El Monte is a city in Los Angeles County, California, United States. The city lies in the San Gabriel Valley, east of the city of Los Angeles.

Chatsworth is a suburban neighborhood in Los Angeles, California, in the San Fernando Valley.

The San Gabriel Valley, often referred to by its initials as SGV, is one of the principal valleys of Southern California, lying immediately to the east of the eastern limits of the city of Los Angeles and occupying the vast majority of the southeastern part of Los Angeles County. Surrounding landforms and other features include the following:

The Rio Hondo is a tributary of the Los Angeles River in Los Angeles County, California, approximately 16.4 miles (26.4 km) long. As a named river, it begins in Irwindale and flows southwest to its confluence in South Gate, passing through several cities. Above Irwindale its main stem is known as Santa Anita Creek, which extends another 10 miles (16 km) northwards into the San Gabriel Mountains where the source, or headwaters, of the river are found.

The Los Angeles County Arboretum and Botanic Garden, 127 acres, is an arboretum, botanical garden, and historical site nestled into hills near the San Gabriel Mountains in Arcadia, California, United States. Open daily, it only closes on Christmas Day.

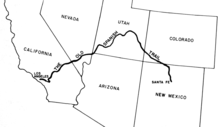
The Old Spanish Trail is a historical trade route that connected the northern New Mexico settlements of Santa Fe, New Mexico with those of Los Angeles, California and southern California. Approximately 700 mi (1,100 km) long, the trail ran through areas of high mountains, arid deserts, and deep canyons. It is considered one of the most arduous of all trade routes ever established in the United States. Explored, in part, by Spanish explorers as early as the late 16th century, the trail was extensively used by traders with pack trains from about 1830 until the mid-1850s.

California's 44th congressional district is a congressional district in the U.S. state of California. The district is centered in South Los Angeles and the Los Angeles Harbor Region. It is currently represented by Democrat Nanette Barragán. The 44th district was created as a result of the redistricting cycle after the 1980 Census.
The Indiana Colony refers to a group of Indiana residents who settled the area known today as Pasadena, California. The group was incorporated on January 31, 1874, by Indiana residents who sought warmer weather after the exceptionally cold winter of 1872–73. The settlers met in the home of Thomas Elliott, and Daniel Berry was selected to visit Southern California with a direction to find suitable land at a suitable price.
California's 31st congressional district is a congressional district in Los Angeles County, in the U.S. state of California. The district is located in the San Gabriel Valley.
Rancho Santa Anita was a 13,319-acre (53.90 km2) land grant in present-day Los Angeles County, California given to naturalized Scottish immigrant Hugo Reid and his Kizh people wife. Reid built an adobe residence there in 1839, and the land grant was formally recognized by Governor Pio Pico in 1845. The land grant covered all or portions of the present day cities of Arcadia, Monrovia, Sierra Madre, Pasadena and San Marino. A small portion of the rancho has been preserved as the Los Angeles County Arboretum and Botanic Garden.

Simi Valley is a city in the valley of the same name in the southeast region of Ventura County, California, United States. Simi Valley is 40 miles (65 km) from Downtown Los Angeles, making it part of the Greater Los Angeles Area. The city sits next to Thousand Oaks, Moorpark, and Chatsworth. As of the 2020 U.S. Census the population was 126,356, up from 124,243 in 2010. The city of Simi Valley is surrounded by the Santa Susana Mountains and the Simi Hills, west of the San Fernando Valley, and northeast of the Conejo Valley. It grew as a commuter bedroom community for the cities in the Los Angeles area, and the San Fernando Valley when a freeway was built over the Santa Susana Pass.
In the history of the American frontier, pioneers built overland trails throughout the 19th century, especially between 1829 and 1870, as an alternative to sea and railroad transport. These immigrants began to settle much of North America west of the Great Plains as part of the mass overland migrations of the mid-19th century. Settlers emigrating from the eastern United States did so with various motives, among them religious persecution and economic incentives, to move from their homes to destinations further west via routes such as the Oregon, California, and Mormon Trails. After the end of the Mexican–American War in 1849, vast new American conquests again encouraged mass immigration. Legislation like the Donation Land Claim Act and significant events like the California Gold Rush further encouraged settlers to travel overland to the west.

Agua Mansa is a former settlement in an unincorporated area of San Bernardino County, near Colton, California, United States. Once the largest settlement in San Bernardino County, it is now a ghost town. Only the cemetery remains.

