Poplar River is a tributary of the Missouri River, approximately 167 miles (269 km) long in Saskatchewan in Canada and Montana in the United States. The river is composed of three main forks – West, Middle, and East Poplar Rivers – that have their source in the Wood Mountain Hills of the Missouri Coteau. Along the river's Middle Fork in Saskatchewan, there is a coal-fired power station. There are also dams built along the river's forks.

Rosetown is a town in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan, at the junction of provincial Highway 7 and Highway 4, approximately 115 kilometres southwest of Saskatoon. The town's motto, "The Heart of the Wheat Belt" reflects its history of being a farming community. It is within the Rural Municipality of St. Andrews No. 287.

Grenfell is a town in Southern Saskatchewan, Canada. It is situated at the junction of Highway 47 and the Trans-Canada Highway 1 130 kilometres (80 mi) east of Regina, the provincial capital. It is 24 kilometres (15 mi) south of the Qu'Appelle Valley where Crooked Lake Provincial Park and Bird's Point Resort are popular beach destinations and are accessed by Highway 47.

Qu'Appelle is a town in Saskatchewan, located on Highway 35 approximately 50 kilometres (31 mi) east of the provincial capital of Regina.
Highway 1 is the Saskatchewan section of the Trans-Canada Highway mainland route. The total distance of the Trans-Canada Highway in Saskatchewan is 654 kilometres (406 mi). The highway traverses Saskatchewan from the western border with Alberta, from Highway 1, to the Manitoba border where it continues as PTH 1. The Trans-Canada Highway Act was passed on December 10, 1949. The Saskatchewan segment was completed August 21, 1957, and completely twinned on November 6, 2008. The speed limit along the majority of the route is 110 kilometres per hour (70 mph) with urban area thoroughfares slowing to a speed of 80–100 kilometres per hour (50–62 mph). Portions of the highway—the section through Swift Current, an 8-kilometre (5 mi) section east of Moose Jaw, and a 44-kilometre (27 mi) section between the West Regina Bypass and Balgonie—are controlled-access. Highway 1 serves as a major east–west transport route for commercial traffic. It is the main link between southern Saskatchewan's largest cities, and also serves as the province's main link to the neighbouring provinces of Alberta and Manitoba.
Fife Lake is a hamlet located between Coronach and Rockglen within Rural Municipality of Poplar Valley No. 12 in south-central Saskatchewan, Canada near the border with the United States. Approximately 40 people inhabited the village of Fife Lake in 2006. It is about 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) east of Rockin Beach Park and Fife Lake.

Coronach is a community in southern Saskatchewan, Canada near the Canada–US border. It was founded in 1926 by the Canadian Pacific Railway and named after Coronach, the horse who had just won The Derby in England that year. Coronach was officially incorporated in 1928.

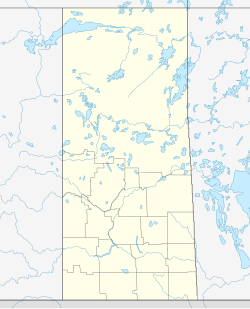
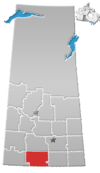
Division No. 3 is one of eighteen census divisions in the province of Saskatchewan, Canada, as defined by Statistics Canada. It is located in the south-southwestern part of the province, adjacent to the border with Montana, United States. The most populous community in this division is Assiniboia.
Highway 2 is a provincial highway in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It is the longest highway in Saskatchewan at 809 km (503 mi). The highway has a few divided sections but is mostly undivided. However, only about 18 kilometres (11 mi) near Moose Jaw, 11 kilometres (7 mi) near Chamberlain, and 21 kilometres (13 mi) near Prince Albert are divided highway. Highway 2 is a major north-south route beginning at the Canada–US border at the Port of West Poplar River and Opheim, Montana customs checkpoints. Montana Highway 24 continues south. It passes through the major cities of Moose Jaw in the south and Prince Albert in the north. Highway 2 overlaps Highway 11 between the towns of Chamberlain and Findlater. This 11 kilometres (7 mi) section of road is a wrong-way concurrency. The highway ends at La Ronge, where it becomes Highway 102.
Highway 36 is a provincial highway in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It runs from Montana Highway 13 at the US border at the Port of Coronach north to Highway 2. It is about 144 kilometres (89 mi) long.

