawtucket Canal was the Merrimack Canal, which powered the Merrimack Manufacturing Company, thus starting the Lowell experiment, and the first planned industrial city in the United States.

Paul Moody was a U.S. textile machinery inventor born in Byfield, Massachusetts. He is often credited with developing and perfecting the first power loom in America, which launched the first successful integrated cotton mill at Waltham, Massachusetts in 1814, under the leadership of Francis Cabot Lowell and his associates.

Waltham is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States, and was an early center for the labor movement as well as a major contributor to the American Industrial Revolution. The original home of the Boston Manufacturing Company, the city was a prototype for 19th century industrial city planning, spawning what became known as the Waltham-Lowell system of labor and production. The city is now a center for research and higher education, home to Brandeis University and Bentley University. The population was 60,636 at the census in 2010.

The Charles River is an 80-mile-long (129 km) long river in eastern Massachusetts. From its source in Hopkinton the river flows in a northeasterly direction, traveling through 23 cities and towns before reaching the Atlantic Ocean at Boston. The Native-American name for the Charles River was Quinobequin, meaning "meandering".
The canal is operated today by Boott Hydro, LLC.