The Los Angeles and San Gabriel Valley Railroad was a railroad founded on Sept. 5, 1883, by James F. Crank with the goal of bringing a rail line to Pasadena from downtown Los Angeles. Los Angeles and San Gabriel Valley Railroad was sold and consolidated on May 20, 1887 into the California Central Railway. In 1889 this was consolidated into Southern California Railway Company. On Jan. 17, 1906 Southern California Railway was sold to the Atchison, Topeka and Santa Fe Railway and called the Pasadena Subdivision. The main line closed in 1994. The railroad later reopened as the MTA Gold Line Light Rail service in July 2003.

Savannah Memorial Park Cemetery also known as El Monte Memorial Park and the Savannah Pioneer Cemetery is the oldest American non-sectarian cemetery in Southern California. The park is located in Rosemead, California, part of the park is in the neighboring city of El Monte. The park has been in continuous operation since its founding in 1850. Some of the burials may date back into the 1840s before Savannah Memorial Park became a Memorial Park. Savannah Memorial Park was designated a California Historical Landmark on March 6, 2012.

The Reid-Baldwin Adobe, formerly called the Hugo Reid Adobe, is an adobe house built in 1839. It is located at the Los Angeles County Arboretum and Botanic Garden in Arcadia, California. The Hugo Reid Adobe was designated a California Historic Landmark on April 3, 1940. The Reid Adobe was built by Scottish−Mexican Hugo Reid on the shore of what is now called Baldwin Lake, with the help of local natives. Reid received the full Mexican land grant for Rancho Santa Anita in 1845, which included 13,319 acres of land. Reid farmed some of the land and planted grape vines.

The Portolá Trail Campsite or Portolá Trail Campsite No. 1 is the spot of the first Europeans to travel and camp overnight in what is now Central Los Angeles, California. The Portolá expedition camped at the site on August 2, 1769. The Portolá Trail Campsite No. 1 was designated a California Historic Landmark (No.655) on Sept. 26, 1958. The Portolá Trail Campsite is located in what is now the Elysian Park entrance, at the NW corner of North Broadway and Elysian Park Drive in the City of Los Angeles in Los Angeles County. The campsite is near the Los Angeles River, which they used as their water supply for the camp. Military officer Gaspar de Portolá was the commander of the expedition for the Spanish Empire with the goal of the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The expedition led to the founding of the first mission in the Los Angeles Basin, the Mission Vieja, on September 8, 1771 and of Alta California. The expedition arrived at Portolá Trail Campsite No. 1 from the San Gabriel Valley, were the Mission San Gabriel would be built later in 1776. As they depart Portolá Trail Campsite No. 1 they traveled west towards Santa Monica Bay, stopping at Portolá Trail Campsite 2, which is in present day Beverly Hills. Portolá Trail Campsite 2 is also a California Historic Landmark (No.665). At San Monica Bay the expedition turned and traveled north to were the future Mission San Fernando would be built in 1797. Form San Fernando the expedition turned west to Ventura, the site of the future Mission San Buenaventura built in 1782.

The Portolá Trail Campsite 2 or Portolá Trail Campsite No. 2 is the spot of the first Europeans to travel and camp overnight in what is now Beverly Hills, California. The Portolá expedition camped at the site on August 3, 1769. The Portolá Trail Campsite No. 2 was designated a California Historic Landmark (No.665) on Nov. 5, 1958. The Portolá Trail Campsite is located in what is now 325 South La Cienega Boulevard between Olympic Boulevard and Gregory, in Beverly Hills. in Los Angeles County. Military officer Gaspar de Portolá was the commander of the expedition for the Spanish Empire with the goal of the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The expedition led to the founding of the first mission in the Los Angeles Basin, the Mission Vieja, on September 8, 1771, and of Alta California. The expedition arrived at Portolá Trail Campsite No. 2 from the Portolá Trail Campsite No. 1 in what is now Elysian Park. They came to camp site 1 from the San Gabriel Valley, were the Mission San Gabriel would be built later in 1776. As they depart Portolá Trail Campsite No. 2 they traveled west towards Santa Monica Bay. At San Monica Bay the expedition turned and traveled north to were the future Mission San Fernando would be built in 1797. Form San Fernando the expedition turned west to Ventura, the site of the future Mission San Buenaventura built in 1782.

The Temporary Detention Camp for Japanese Americans / Santa Anita Assembly Center is one of the places Japanese Americans were held during World War II. The Santa Anita Assembly Center was designated a California Historic Landmark (No.934.07) on May 13, 1980. The Santa Anita Assembly Center is located in what is now the Santa Anita Racetrack in Arcadia, California in Los Angeles County.

The Mojave Road Los Angeles was designated a California Historic Landmark on March 19, 1985. It runs from Drum Barracks in Los Angeles County to the Colorado River in San Bernardino County, California.