Kenaston is a village in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan within the Rural Municipality of McCraney No. 282 and Census Division No. 11. Kenaston is located on Highway 11 at the junction of Highway 15 and is also near Highway 19. This is a scenic area of Saskatchewan situated within the rolling Allan Hills. Kenaston is located between Danielson Provincial Park and Blackstrap Provincial Park.

Rama is a village in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan within the Rural Municipality of Invermay No. 305 and Census Division No. 9. It is located 44 km west of Canora and 60 km east of Wadena at the intersection of Highway 5 and Highway 754.
Gladmar is a Dissolved village in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan located 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) north of Highway 18 as it runs east from Highway 6 towards Lake Alma. Gladmar is approximately 18.4 kilometres (11.4 mi) north of the Canada–United States border. It is part of the Rural Municipality of Surprise Valley No. 9 and Census Division No. 2.
Ruthilda is a former village in the Rural Municipality of Grandview No. 349, Saskatchewan, Canada. It dissolved from village status to become part of the Rural Municipality of Grandview No. 349 on December 31, 2013. Ruthilda is located about 5 km south of Highway 51 approximately 30 km southwest of the Town of Biggar.
Stranraer is an unorganized hamlet located in the Rural Municipality of Mountain View No. 318 in Saskatchewan on Highway 31 and along a now abandoned section of the Kerrobert-Rosetown Canadian Pacific Railway line. The community is along the course of Eagle Creek.
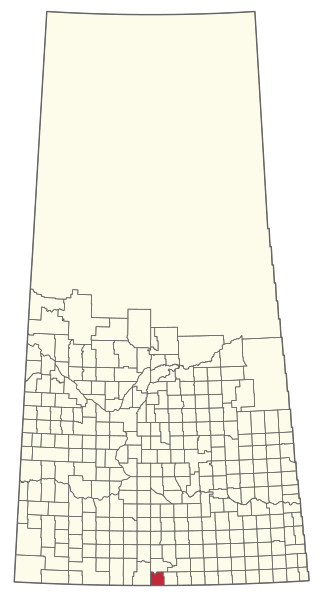
The Rural Municipality of Poplar Valley No. 12 is a rural municipality (RM) in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan within Census Division No. 3 and SARM Division No. 2. It is located in the southern portion of the province. It is adjacent to the United States border, neighbouring Daniels County in Montana.
The Southern Rails Cooperative Ltd. (SRCL) is a Canadian short line railway company operating on trackage in southwest Saskatchewan. Southern Rails Cooperative was the first shortline railway to operate in Saskatchewan and operated as the first modern common carrier shortline railway. The railway is a farmer owned co-operative that operates two short-line railways in Saskatchewan, totalling 71 km of trackage: the former Canadian Pacific Railway Colony subdivision that runs from Rockglen to Killdeer, and the former Canadian National Railway Avonlea subdivision that runs from Avonlea to Parry, The company subsequently expanded along the Avonlea subdivision into Moose Jaw.
The Fife Lake Railway is a Canadian shortline railway company operating on trackage in Saskatchewan, Canada. The railway is owned by seven local municipalities. The Fife Lake Railway took over the former Canadian Pacific Railway Fife Lake subdivision consisting of 94 km of trackage.

Horizon, located on the south side of Channel Lake, is a hamlet in Bengough Rural Municipality No. 40, Saskatchewan, Canada. It previously held the status of village until December 31, 1973. The hamlet is located 60 km (37 mi) east of the Town of Assiniboia on highway 13.
Fife Lake is a fresh water prairie lake in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It is in the south-central part of the province at the eastern end of the Wood Mountain Hills. The entire lake and its shoreline is designated an Important Bird Area (IBA) of Canada to protect the nationally endangered piping plover. While there are no communities along the lake's shore, there is a park and campground at the southern end. Nearby communities include Fife Lake, Rockglen, and Lisieux. Access is from Highway 18.